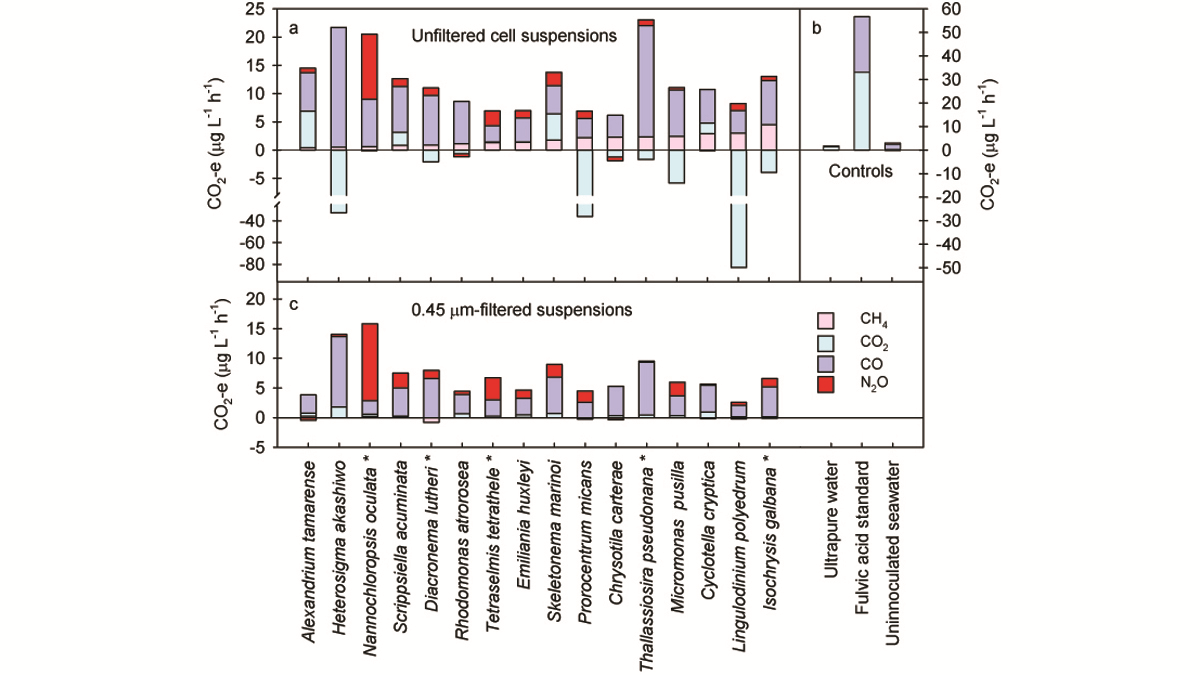
Phytoplankton remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere; a new study reveals that marine phytoplankton can also produce greenhouse gases when exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences
Earthly Lava Tubes May Offer Insights into Extraterrestrial Life
New research finds that Actinobacteria in lava caves fix carbon and survive independent of surface inputs, offering a fresh perspective in the search for life beyond Earth.
Minimal Evidence of Permafrost Carbon in Siberia’s Kolyma River
New research finds that Arctic rivers currently transport limited permafrost-derived dissolved organic carbon, which has implications for understanding the region’s changing carbon cycle—and its potential to accelerate climate change.
Does the Priming Effect Happen Underwater? It’s Complicated
A new meta-analysis finds evidence that adding fresh organic material can increase decomposition rates, but when and why that happens remain unclear.
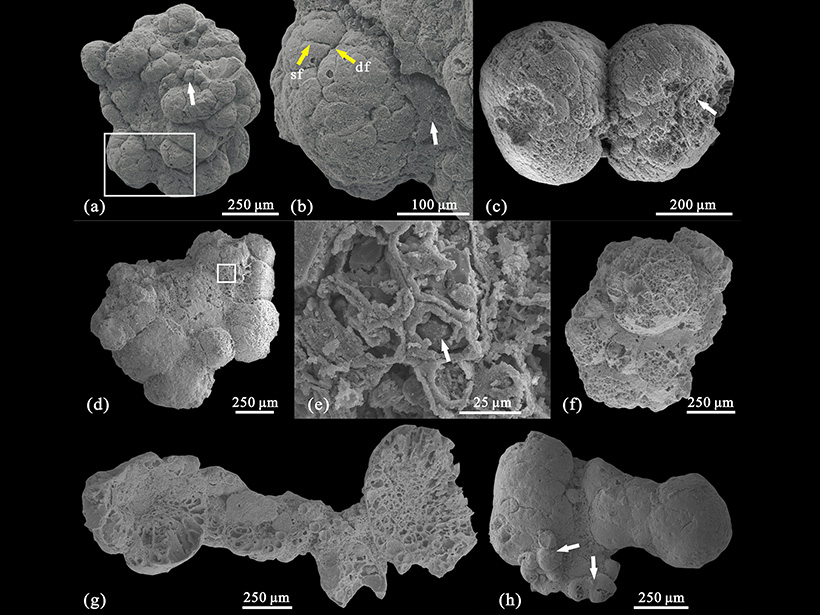
Multicellular Algae Discovered in an Early Cambrian Formation
A new study describes eukaryotic organisms found organized in a cortex-medulla pattern in southern China’s Kuanchuanpu Formation.
Examining the Intricacies of Ozone Removal by Deciduous Forests
A new study looks into how air movement in the atmospheric boundary layer affects ozone removal by deciduous forests, which are a significant ozone sink.
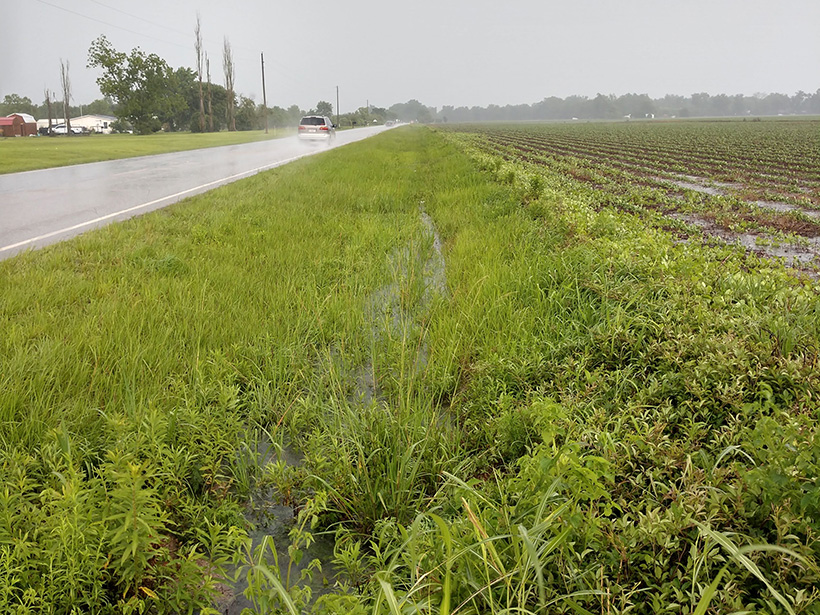
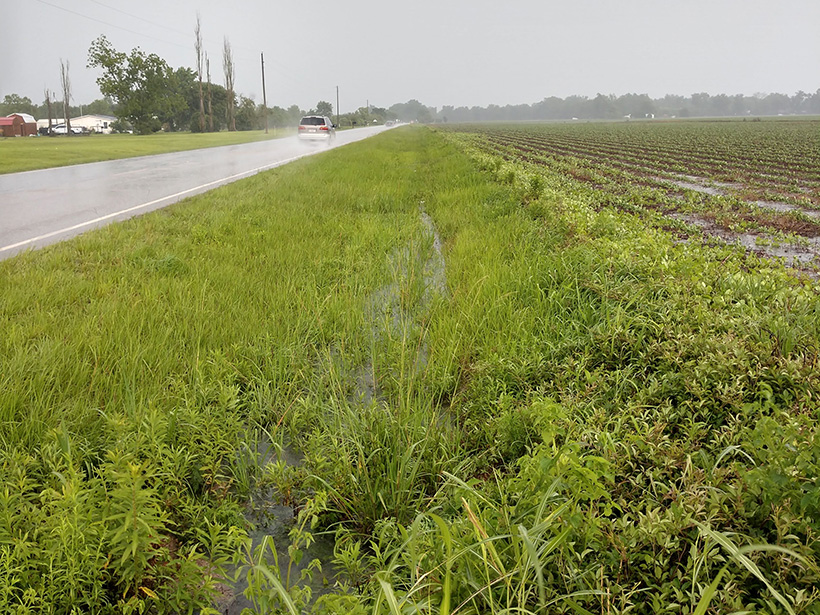
Roadside Ditches Are Effective at Nitrogen Removal
Researchers compared the nitrogen removal potential by microbes in ditches that drained forested, urban, and agricultural lands and discovered that roadside ditches are important areas for removing nutrients.
Una mirada global al carbono orgánico superficial del suelo
El carbono orgánico del suelo es un elemento importante para la salud de los ecosistemas y del clima. En la actualidad la teledetección permite a los científicos observar globalmente esta importante pieza del rompecabezas del carbono.
Las brechas en las redes ambientales en América Latina
A pesar de su notable influencia en los ciclos globales del carbono y el agua, América Latina representa una proporción relativamente pequeña de sitios FLUXNET, lo que limita la representatividad de la red en la región.