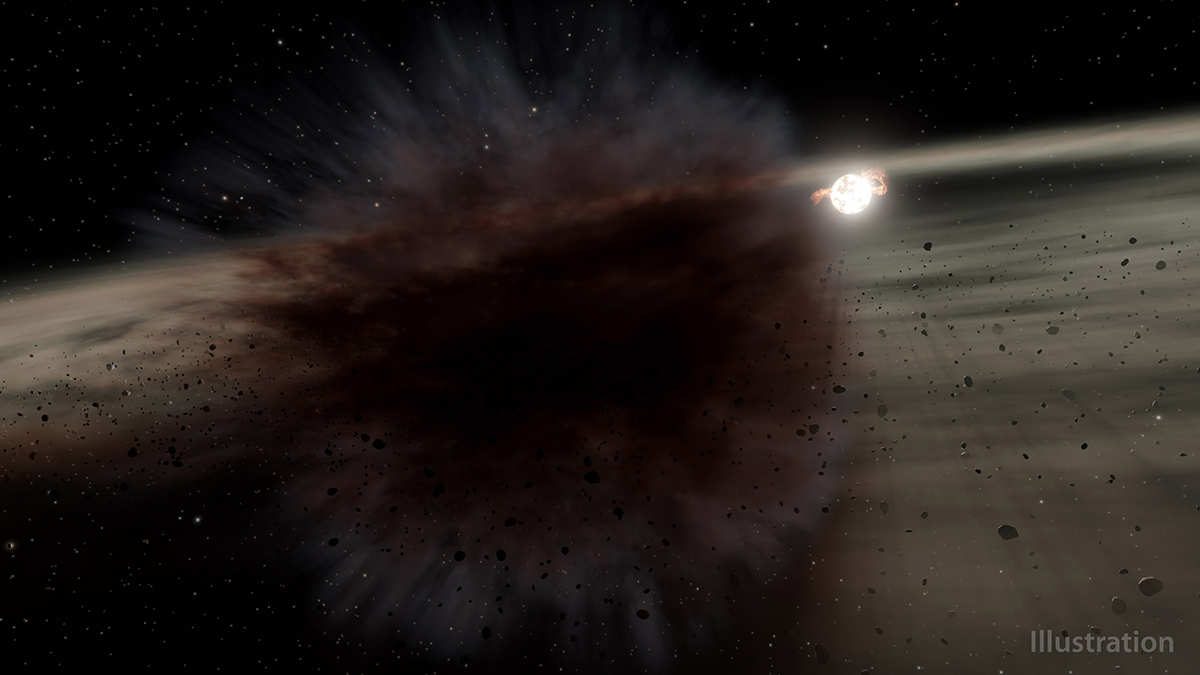
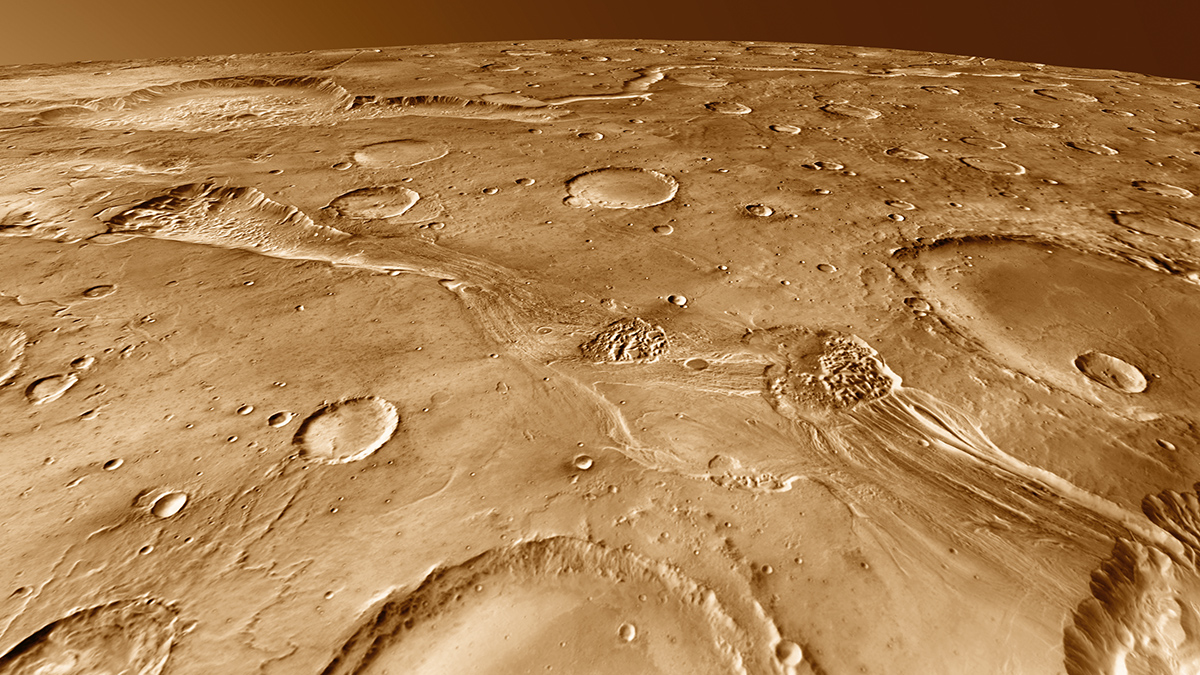
An unusual concentration of impact craters suggests that they may have been caused by the breakup of an asteroid that created a temporary debris ring around Earth.
meteors & meteorites
These Five Craters May Have Birthed a Third of Martian Meteorites
Researchers have homed in on five craters on the Red Planet that are the likely sources of Martian meteorites.
The Origin of the Moon’s Thin Atmosphere Might Be Tiny Impacts
Minuscule meteoroids slamming into the lunar surface could be kicking up most of the atoms that make up the lunar exosphere.
Parts of Mars Might Be Younger Than We Thought
Data from InSight’s seismometer suggest more impactors strike the Red Planet than expected.
The Past, Present, and Future of Extraterrestrial Sample Return
Retrieving samples from distant solar system bodies has revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos and our place in it.
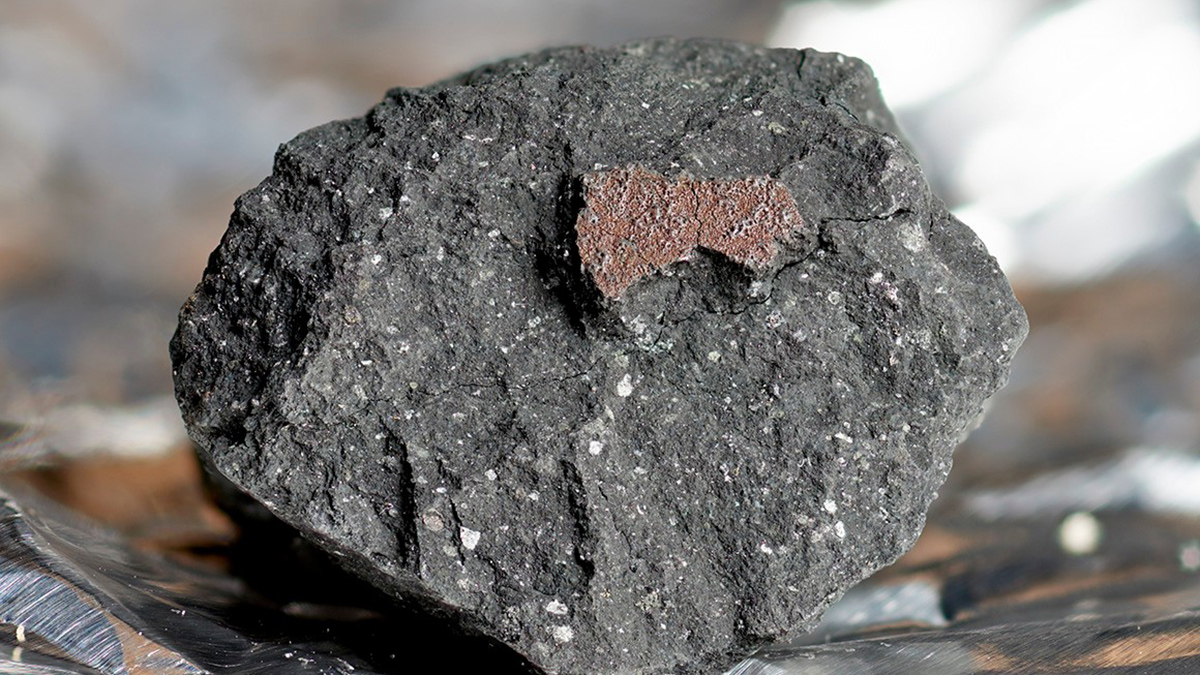
A Splashy Meteorite Was Forged in Multiple Collisions
The Winchcombe meteorite was recovered, largely from a driveway, just hours after it fell to Earth, preserving evidence that its early relatives could have filled Earth’s oceans.
Introducing the New Editor-in-Chief of JGR: Planets
Learn about the person taking the helm of JGR: Planets and their vision for the coming years.
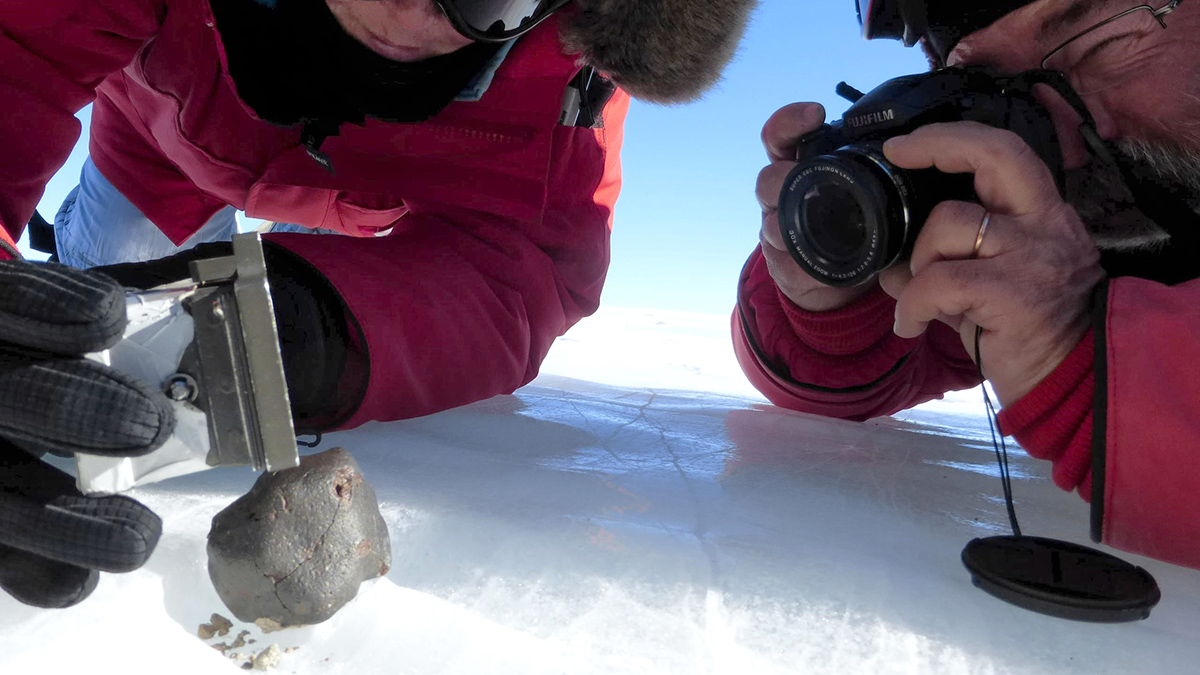
Antarctic Meteorites Are Going, Going, May Soon Be Gone
If warming ice gobbles up meteorites, science may lose a cheap source of space rocks.
Hand Magnets Destroy the Magnetic Record of Meteorites
Meteorite collectors often use strong magnets for classification, but this approach destroys crucial evidence of processes active in the early solar system.
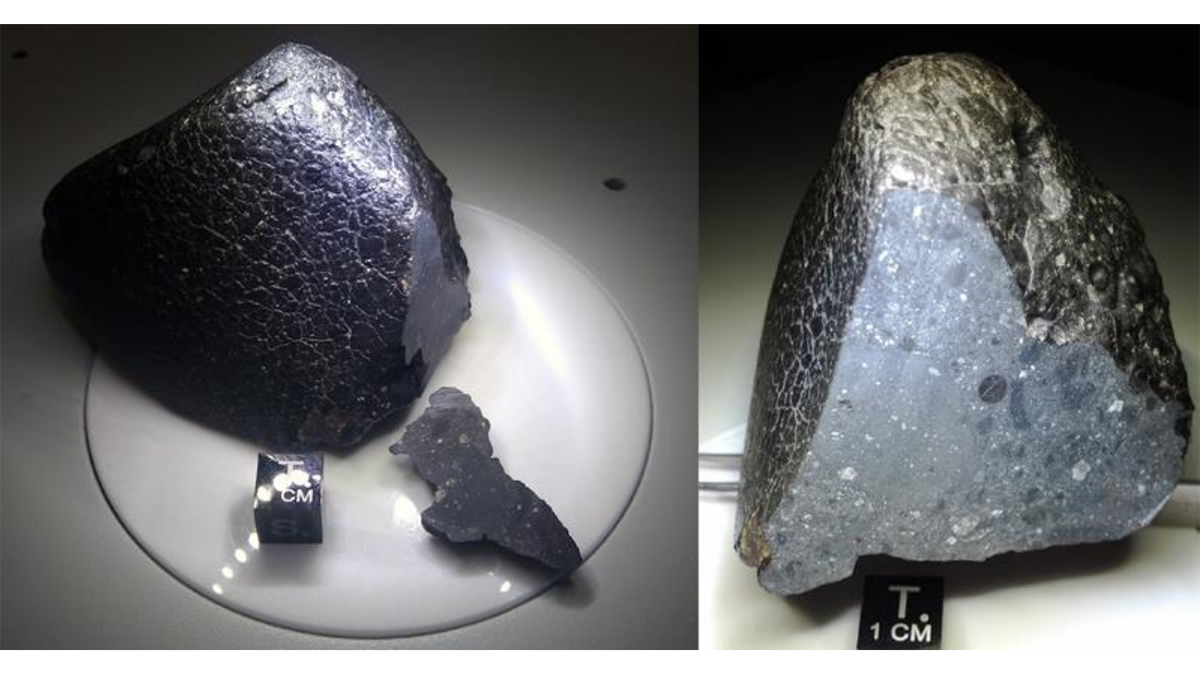
Molten Meteorites Didn’t Deliver Earth’s Water
A new study has ruled out large, once-molten meteorites called achondrites as sources of Earth’s water.