Jianli Chen, Bridging Old and New Gravity Data Adds 10 Years to Sea Level Record


Jianli Chen, Bridging Old and New Gravity Data Adds 10 Years to Sea Level Record
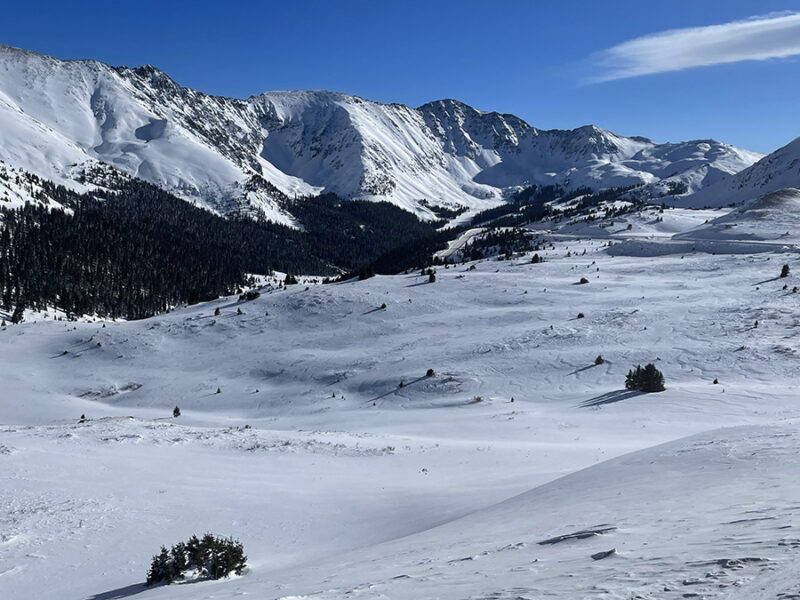

The recent SnowEx campaign and the new NISAR satellite mission are lighting the way to high-resolution snowpack monitoring and improved decisionmaking in critical river basins around the world.

Researchers have mapped the ancient Stad Slide off the coast of Norway to better understand what triggered it, and the hunt is on for the tsunami it might have unleashed.
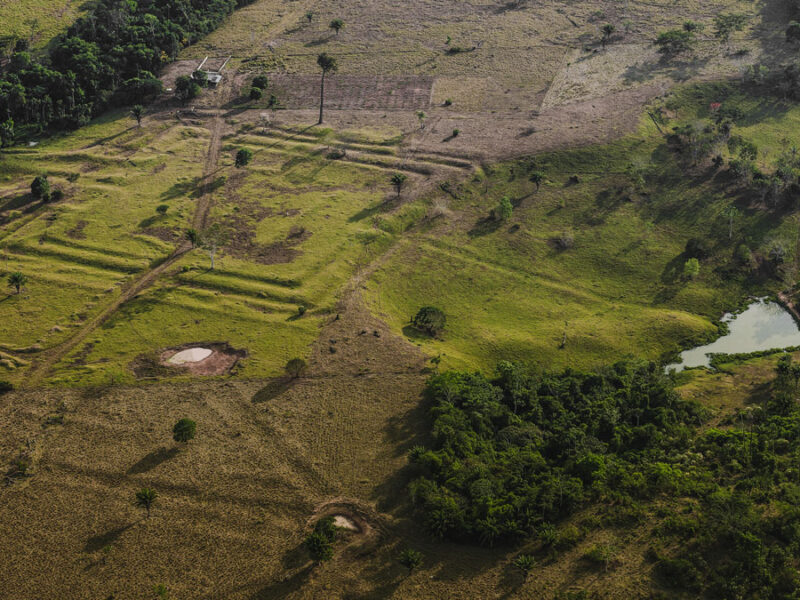

Portions of the forest managed by pre-Columbian populations hold higher biomass and are more able to withstand climate change.
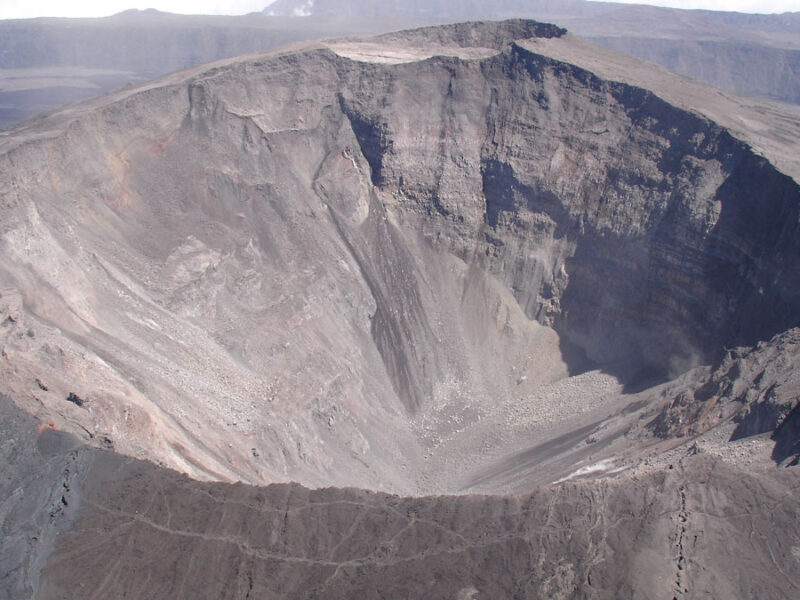

Research into the hazardous collapses of basaltic volcanoes has revealed common physical processes, but addressing remaining questions requires learning more from historical events.
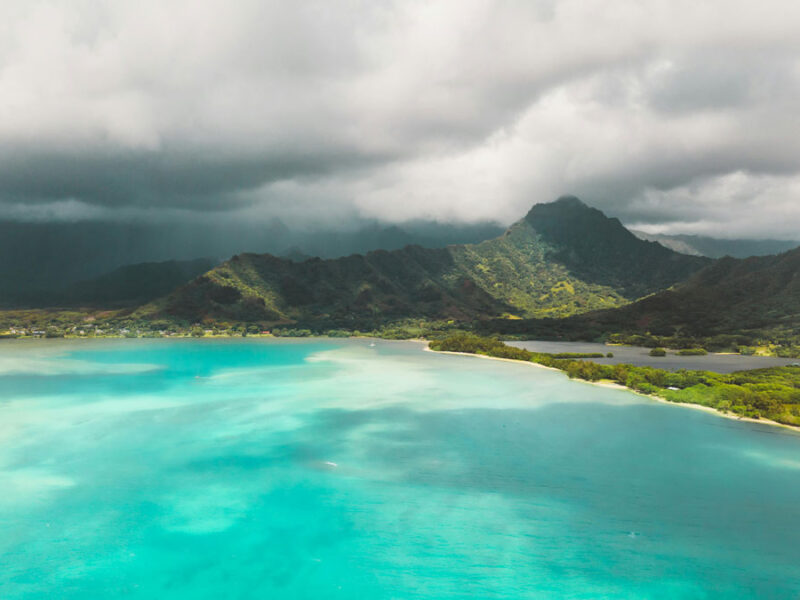

Isolated islands that depend on rainfall could benefit from improved forecasting of near-future events, and understanding the Madden-Julian Oscillation could hold an important key.
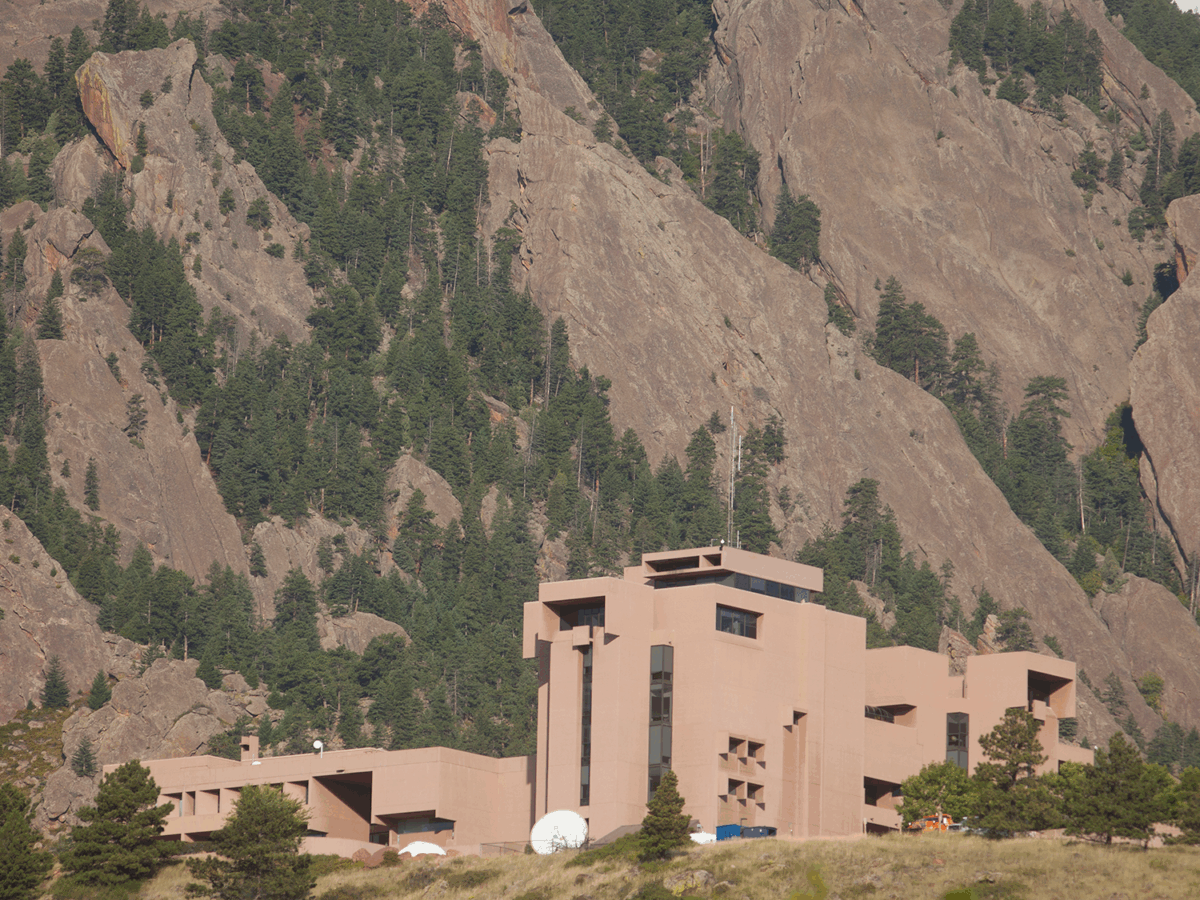

The Trump administration is planning to dismantle the National Center for Atmospheric Research, one of the world’s leading climate and Earth science research laboratories, according to a statement from Russ Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, to USA Today.
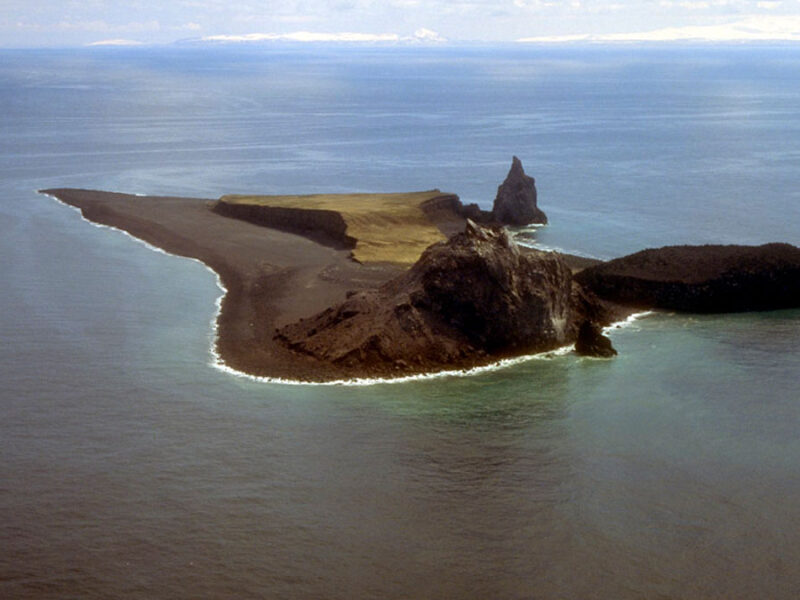

It’s now become easier to forecast the next eruption of Alaska’s Bogoslof volcano. New research led by Pavel Izbekov, a volcanologist at the Alaska Volcano Observatory, is applying the foundations of diffusion chronometry—the study of chemical change in crystals over time—to a new eruption forecasting approach. Izbekov’s team used crystal clusters and their collective records…

The 20th annual Arctic Report Card reveals new highs in temperature and new lows in sea ice, as well as an uncertain outlook for the availability of federal data.

Duplicating artifacts that preserve records from biblical times is a lucrative business. A method used for both dating artifacts and reconstructing Earth’s history could identify phony pieces.
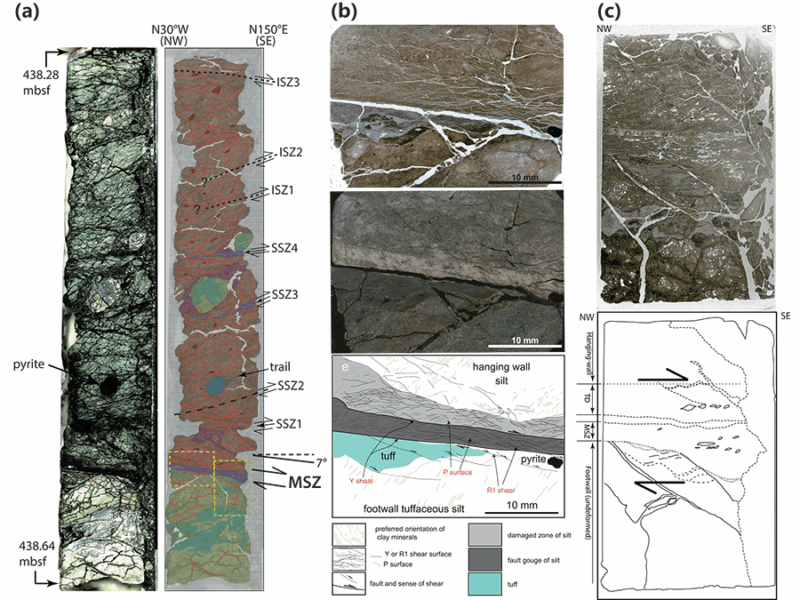
A database of frictional properties from IODP drilling materials explores the range of slip spectrum and the generation of slow to fast earthquakes in the Nankai subduction zone in light of mineralogy.
Something went wrong. Please refresh the page and/or try again.