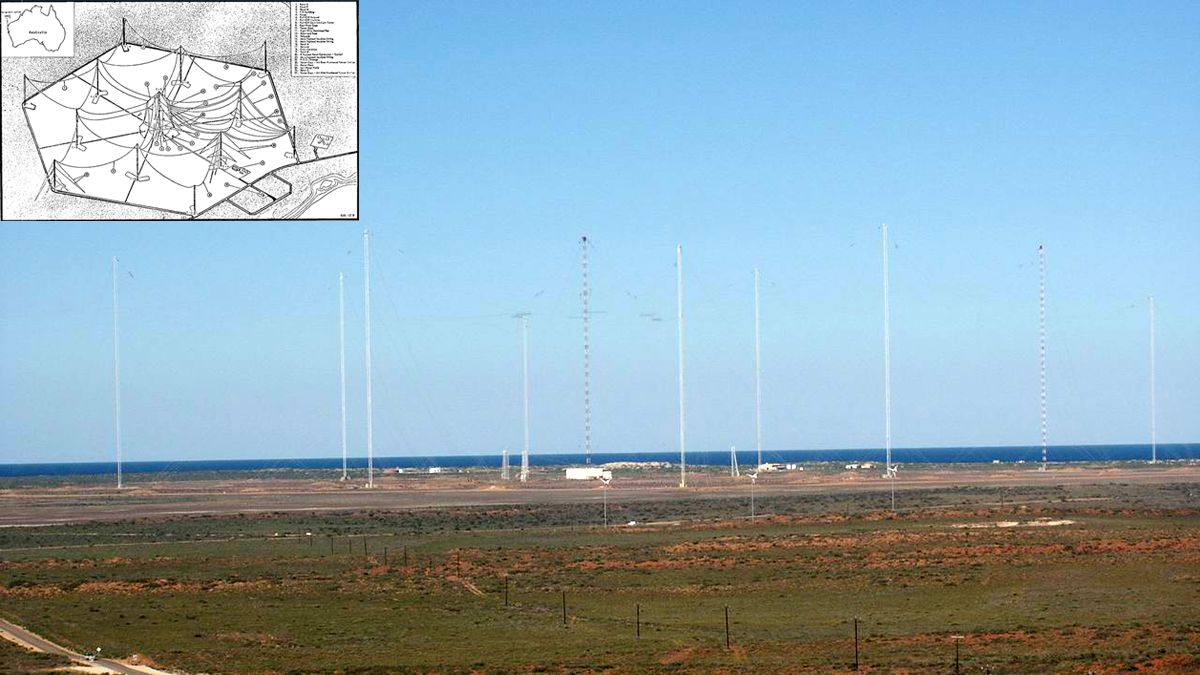
A U.S. Navy transmitter in Australia produces wisps of electron loss as observed by the Colorado Inner Radiation Belt Experiment (CIRBE) CubeSat in Low Earth Orbit.
Editors’ Highlights
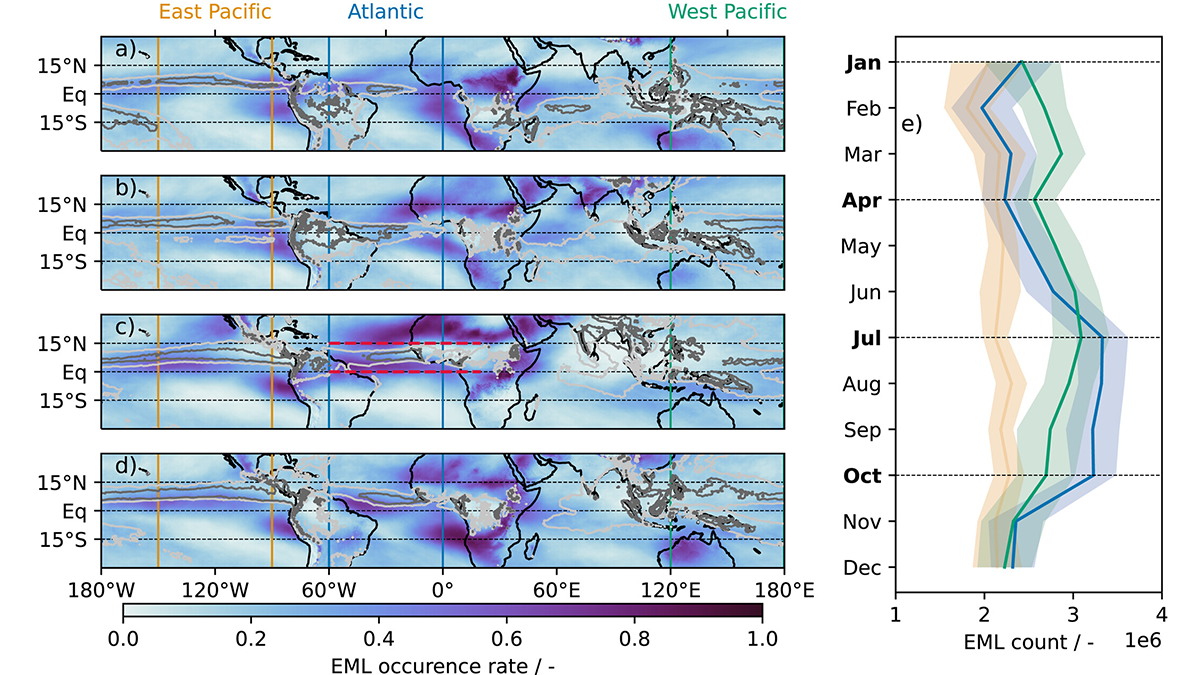
Characteristics of Moist Layers over the Tropical Atlantic
In a new study, characteristics of elevated moist layers, their seasonality, spatial distribution, structure, and the coupling of mid-tropospheric circulation and convection are examined over the tropical Atlantic.
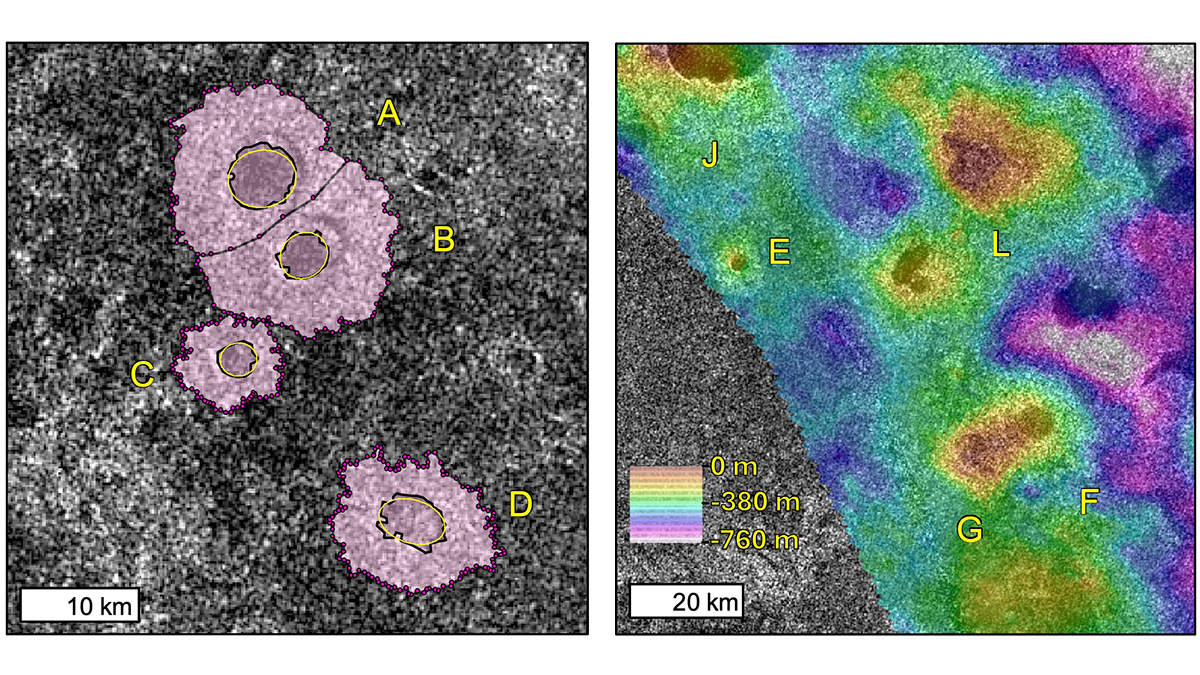
The Explosive Origins of Titan’s Rampart Craters
In a new study, volcanic explosions are explored and modeled to understand the possible origins of rampart craters on Titan and determine whether their formation can source atmospheric methane.
Compositional Anomalies Complicate Our Model of Mantle Convection
A new study expands on recent research which suggests that oceanic crust accumulates in the mid-mantle. The new seismological constraints advance our understanding of thermo-chemical planetary evolution.
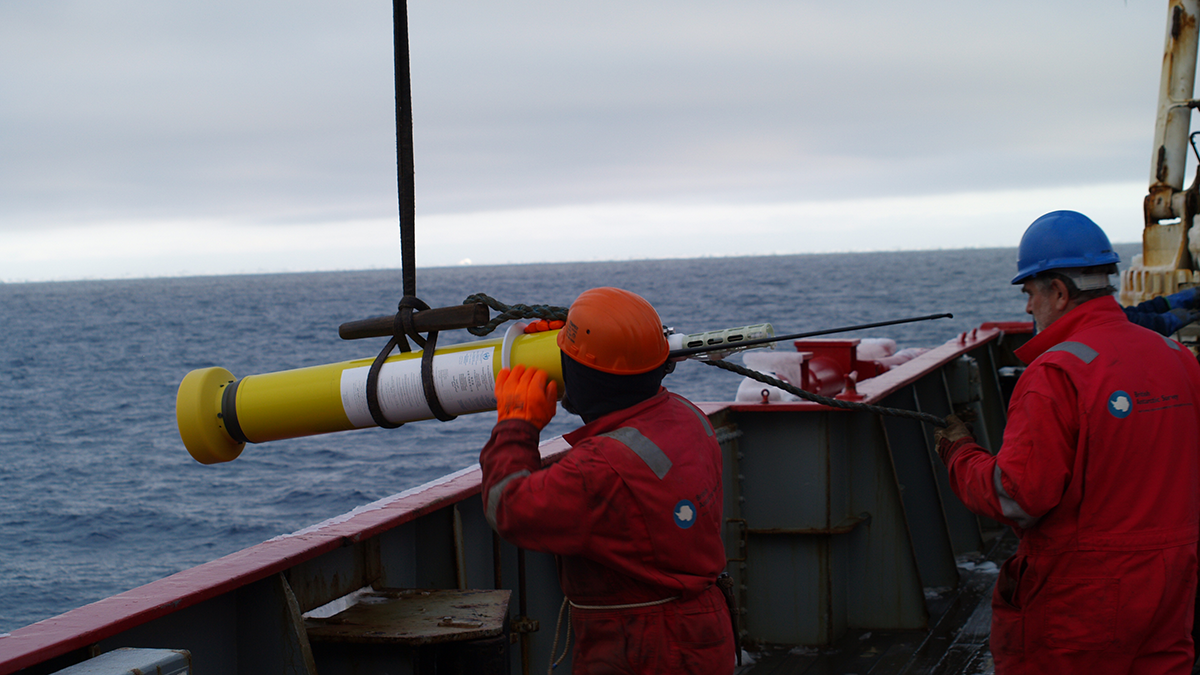
Are Rogue Argo Floats Skewing Ocean Salinity Data Products?
Global ocean salinity products have become increasingly inconsistent since 2015, coinciding with a drift to higher salinity values in a number of Argo sensors.
Physics and Biology as Likely Stream Bedfellows
Streambeds are key sites for removal of nutrients and other contaminants through microbial processes, but are limited by diffusion, which can now be modeled from streambed physical properties.
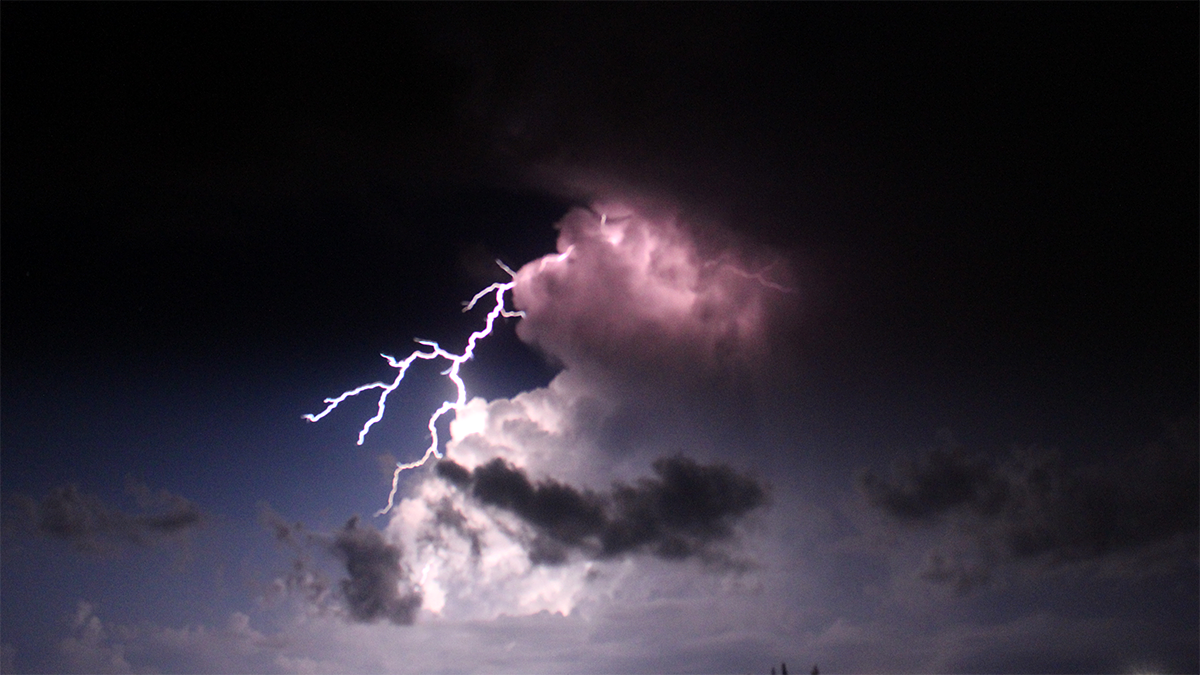
Lightning Initiating at High Altitudes May Develop Continuously
Recent radio observations reveal a new mode of initial lightning development in the form of continuous initial breakdown burst of several kilometers in length at high altitudes within thunderstorms.
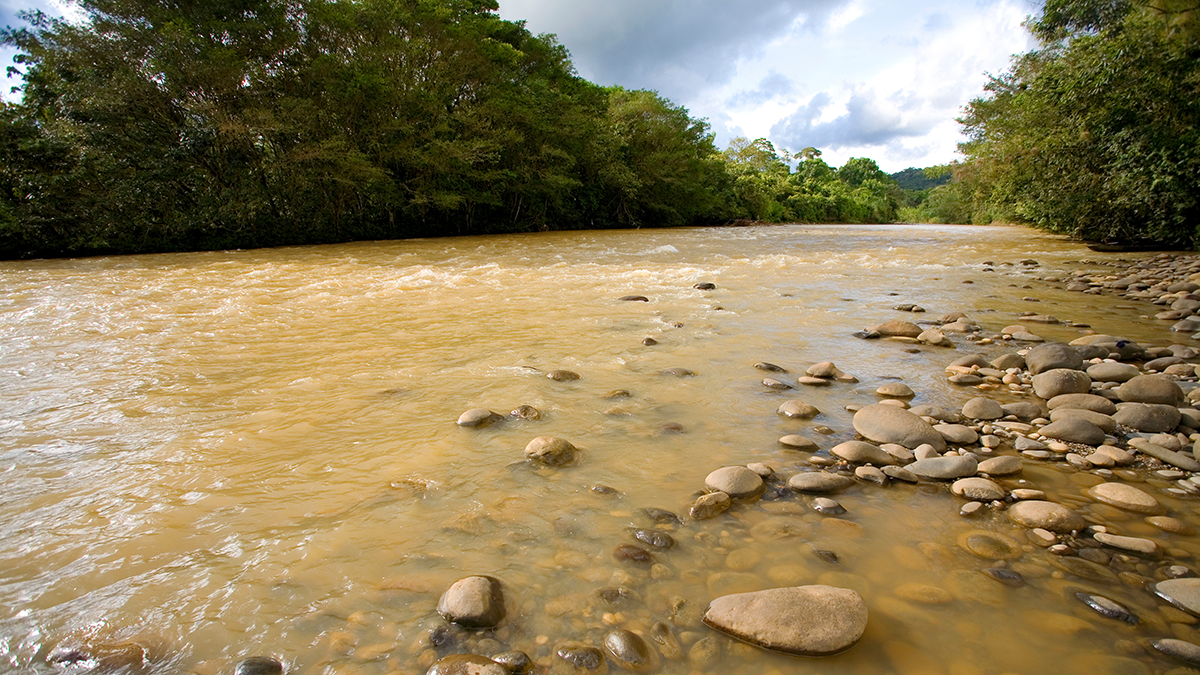
Elementary, My Dear: Al & Be Give Evidence of Past Climate Change
10Be and 26Al concentrations in river sand reveal an increase in erosion rate in the Brazilian Highlands consistent with the Mid-Pleistocene Transition, a major climatic shift that occurred about 1 million years ago.
Unusual Occurrence of STEVE: An Aurora-Like Glow
STEVE is a mysterious purple-white arc near the aurora, typically seen after space disturbances called substorms. A new study reveals a rare STEVE event without a substorm, prompting questions about its origin.
The Future of Martian Paleomagnetism
Samples collected by the Perseverance Rover have great potential for providing insights into the history of Mars’ magnetic field.