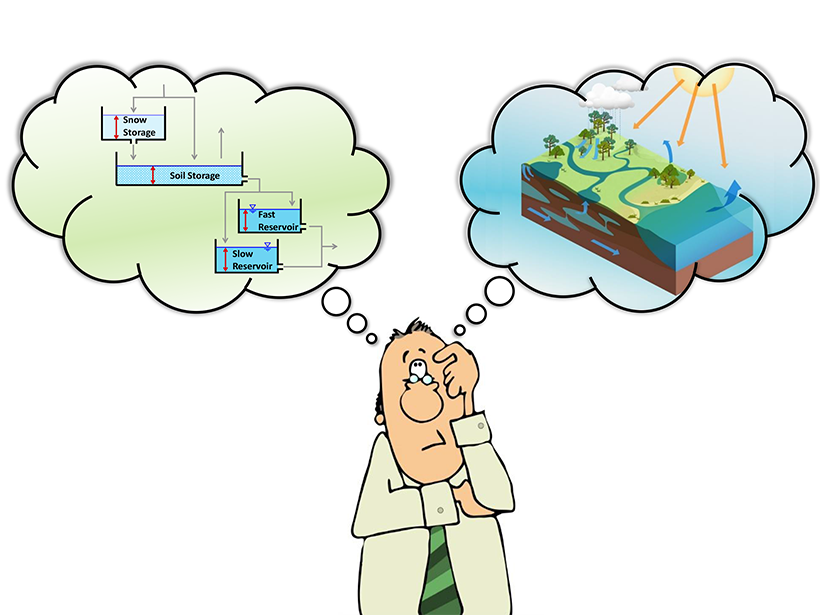
According to a new study, the performance metric–based methods currently used to evaluate dynamical model sensitivity are based upon faulty reasoning and need to be reenvisioned.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
How Long Can Celestial Bodies Retain Ice?
A new model suggests that many objects in the outer asteroid belt may still harbor deposits that formed around the time of their accretion.
Rising Temperatures Reduce Colorado River Flow
Hotter conditions have played a much greater role in reducing flow during the ongoing Millennium Drought than in a mid-20th century drought.
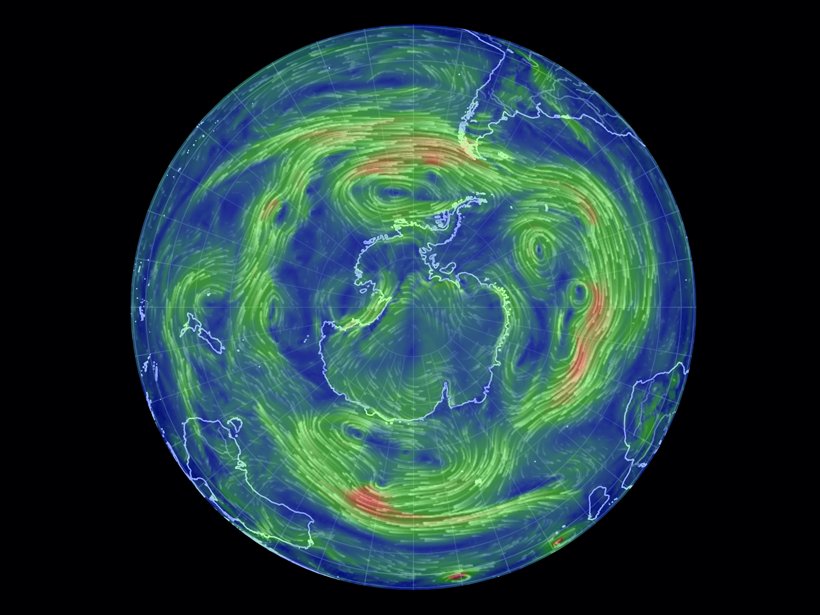
Estimating the Likelihood of Future Temperature Extremes
A prototype model allows scientists to investigate how wind eddies and other atmospheric phenomena may affect the prevalence of heat waves and cold snaps in the Southern Hemisphere.
Eddies Influence Productivity in the Subtropical Open Ocean
Ocean eddies may help recycle nutrients within giant current systems that encircle “desert” surface waters.
New Hints About How Martian Moons Formed
A new study finds that Phobos includes chunks of Martian crust.
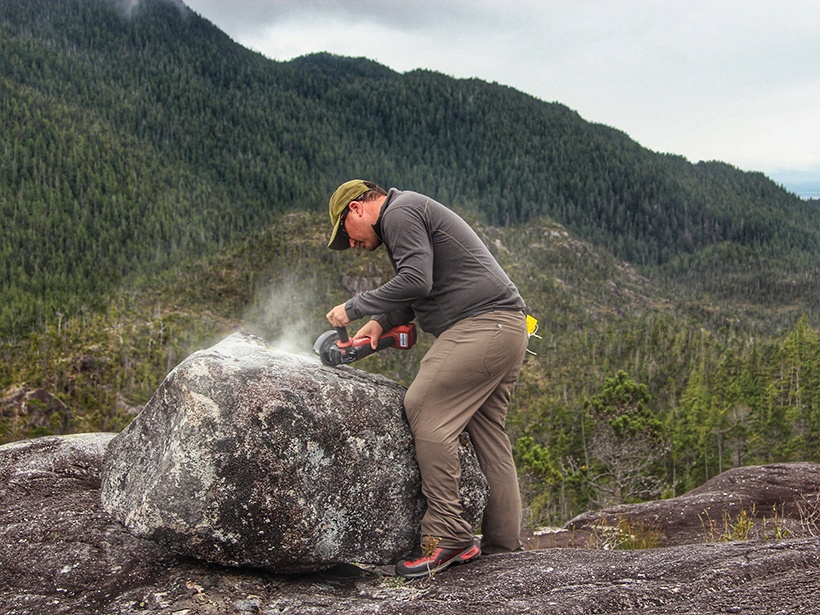
More Evidence Humans Migrated to the Americas via Coastal Route
A new chronology shows that ice-free areas existed along the British Columbia coast earlier than previously thought.
Balancing Robustness and Cost in Hydrological Model Optimization
A new study presents a framework for finding the best optimization algorithm.
Observations Show Gravity Waves Above Antarctica Dance in Winter
Year-round observations show gravity waves above Antarctica exhibit seasonal patterns that peak in winter, which could help researchers trace the source of this mysterious phenomenon.
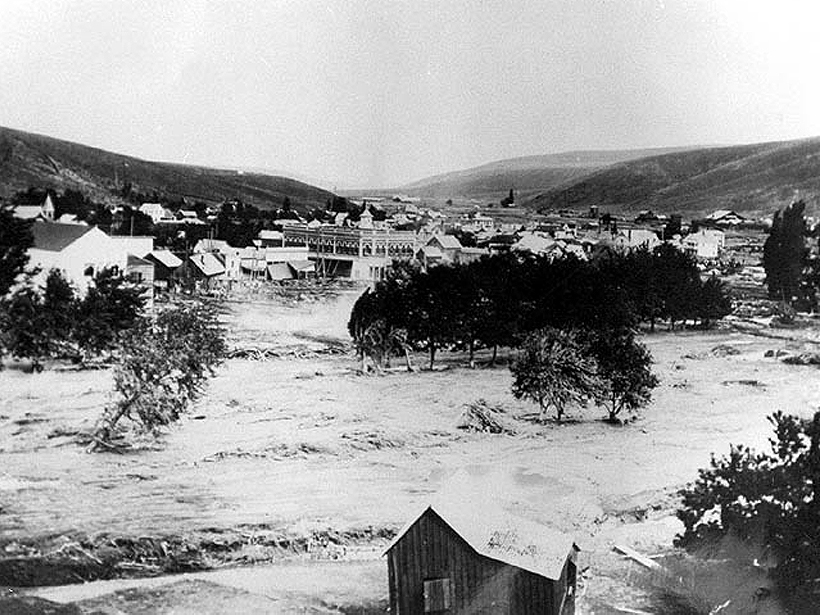
The Meteorological Culprits Behind Strange and Deadly Floods
A new study examines how unusual meteorology interacted with topography and other local conditions to generate some of the most devastating floods in American history.