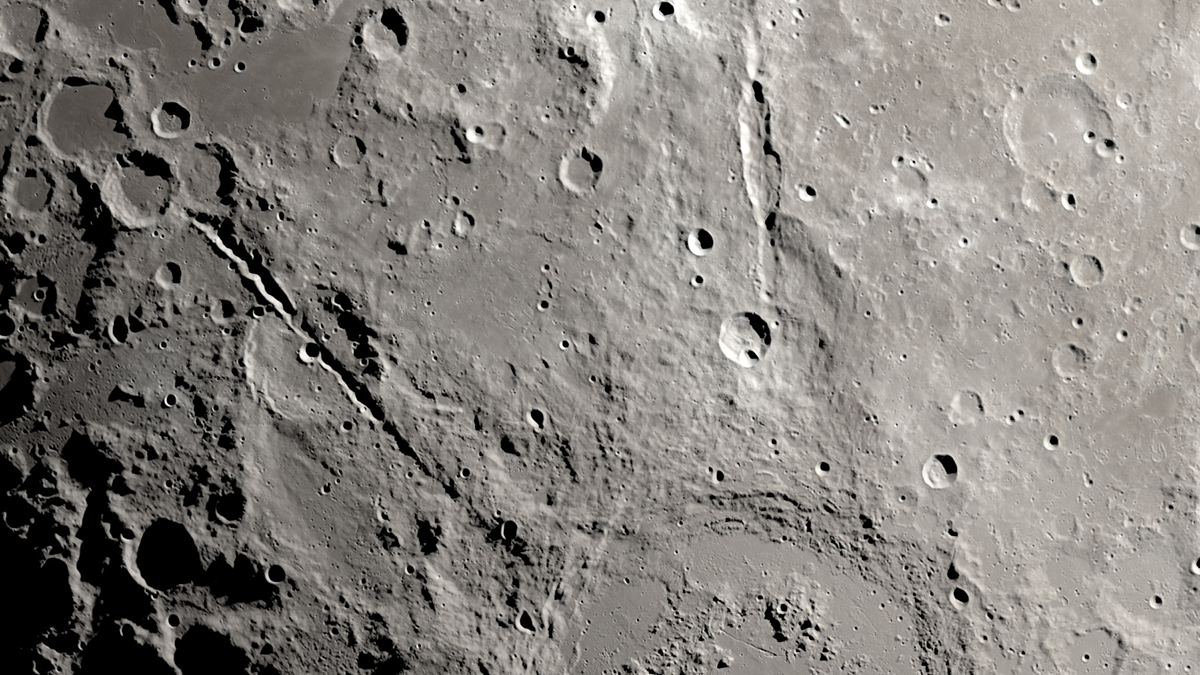
Two valleys extending away from a giant crater suggest that upcoming Artemis missions are more likely to sample ancient lunar terrain than impactor material.
Space & Planets
Come on Feel the Noise: Machine Learning for Seismic-Wind Mapping on Mars
Wind vibrations measured by NASA’s InSight mission seismometer are mapped into wind speed and direction to detect major annual weather patterns and open new possibilities for planetary instrumentation.
Cinturones polvorientos ofrecen una visión más clara de la formación de exoplanetas
Las observaciones en longitudes de onda milimétricas de polvo y guijarros en 74 sistemas estelares sugieren que las migraciones planetarias podrían ser más comunes de lo que pensábamos.
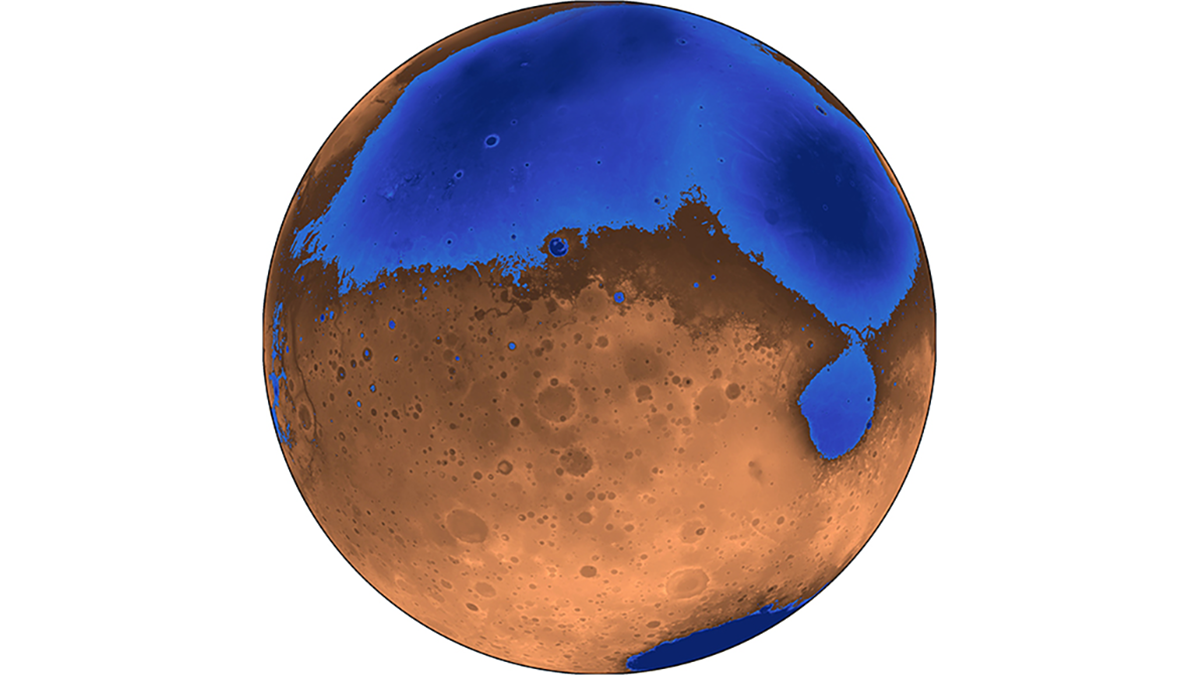
Buried Sediments Point to an Ancient Ocean on Mars
Ground-penetrating radar data collected by the Zhurong rover reveal gently sloping sediments in Mars’s northern lowlands that hint at a shoreline.
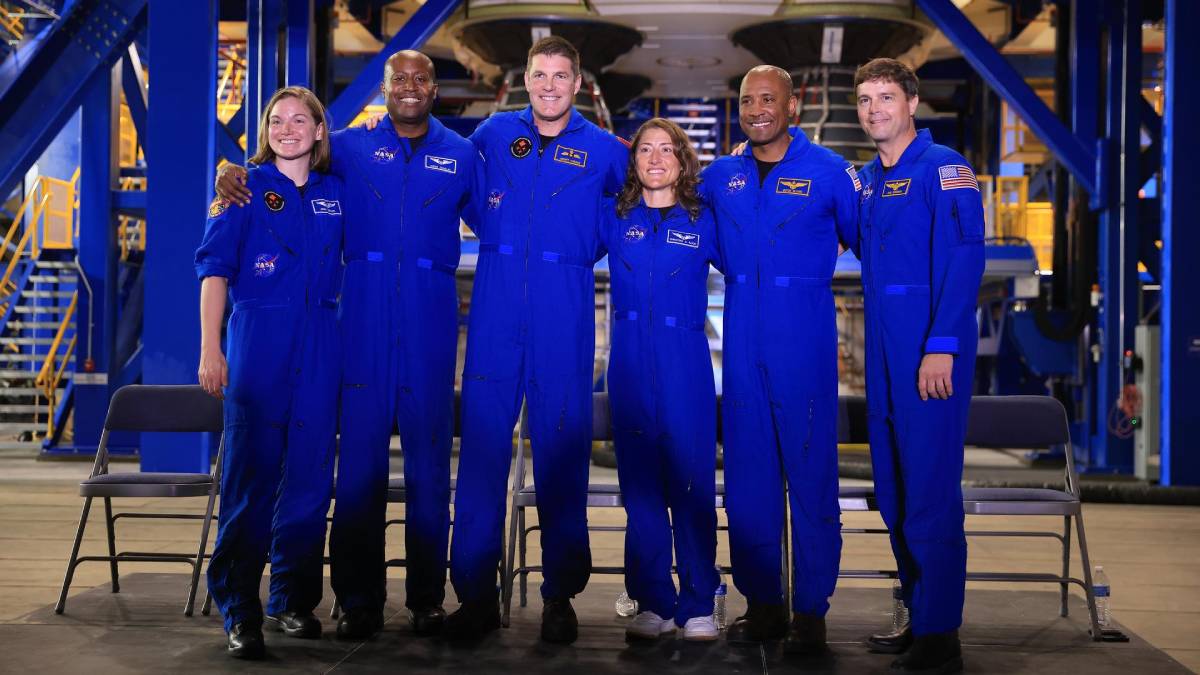
NASA Abandons Pledge to Put Women, Astronauts of Color on the Moon
NASA has dropped its commitment to land the first woman, the first person of color, and the first non-American astronaut on the Moon through the Artemis program.
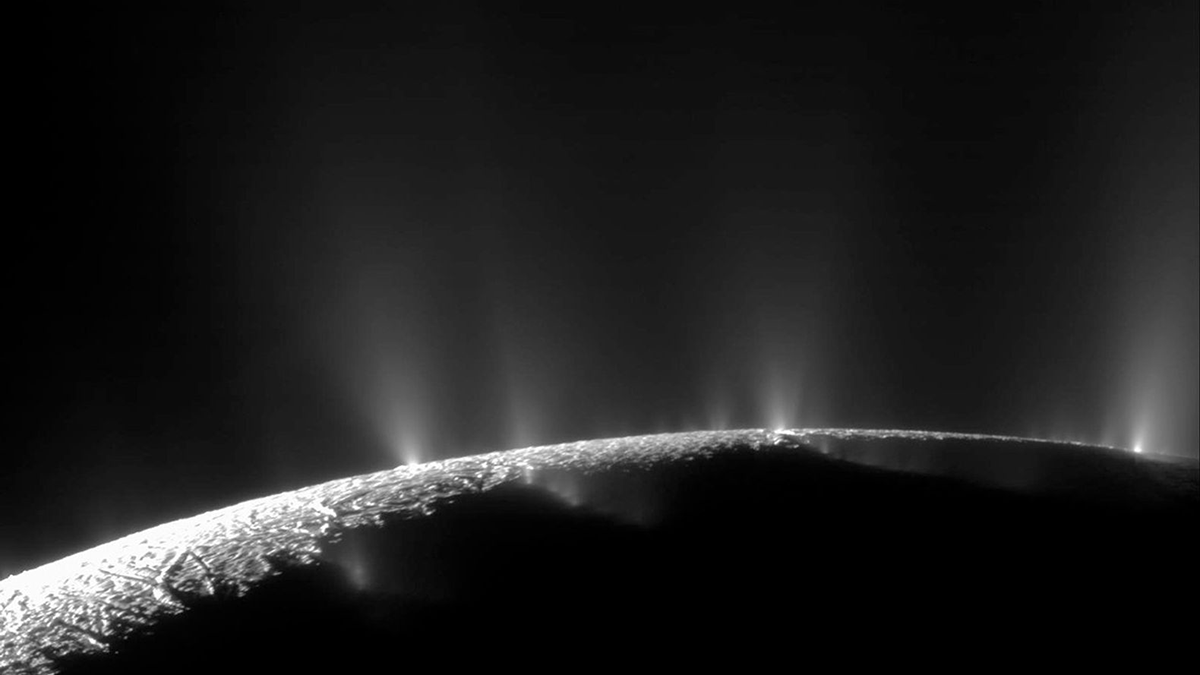
Using Algorithms to Help Find Life on Icy Ocean Worlds
Scientists could use machine learning to analyze atmospheric samples in order to help identify microbes on frozen moons. They’re testing the concept using bottles of brine and smelly bacteria.
French Scientist, En Route to Conference, Denied U.S. Entry for Trump-Critical Messages
On 9 March, a French researcher traveling to a science conference near Houston, Texas, was denied entry to the United States and expelled back to France.
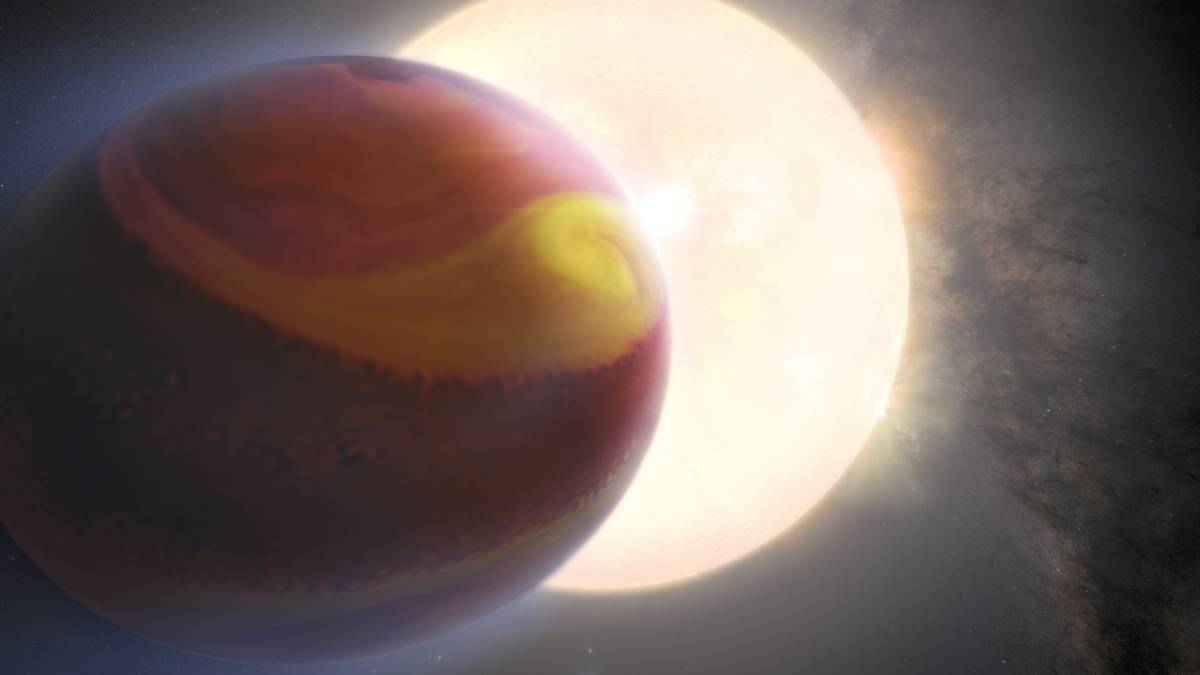
First 3D Map of Exoplanet Weather Reveals Superfast Jet
New observations also answer a long-standing question about where this ultrahot planet keeps its titanium.
Martian Dust Will Be a Health Hazard for Astronauts
Prolonged exposure to the Red Planet’s regolith, which contains carcinogens and toxic metals, could pose respiratory threats and increase chronic disease risk.
Explaining Mars’ Mysteriously Magnetic Crust
Fluid-rock interactions on ancient Mars may have produced abundant magnetic minerals that preserved unusually intense records of the planet’s now-extinct magnetic field.