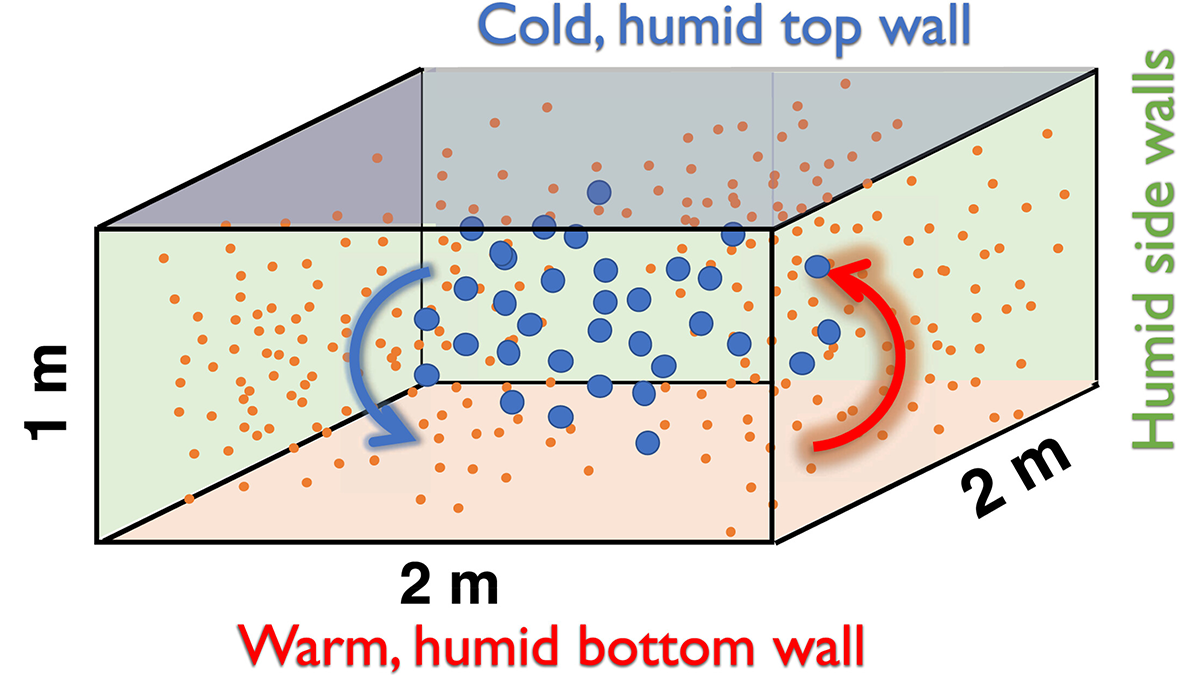
Researchers benchmark seven cloud models against cloud chamber measurements to reveal how well models capture aerosol-cloud-turbulence interactions and where models still diverge.
Jiwen Fan
Editor, Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems
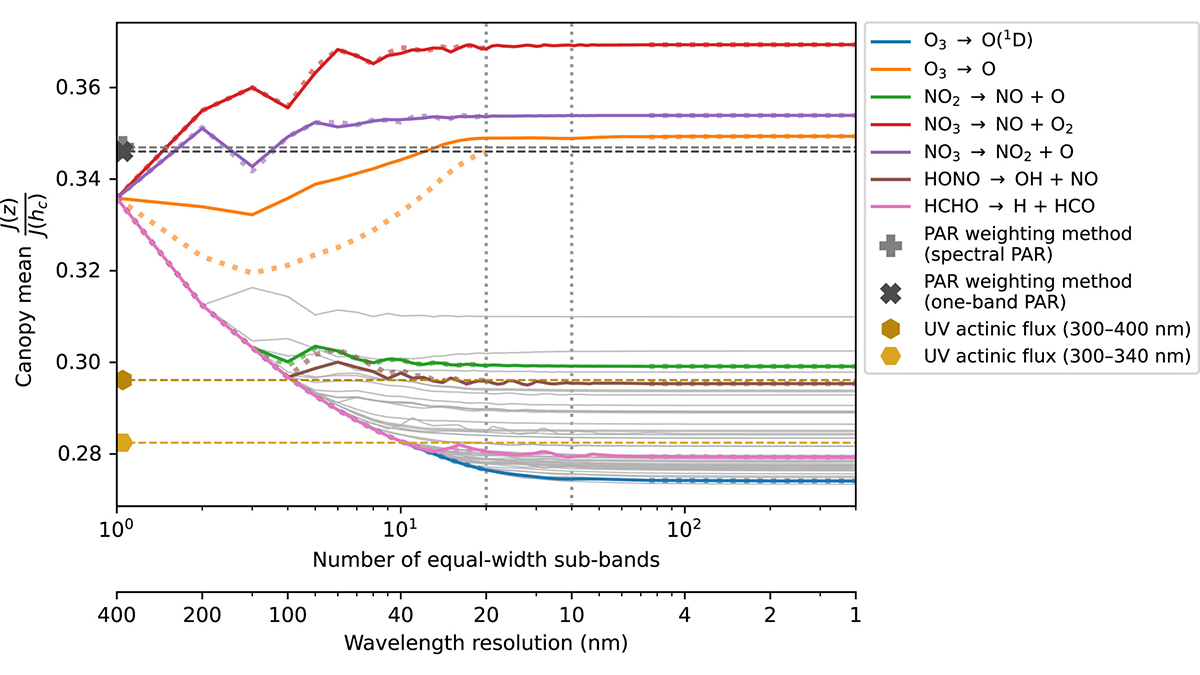
Spectral Solar Radiative Transfer in Plant Canopies
Spectrally resolved radiative transfer is needed to compute reliable estimates of sunlight transmission and photolysis of molecules within plant canopies.
A Powerful New Model for U.S. Climate–Air Quality Interactions
NOAA’s Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory has developed a new variable-resolution global chemistry-climate model for research at the nexus of U.S. climate and air quality extremes.
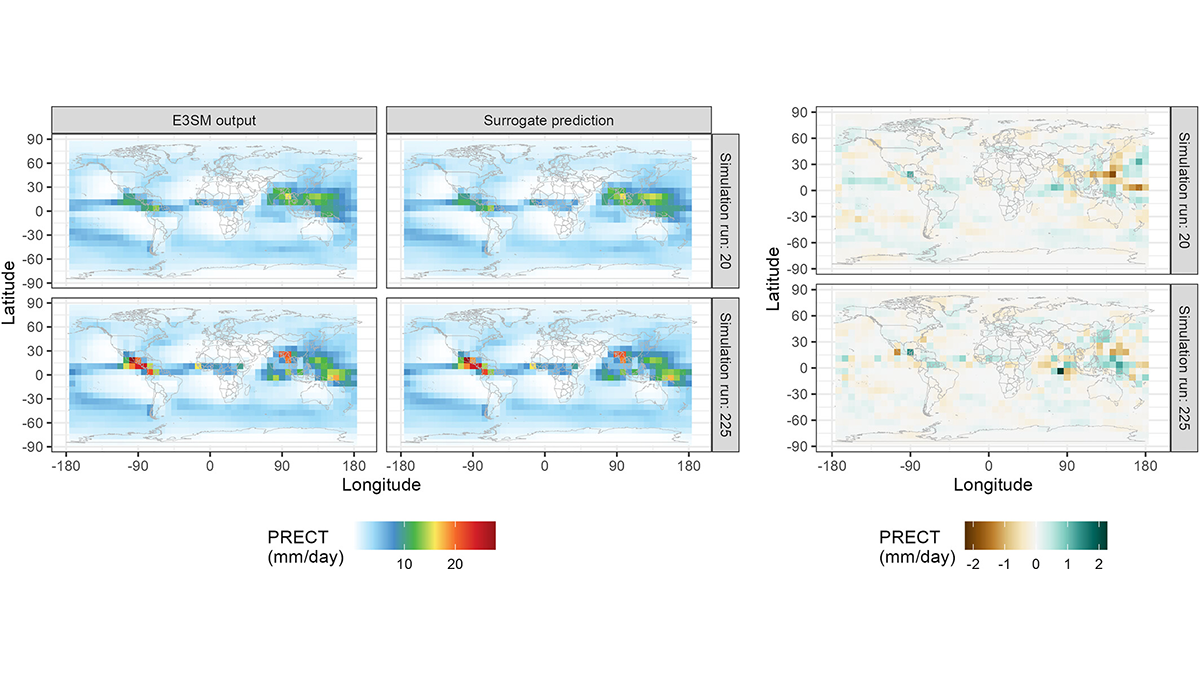
Autocalibration of the E3SM Atmosphere Model Improves Model Fidelity
A surrogate model was trained to predict E3SM atmosphere model spatial fields as a function of uncertain physical parameters and used to optimize the parameters for present-day climate.
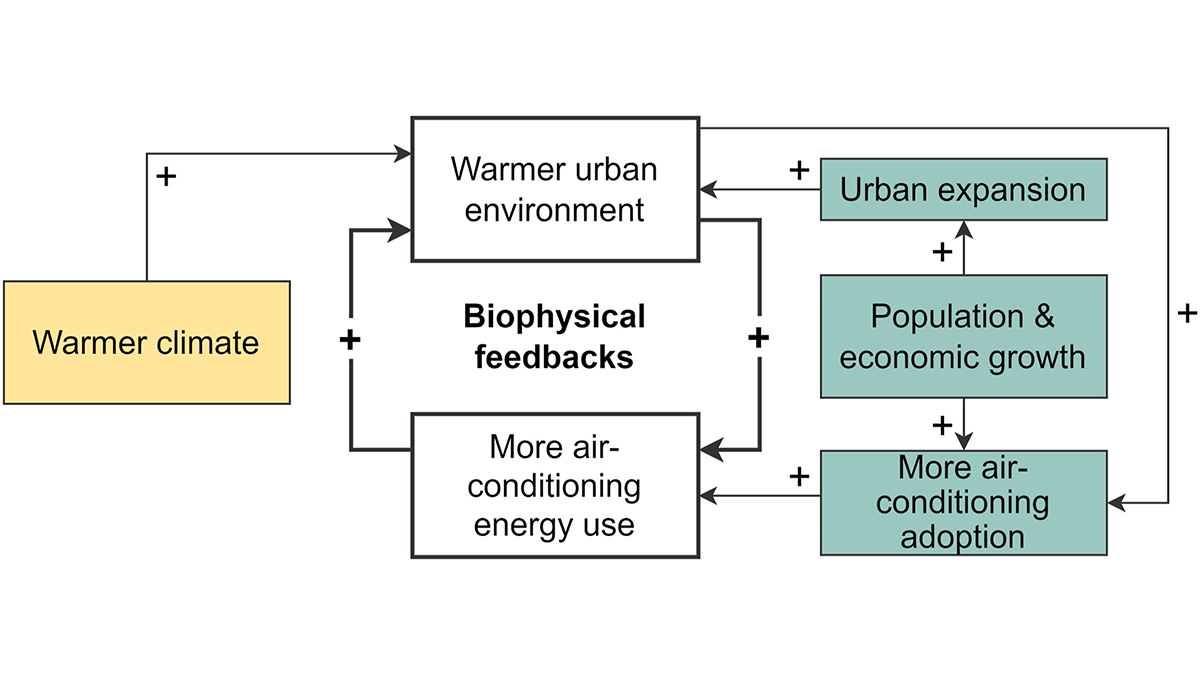
A New Scheme to Empower Global Air-Conditioning Energy Modeling
An explicit air-conditioning adoption scheme and a global dataset improve urban energy demand modeling and unlock exciting capabilities in Earth system models.
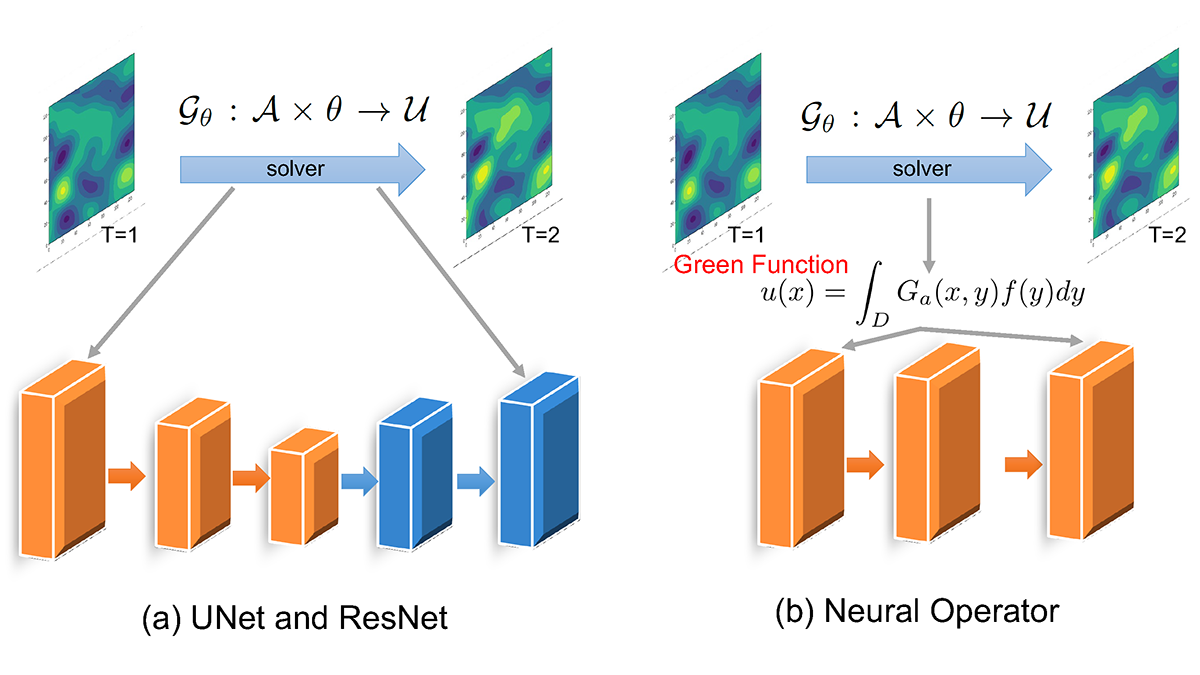
Machine Learning Accelerates the Simulation of Dynamical Fields
Fourier neural operator solvers accurately emulate particle-resolved direct numerical simulations and significantly reduce the computational time by two orders of magnitude.
Urban Greening Could Help Achieve Carbon Neutrality Goals
A new modeling framework highlights that urban greening is a sustainable solution to achieve environmental co-benefits in mitigating heat and carbon emissions.
New Aerosol Model Better Represents Black Carbon Properties
An improved representation for black carbon microphysical and optical properties alleviates overestimations of aerosol absorption efficiency in global climate models.
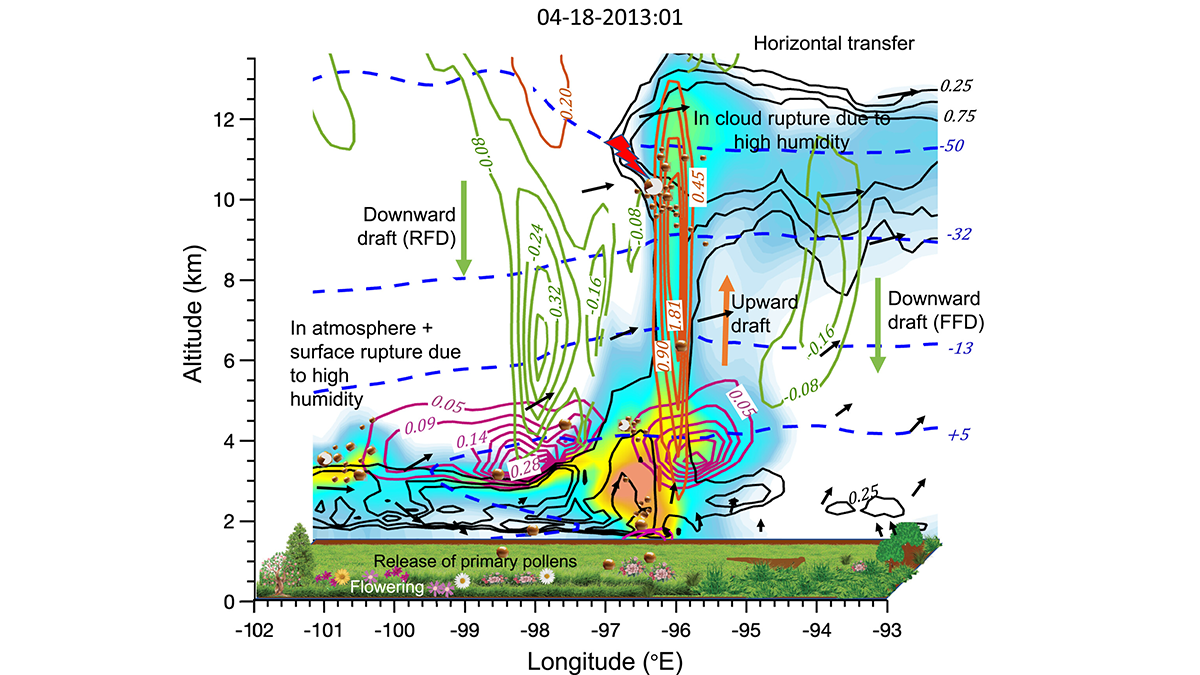
Simulating the Journey of Pollen in the Atmosphere
A new study couples an emission and transport scheme of pollen from vegetation, and explores pollen’s evolution in different atmospheric conditions and its impacts on clouds and precipitation.
Simulating Clouds on Arbitrary Grids in Any Spatial Direction
A new non-column based spectral element implementation of cloud microphysics enables full 3D flexibility in computing clouds and improves computational efficiency.