Although the total surface area of Earth’s lakes emits less methane than previously believed, it is still among the largest natural methane sources.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences
Using Sap Flow to Infer Plant Hydraulic Properties
The internal hydraulic properties of plants are difficult to measure but may be inferred from observable sap flow.
Una nueva perspectiva sobre la vida microbiana en las aguas termales del Parque Yellowstone
Una investigación sobre los rangos de hábitat de microorganismos en las fuentes hidrotermales del parque nacional Yellowstone muestran condiciones ambientales propicias para la interacción entre cianobacterias y algas.
How Forest Structure Drives Productivity
Data from northern Wisconsin forest sites uncovered that vertical heterogeneity metrics are the most influential factors underlying rates of photosynthesis.
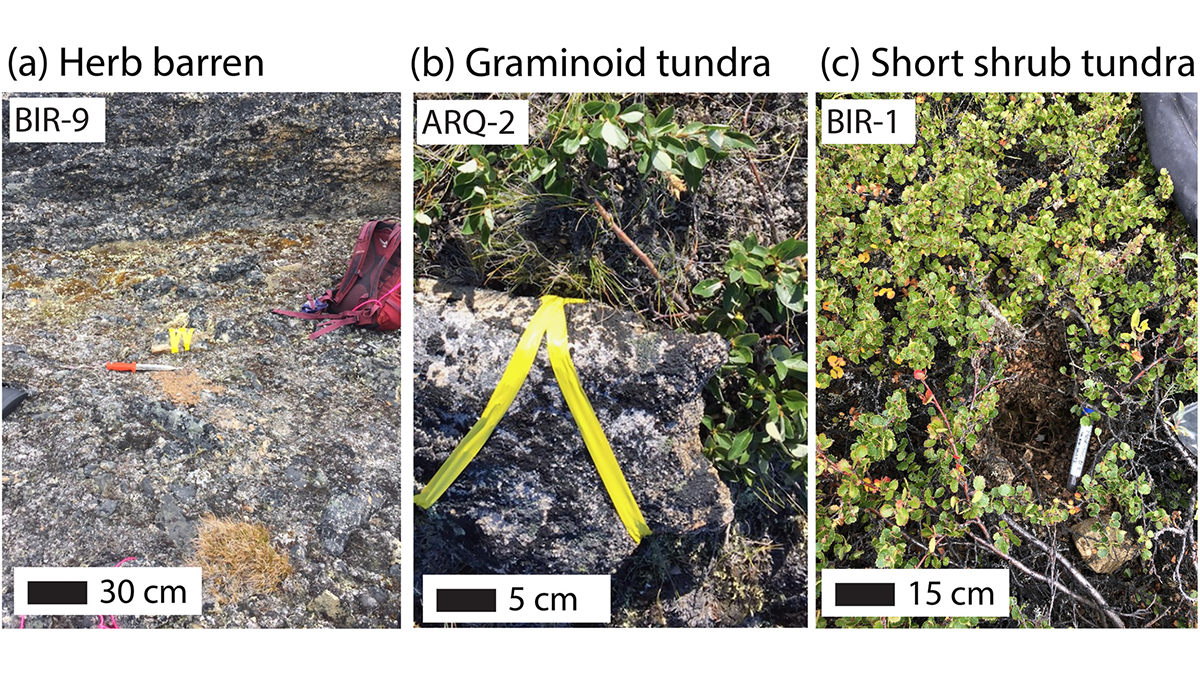
It’s Cool to be Short When You’re in the Arctic Permafrost
Extensive ground temperature measurements complicate our understanding of how vegetation cover, snow duration, and microtopography influence the pace of permafrost thaw in a changing climate.
A Future Without Ice Cover
Winter is fading away, but the answers may be beneath the ice; a new collection on winter limnology tackles the unknowns.
Mediciones pareadas de gases: ¿un nuevo trazador biogeoquímico?
Una técnica que mide la relación entre el dióxido de carbono producido y el oxígeno consumido podría mejorar las predicciones de la respuesta del suelo al cambio climático.
Paired Gas Measurements: A New Biogeochemical Tracer?
A technique that measures the ratio of carbon dioxide produced to oxygen consumed could improve predictions of soil’s response to climate change.
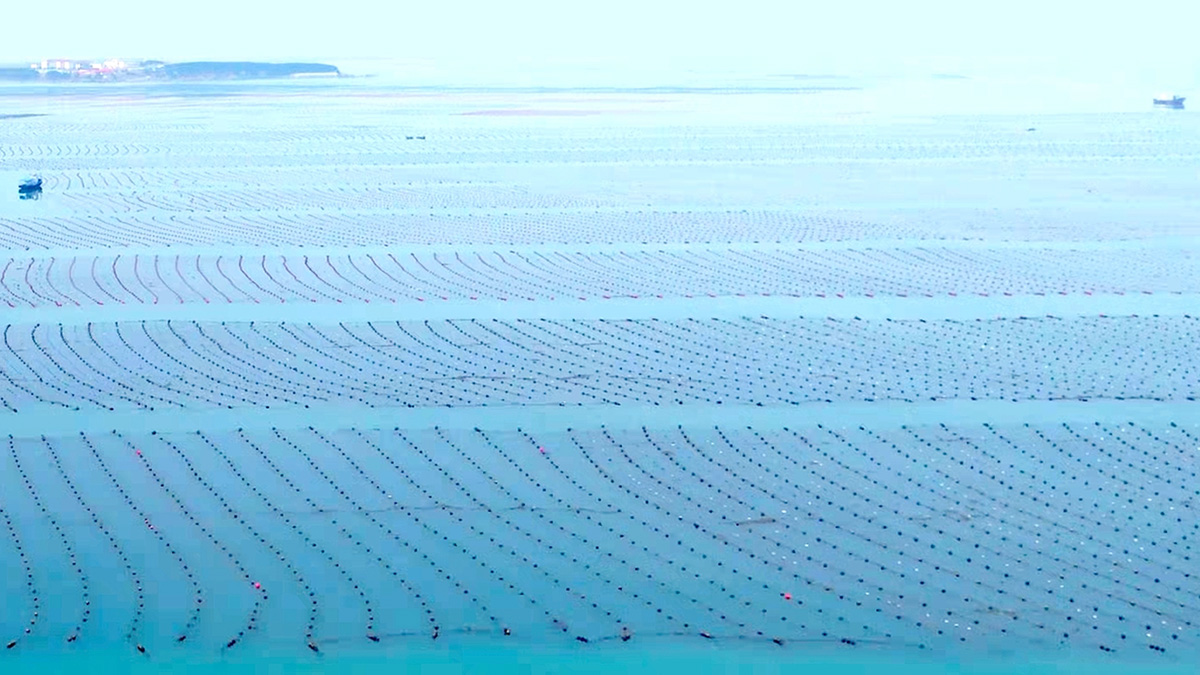
Coastal Aquaculture Can Reduce Nutrient Transport
High-resolution simulations of China’s Sanggou Bay show that suspended aquaculture alters hydrodynamics and weakens transport of nutrients to the area from offshore bottom water.