I SCREAM, you SCREAM, we all SCREAM for faster climate modeling.
Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems (JAMES)
Equation Discovery for Subgrid-Scale Closures
Machine learning can discover closure equations for fluid simulations. A new study finds that common algorithms rediscover known, unstable closures, which can be stabilized with higher-order terms.
Ocean Impacts on European Winter Weather
State-of-the-art high-resolution models are needed to reveal the ocean’s role in driving extra-tropical weather systems.
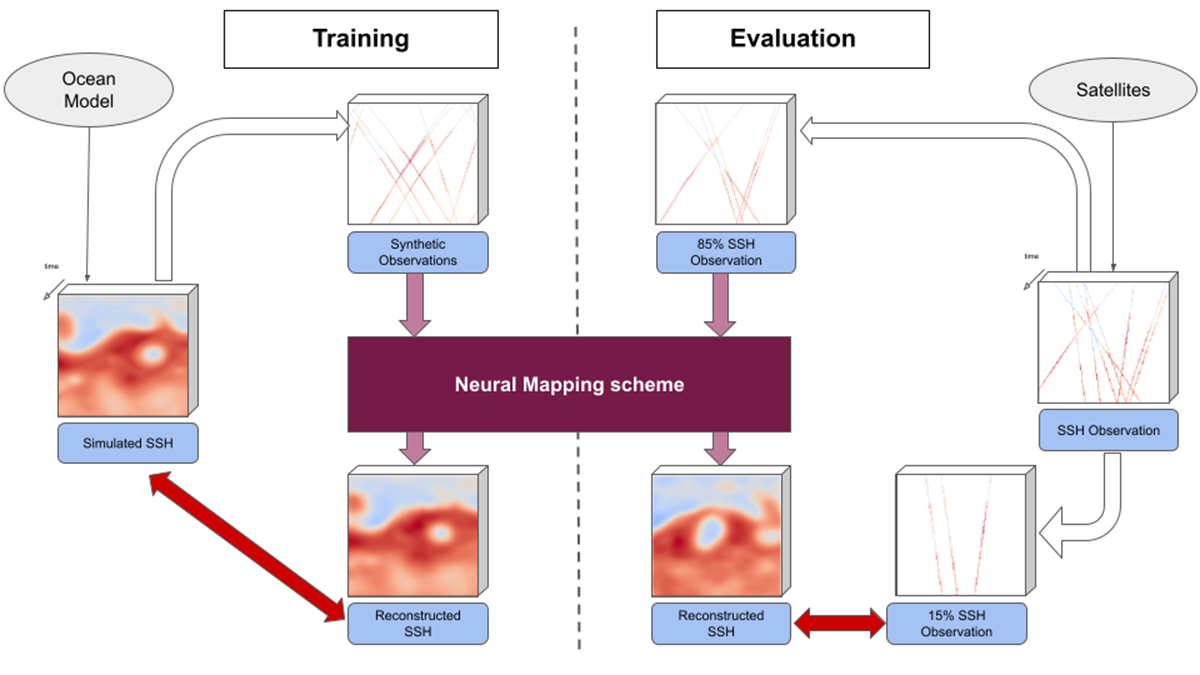
Physics + Machine Learning Provide a Better Map of Ocean Measurements
A new study offers a compelling example where the merger of dynamical modeling, machine learning, and ocean measurements enhances oceanographic understanding, monitoring, and mapping.
Machine Learning Masters Weather Prediction
Community datasets and evaluation standards are needed to further advance machine learning for weather prediction.
A Fast and Accurate Open-Source Atmospheric Transport Model
A new zonally-averaged atmospheric transport model will be useful for estimating emissions of ozone-depleting substances and greenhouse gases.
A Powerful New Model for U.S. Climate–Air Quality Interactions
NOAA’s Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory has developed a new variable-resolution global chemistry-climate model for research at the nexus of U.S. climate and air quality extremes.
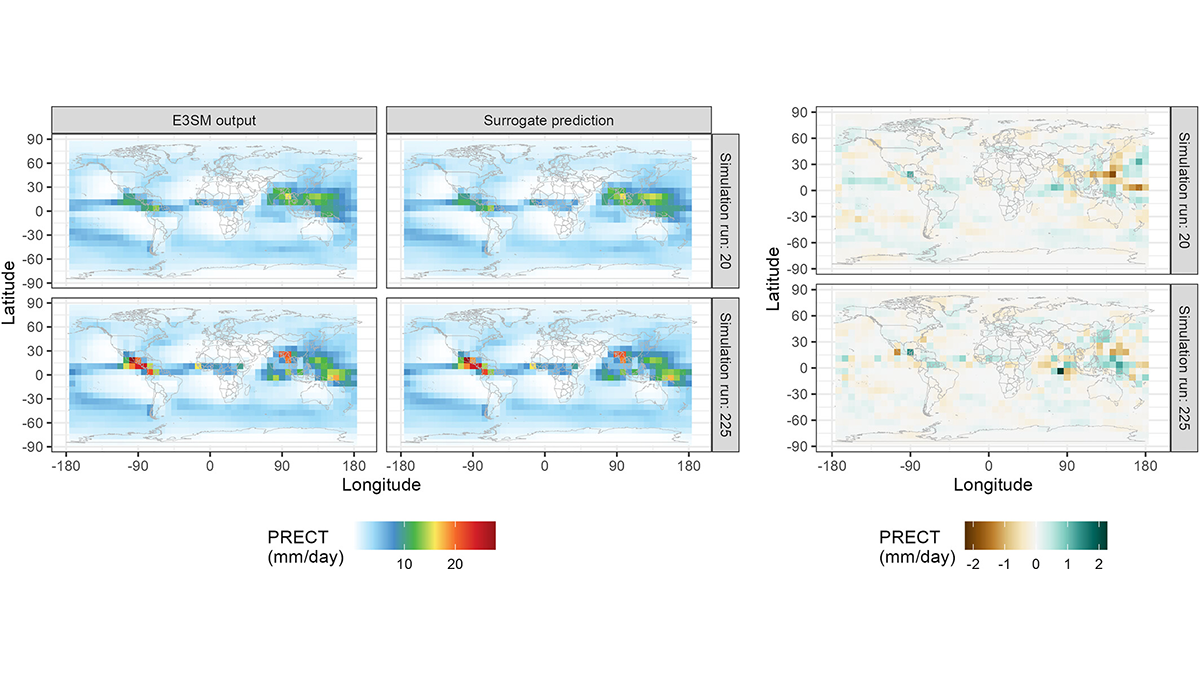
Autocalibration of the E3SM Atmosphere Model Improves Model Fidelity
A surrogate model was trained to predict E3SM atmosphere model spatial fields as a function of uncertain physical parameters and used to optimize the parameters for present-day climate.
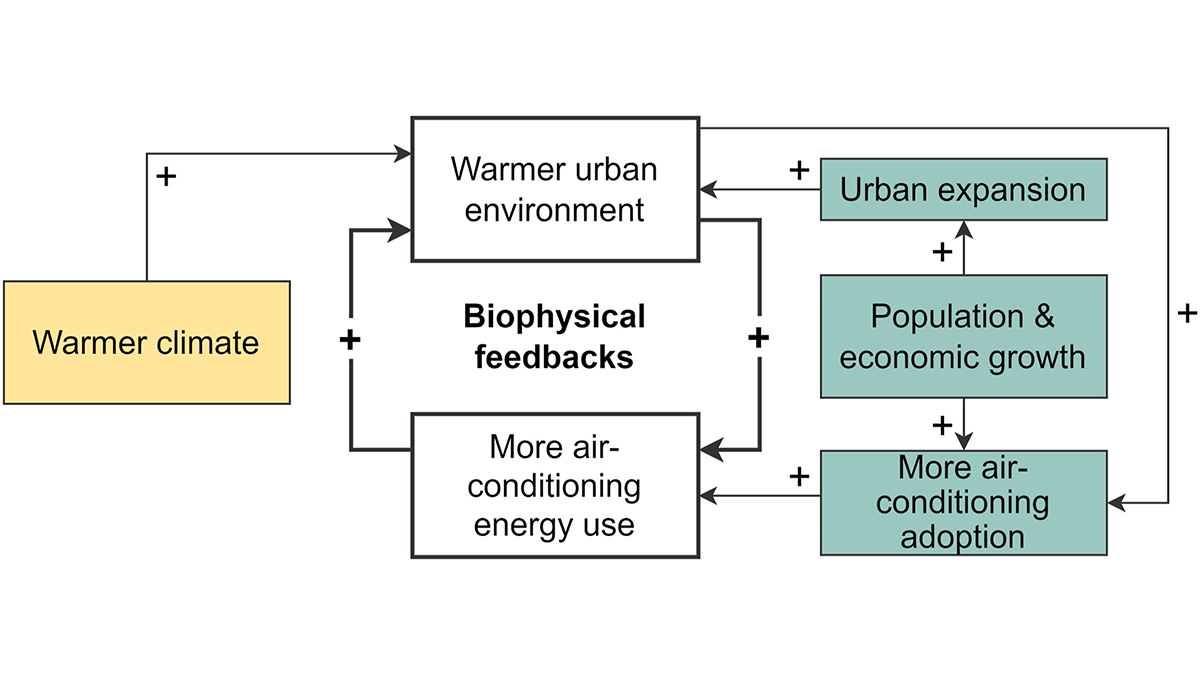
A New Scheme to Empower Global Air-Conditioning Energy Modeling
An explicit air-conditioning adoption scheme and a global dataset improve urban energy demand modeling and unlock exciting capabilities in Earth system models.
Verifying the Mathematics Behind Ocean Modeling
A series of test cases designed to confirm the accuracy of ocean models could help improve our understanding of large-scale climate processes.