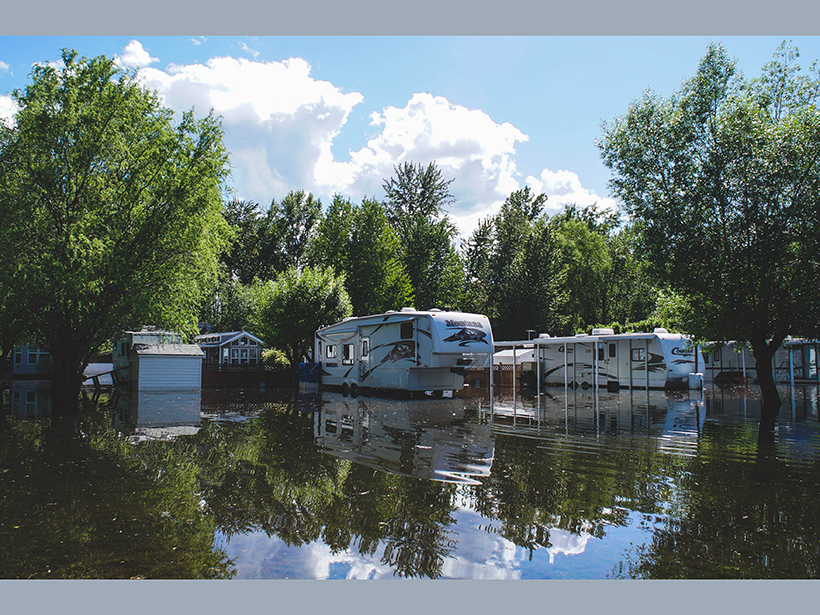
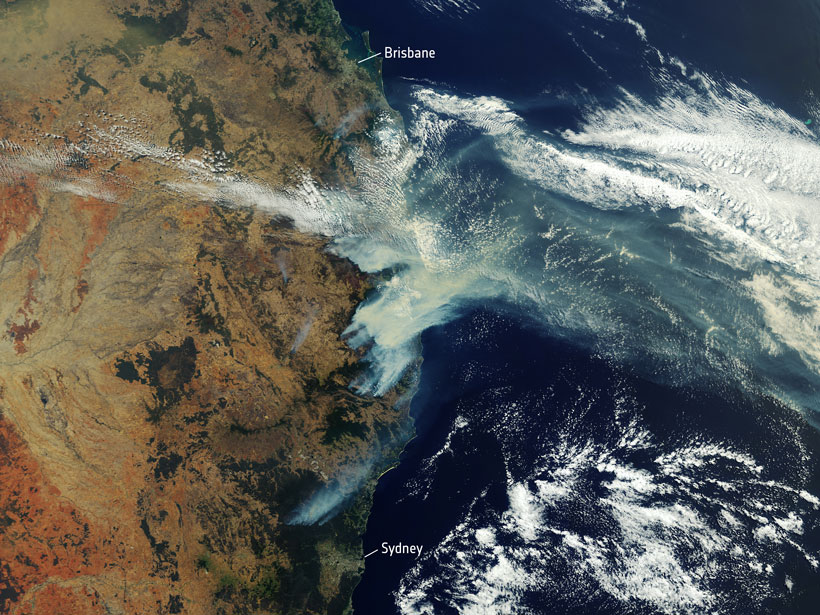
New research highlights differences in drought and flood hazards globally under 1.5°C versus 2°C temperature increases and estimates associated human and economic effects.
David Shultz
Land Motion Offers Insights into Cascadia Earthquake Cycle
Comparing recent GPS data with a longer record of sea level along the western coast of North America allows researchers to home in on interseismic deformation above the Cascadia megathrust.
Tracking Tropospheric Ozone Since 1979
Stratospheric ozone depletion between 1979 and 2010 resulted in a slight decrease of ozone in the troposphere during that period despite increased ozone production from anthropogenic emissions.
A Revised View of Australia’s Future Climate
The most recent generation of models of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project better captures rainfall drivers, extreme heat events, and other facets of regional climate.
Hardwood Forest Soils Are Sinks for Plant-Produced Volatiles
New research identifies temperature, moisture, and soil fungi as important factors in influencing how biogenic volatile organic compounds cycle between plants and the atmosphere.
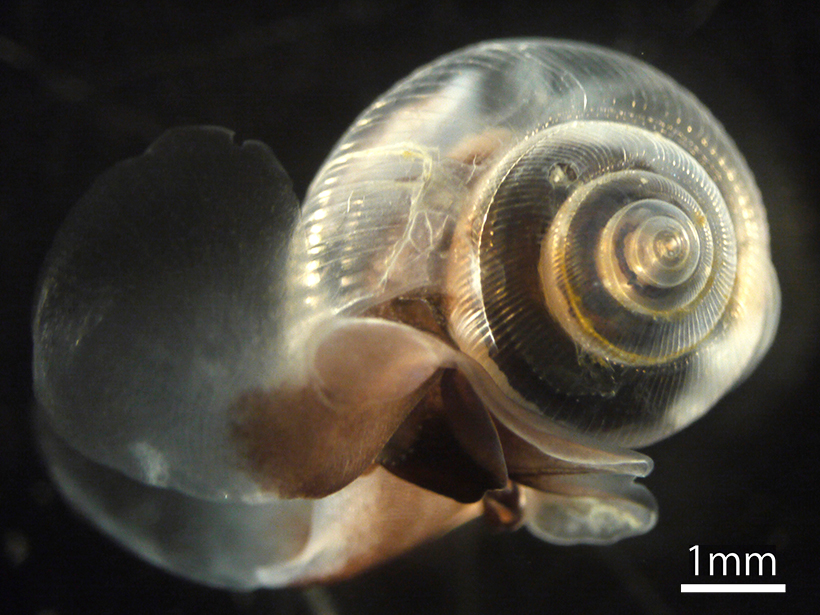
Arctic Plankton Populations Vary by Season
Planktonic foraminifera and sea snail numbers swell from April to June in the Barents Sea, but contrary to predictions, the organisms do not appear to be affected directly by high methane levels.
The Climate and Health Impacts of Gasoline and Diesel Emissions
New research tallies the effects of gas- and diesel-burning vehicle emissions on the climate, as well as on human health. Together, the emissions cause more than 200,000 premature deaths each year.
A Graceful Way to Study Daily Water Storage on Land
A new analysis technique could help scientists improve the temporal resolution of satellite gravity data and see trends in terrestrial water storage and movement in near real time.
Organic Matter in Arctic River Shows Permafrost Thaw
Samples from two waterways in northern Siberia—the main stem of the Kolyma River and a headwater stream in the river’s watershed—indicate the differing sources and ages of carbon they contain.
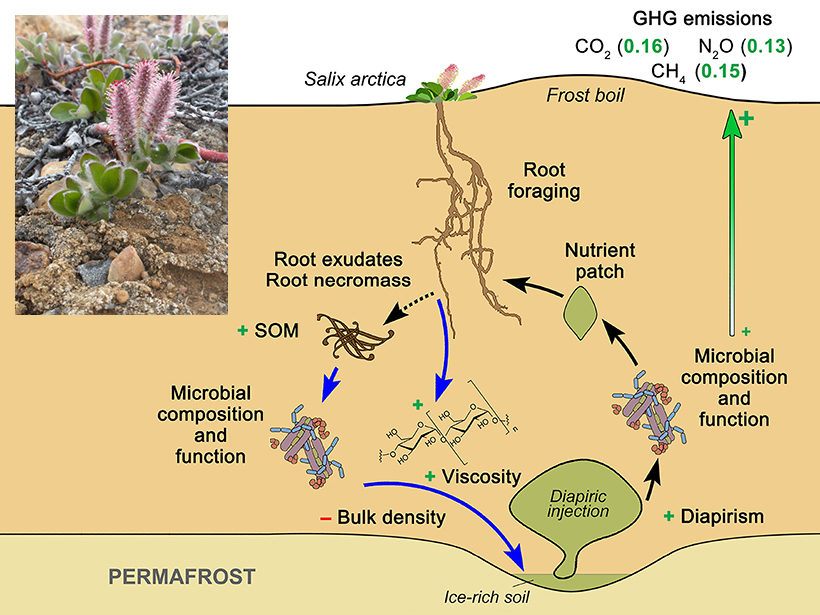
Floating Patches of Soil Nutrients in Soil Help Explain Arctic Thawing
Nutrient-rich diapirs have a complex relationship with soil microbes and play an important role in carbon and nitrogen nutrient cycling, making them crucial for understanding feedbacks in the Arctic.