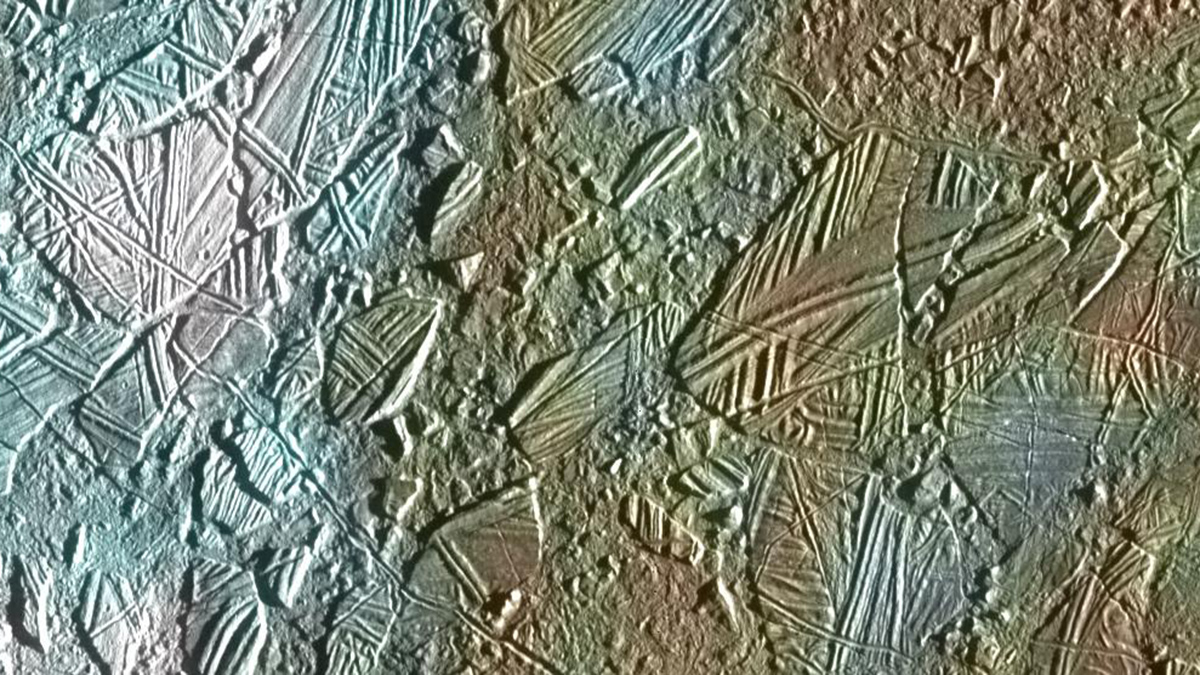
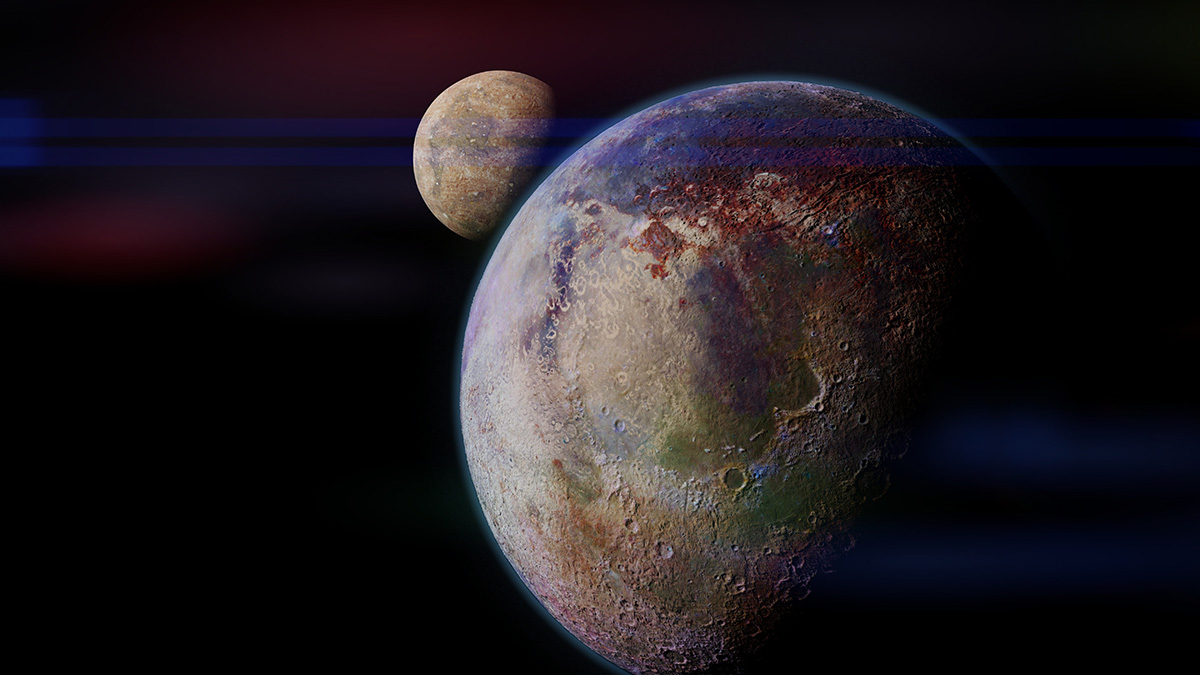
Researchers have shown that oceans buried below layers of ice are more common than previously thought.
exoplanets
A Planet Is Dramatically Losing Its Atmosphere
Helium that was once part of the atmosphere of the extrasolar planet HAT-P-32b is being ripped away and forming two giant streamers of gas several million kilometers long.
Nearby Volcano Planet Likely Fueled by Tidal Heating
A gravitational dance between a newly discovered exoplanet and its host star may be driving extreme volcanism on its surface.
Rocky Exoplanet May Have Magnetic Field
Magnetic interactions between stellar wind and the planet likely caused extrasolar space weather.
Exoplanets May Support Life in the Terminator Zone
A new study finds that the intersection between a searing dayside and a freezing nightside could be habitable.
Hydrogen May Push Some Exoplanets off a Cliff
High-pressure reactions of hydrogen and iron could explain gaps in the distribution of exoplanets.
Marauding Moons Spell Disaster for Some Planets
In solar systems beyond our own, some moons might eventually collide with their host planets, new simulations suggest.
“Hot Jupiter” Is in a Possible Death Spiral
Kepler’s first exoplanet is migrating toward its star, an evolved subgiant that is much bigger than first thought.
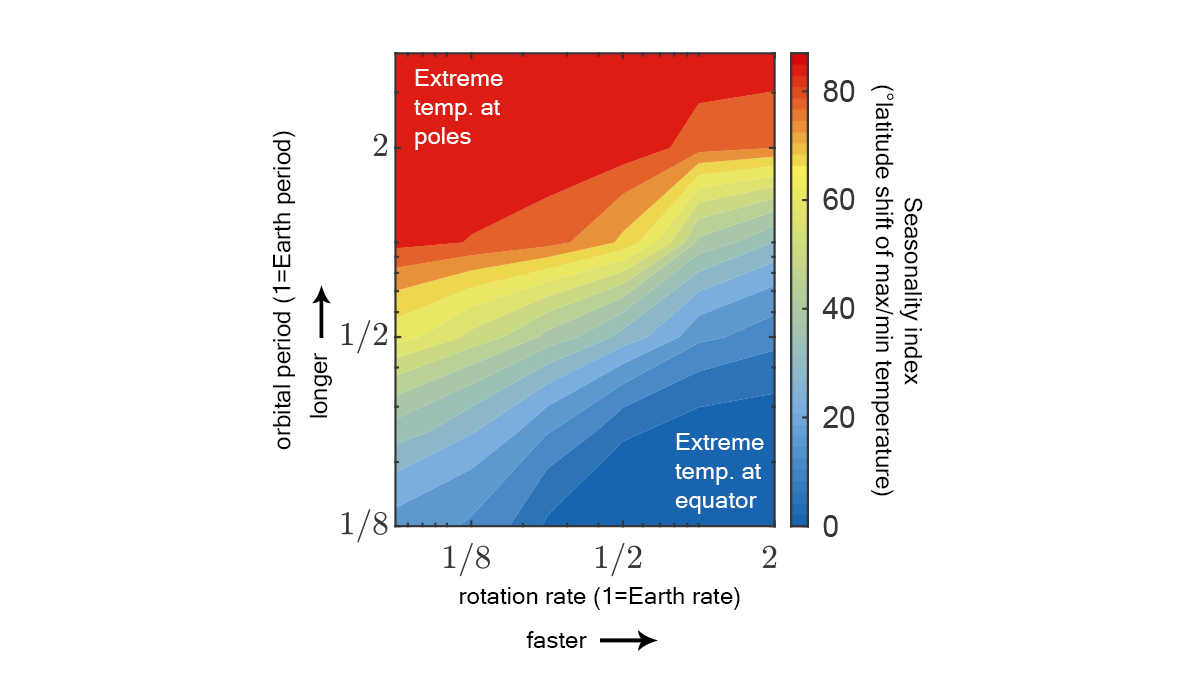
Extremeness of Seasons Determined by Planetary Motion Parameters
We’ve long known that a planet’s orbital period and tilt determine length and intensity of seasons. We now see rotation rate matters too: max temperature shifts poleward as rotation slows.
Massive Stars May Commit Grand Theft Planet
New simulations show that planets around young, massive stars may have been captured or stolen rather than homegrown.