Reducing the number of fixed assumptions may improve the accuracy of complex process-based models.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
Dynamics of the Earth's Surface in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau
River erosion increased rapidly following rock uplift events in the plateau approximately 11 million years ago.
New Insights into Currents in Earth's Magnetic Field
Multisatellite missions give scientists a more complete view of the intense currents that bounce back and forth along our planet's magnetic field lines.
Regional Nuclear War Could Cause a Global Famine
A detonation of less than 0.03% of the current global nuclear arsenal could cause fires that clog the air with soot. This soot could block solar radiation, leading to worldwide crop shortages.
Researchers Track Moving Ice Shelves to Estimate Antarctic Ice Loss
A new method will help scientists monitor the basal melt of ice sheets in Antarctica.
What Causes Extreme Hail, Tornadoes, and Floods in South America?
A study of extreme weather in South America shows seasonal and spatial patterns, which, if better understood, could help save lives and minimize damage to property.
When the Sun Goes Quiet, Titan Gets Gassy
Observations from NASA's Cassini probe show that the level of methane in Titan's atmosphere depends on the Sun's 11-year cycle of magnetic activity.
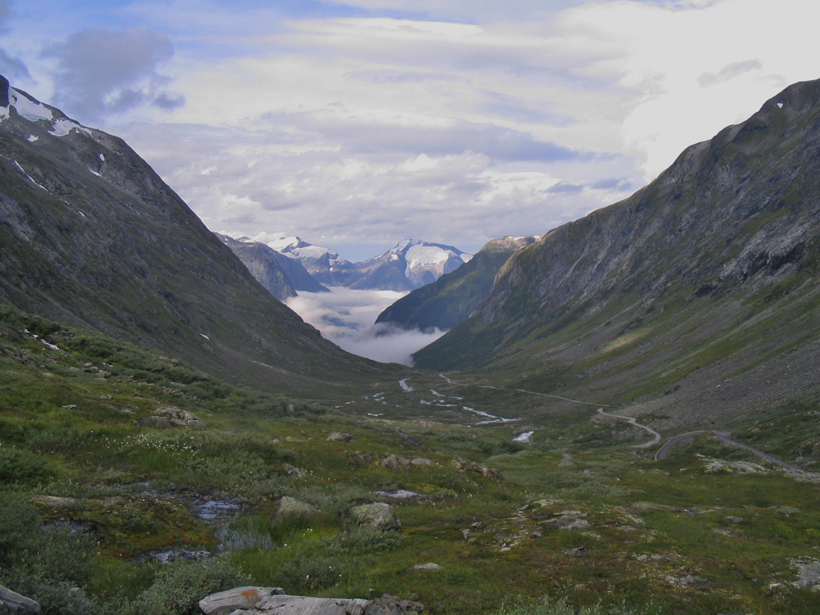
New Insights into the Formation of Old Norwegian Mountains
Researchers look to minerals in rocks from Norway's Western Gneiss Region to determine when the mountain-making period came to a close in the region.
Deep Atlantic Conduit Boasts Longest Billow Train
Some 4000 meters below sea level, swirling patterns of more than 250 consecutive breaking waves up to 100 meters tall stretch through the Atlantic Ocean's Romanche Trench.
Global Atmospheric Model Simulates Fine Details of Gravity Waves
Whole-atmosphere general circulation model captures many aspects of mesoscale gravity wave structures—down to the tens of kilometers—and resulting temperatures and tides.