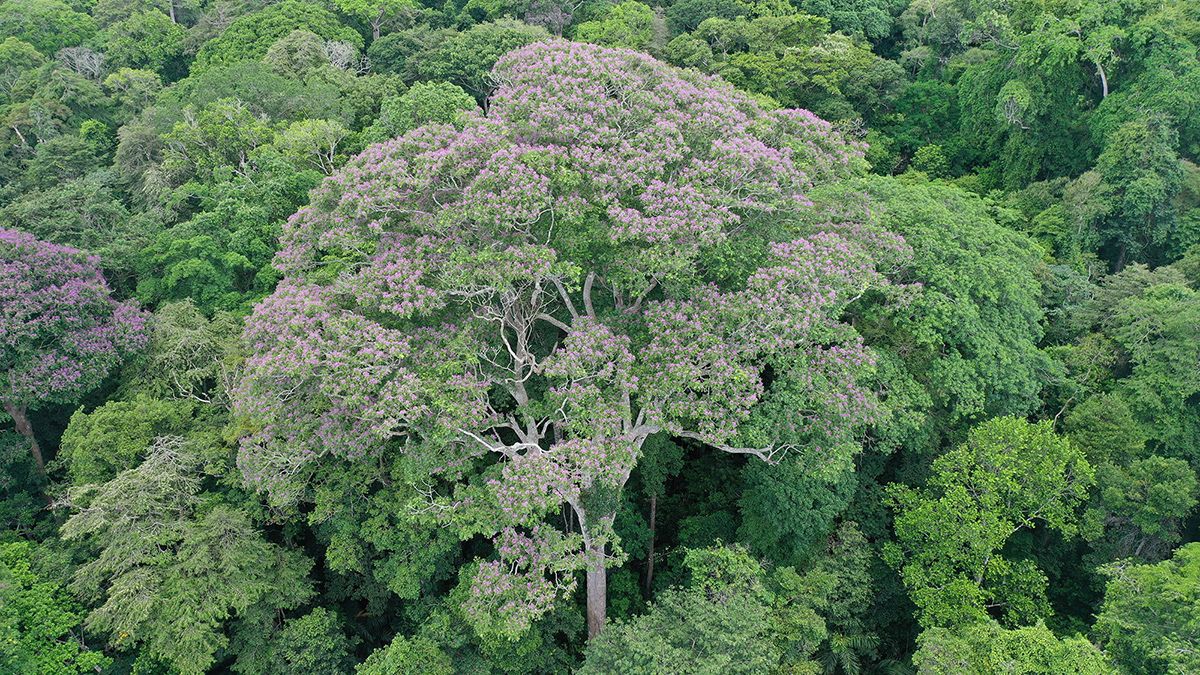
Direct lightning strikes cause minimal damage to Dipteryx oleifera. But these same strikes effectively kill parasitic vines and neighboring trees that compete with the species for light and nutrients.
Katherine Kornei
Katherine Kornei is a freelance science journalist covering Earth and space science. Her bylines frequently appear in Eos, Science, and The New York Times. Katherine holds a Ph.D. in astronomy from the University of California, Los Angeles.
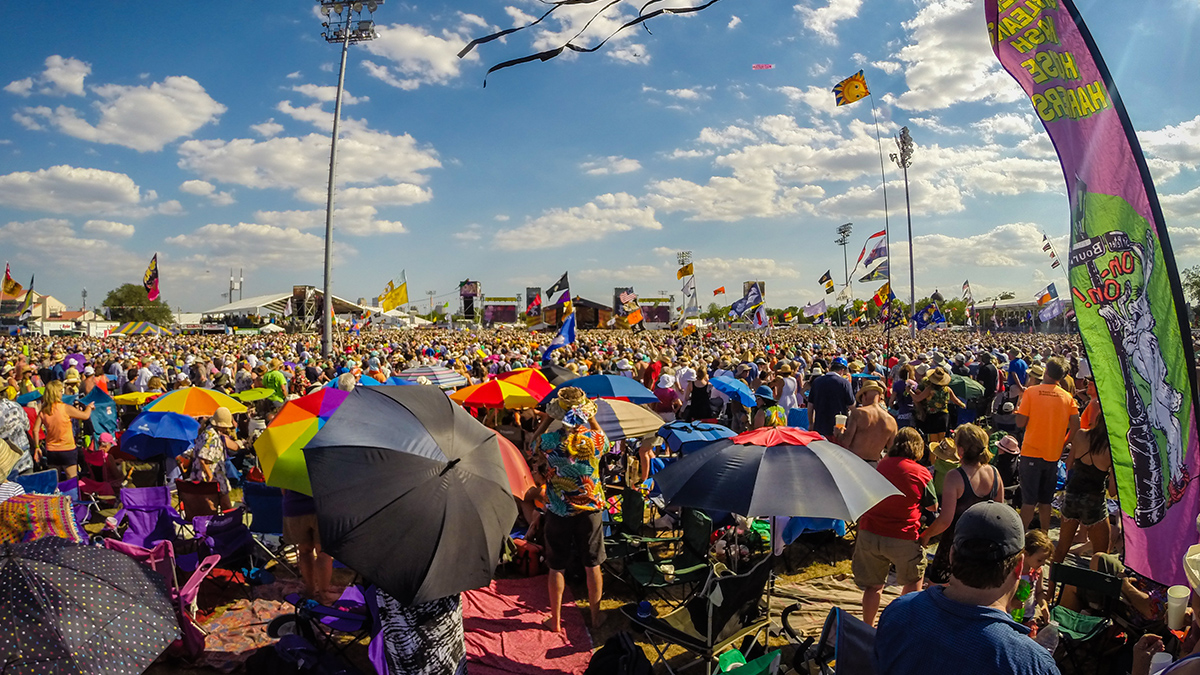
Large Outdoor Gatherings Expose Event-Goers to Severe Weather
Researchers pinpointed the riskiest events in terms of lightning and tornado exposure by mining data from more than 16,000 large outdoor gatherings.
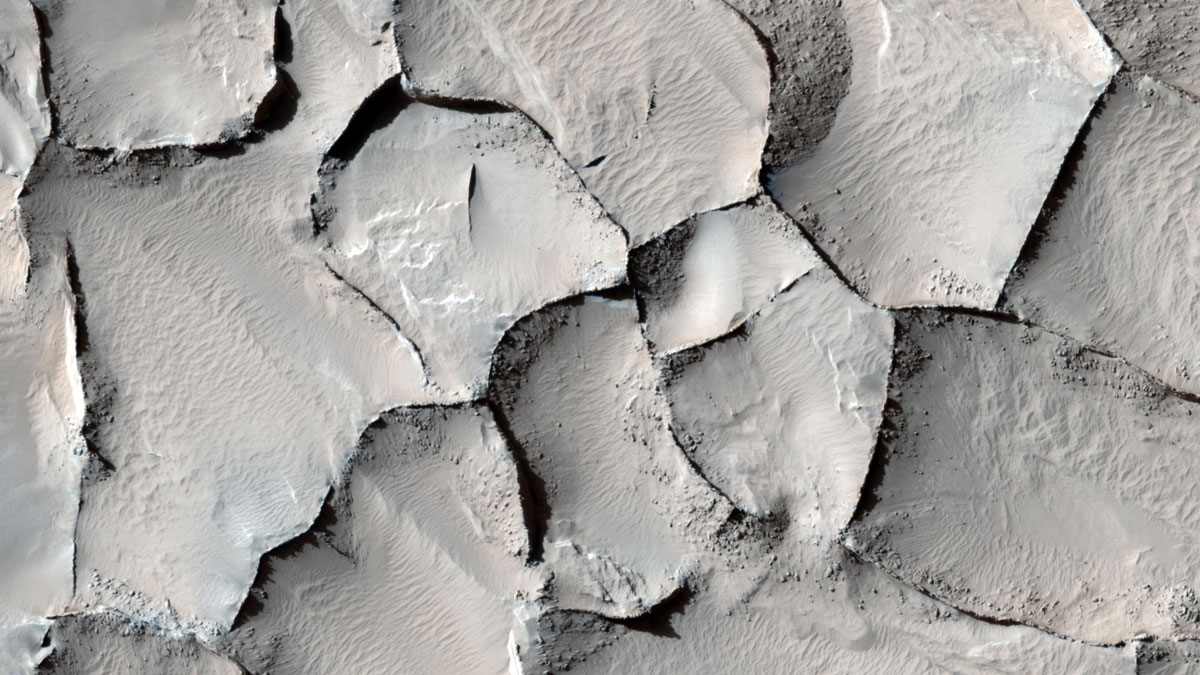
Cracks on Planetary Surfaces Hint at Water
Imagery of fractured terrain on Venus, Mars, and Jupiter’s moon Europa pinpoints environments influenced by water.
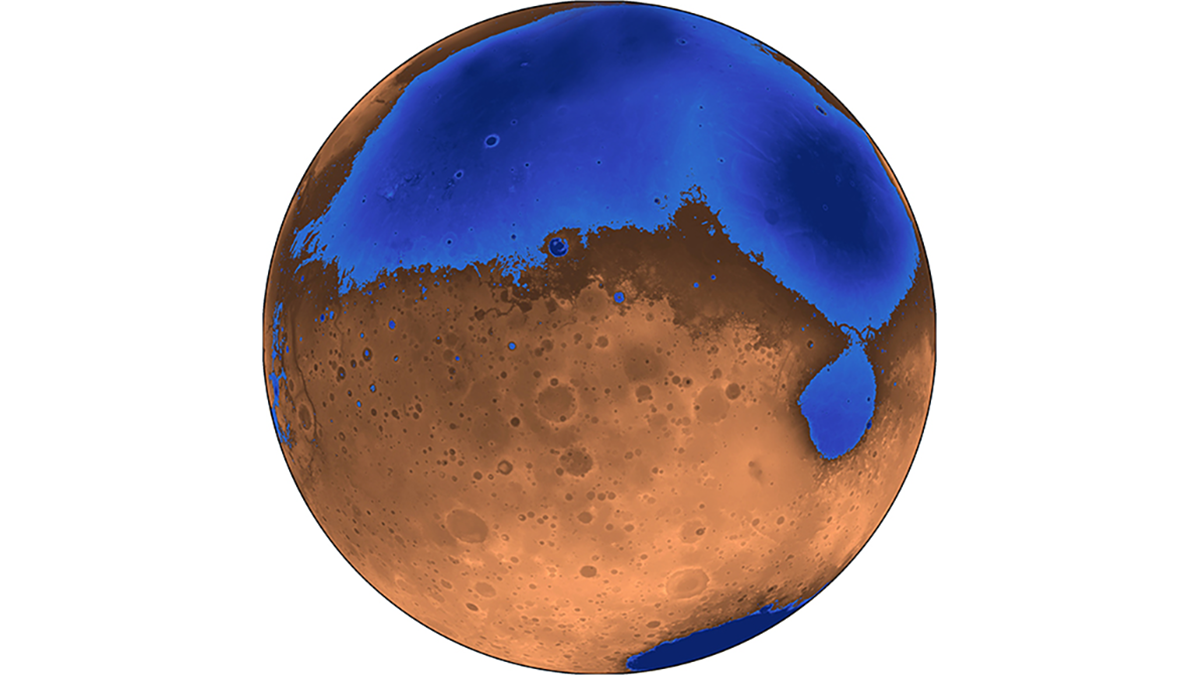
Buried Sediments Point to an Ancient Ocean on Mars
Ground-penetrating radar data collected by the Zhurong rover reveal gently sloping sediments in Mars’s northern lowlands that hint at a shoreline.
Panama Canal Logistics Are at the Mercy of Weather and Climate
Regional weather variability and climate change make operating the canal a challenge.
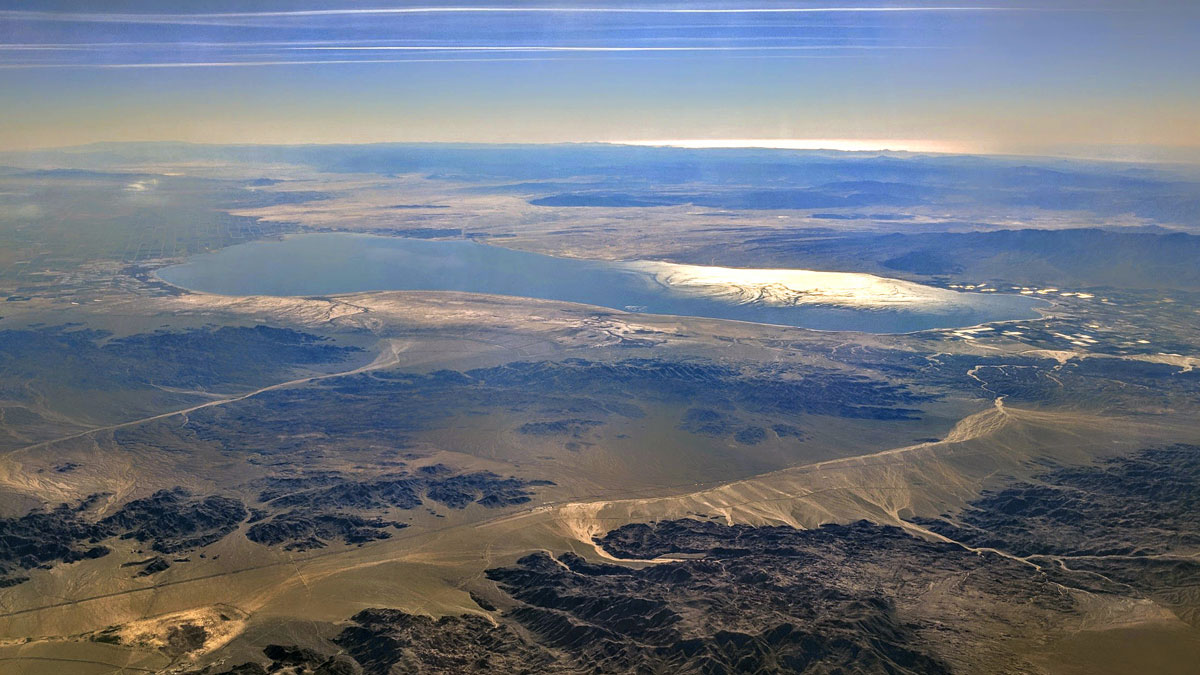
The Deleterious Dust of the Salton Sea
Coarse particulate matter deriving from California’s largest lake is linked to an increased risk of respiratory-related hospitalizations.
Ice Core Records Shed Light on a Volcanic Mystery
By analyzing sulfur and volcanic ash entrained in ice cores, researchers pinpointed a caldera in the remote Kuril Islands as the site of an unidentified 19th century eruption.
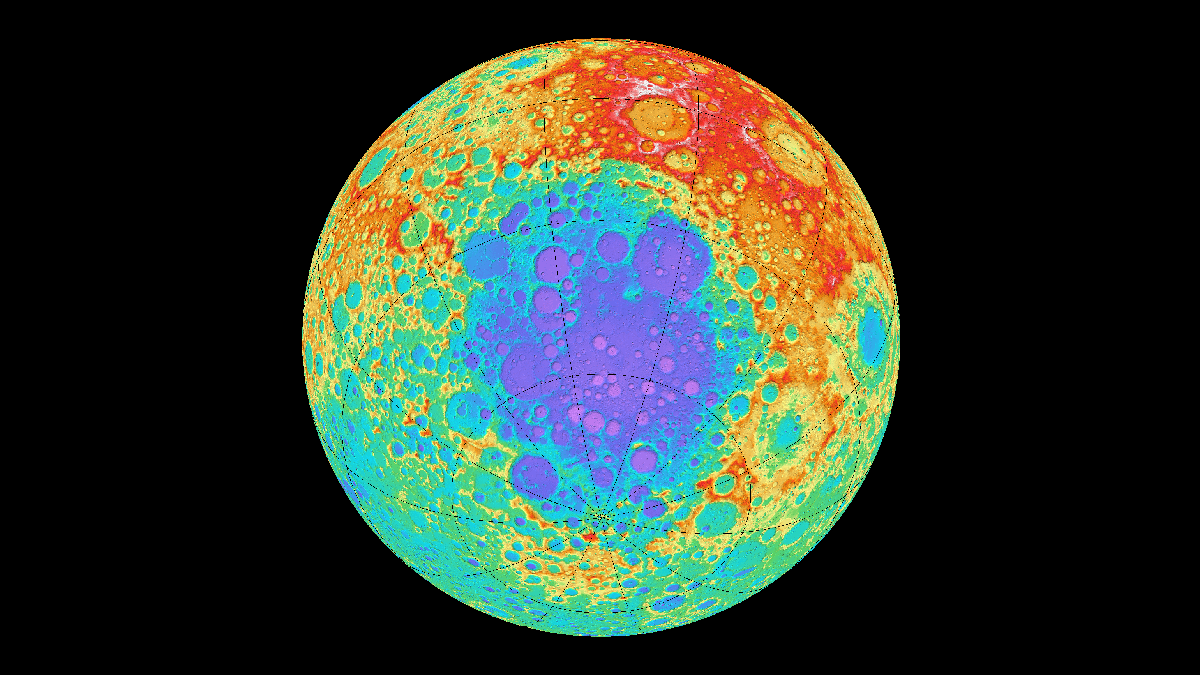
Meteorite Sheds Light on the Moon’s Impact History
Analysis has revealed the South Pole–Aitken basin is significantly older than other impact basins on the Moon, a finding that has implications for the evolution of the early solar system.
Martian Meteorite Points to Ancient Hydrothermal Activity
The Red Planet had water—in the form of a hydrothermal system—4.45 billion years ago, new analyses of a Martian meteorite suggest.
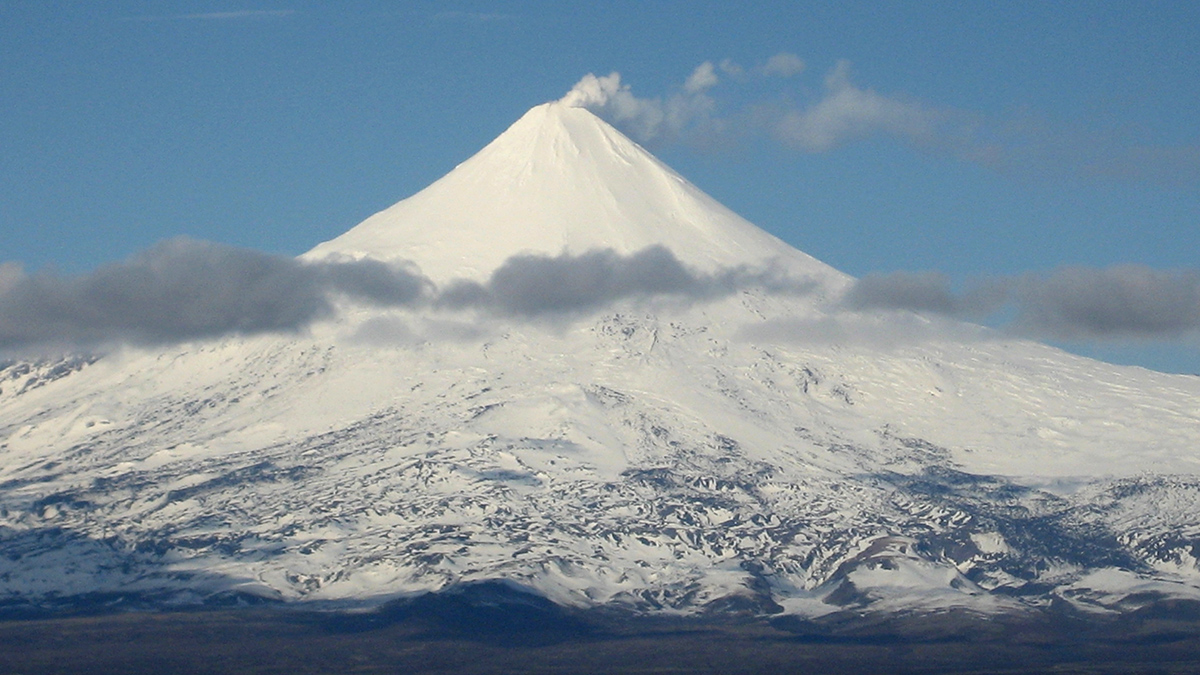
Glaciers near Active Volcanoes Flow Faster
Monitoring glacier velocity could help predict volcanic activity, a study of more than 210,000 glaciers suggests.