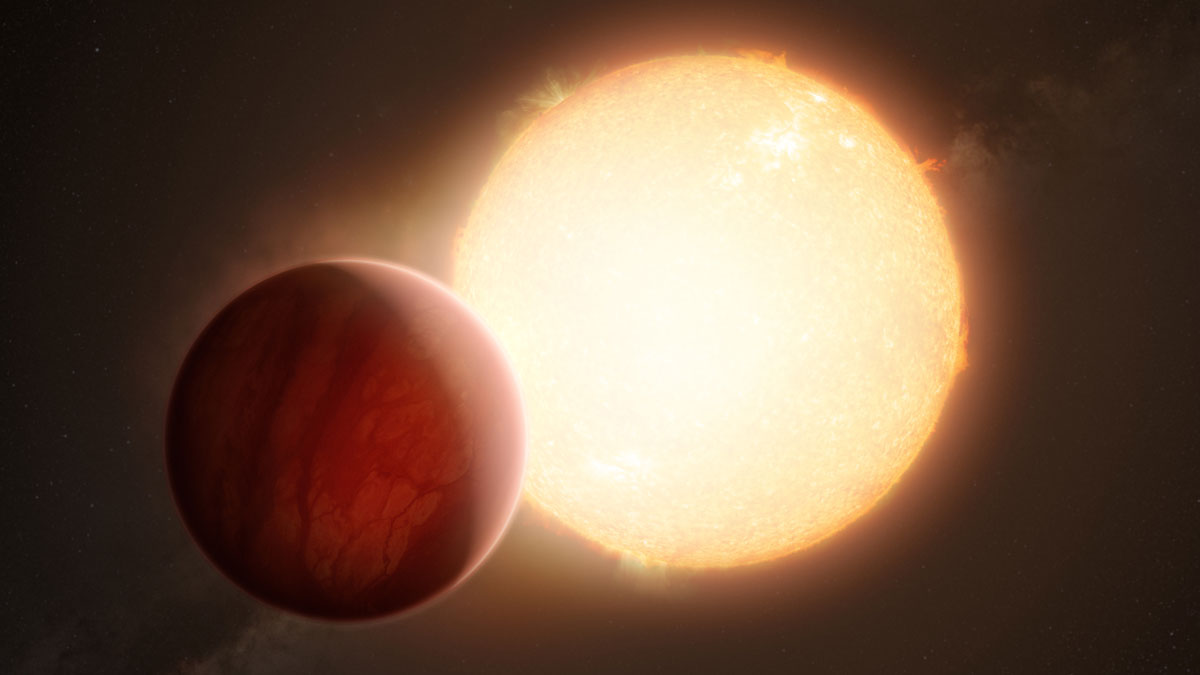
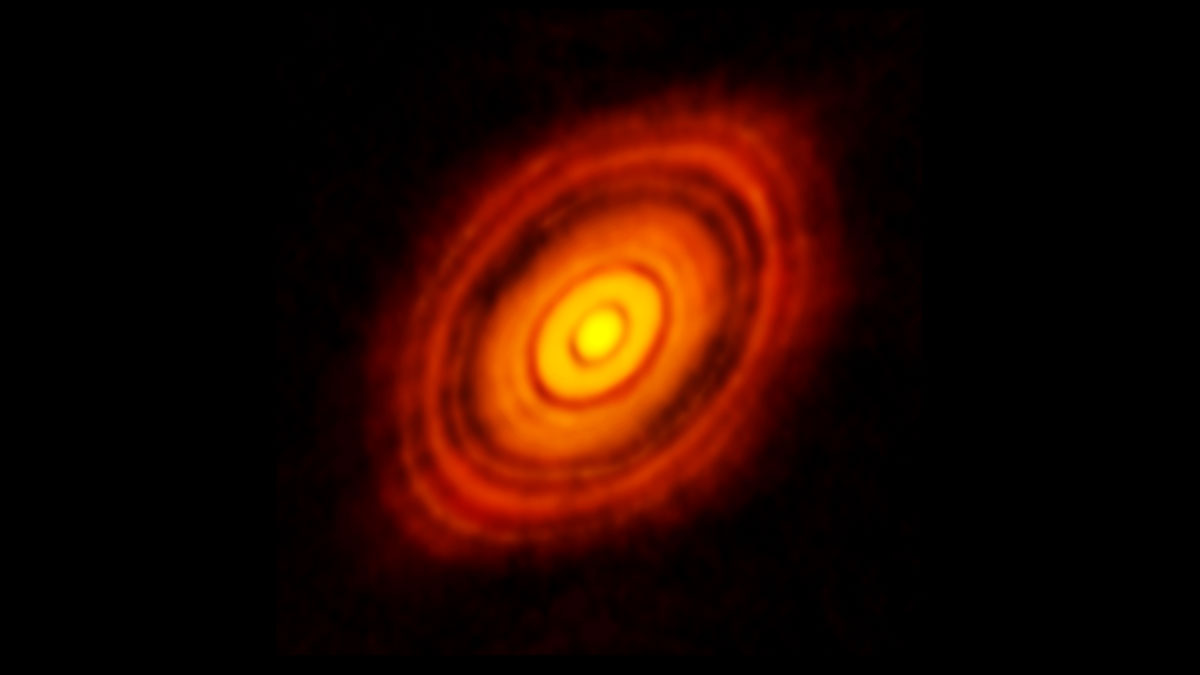
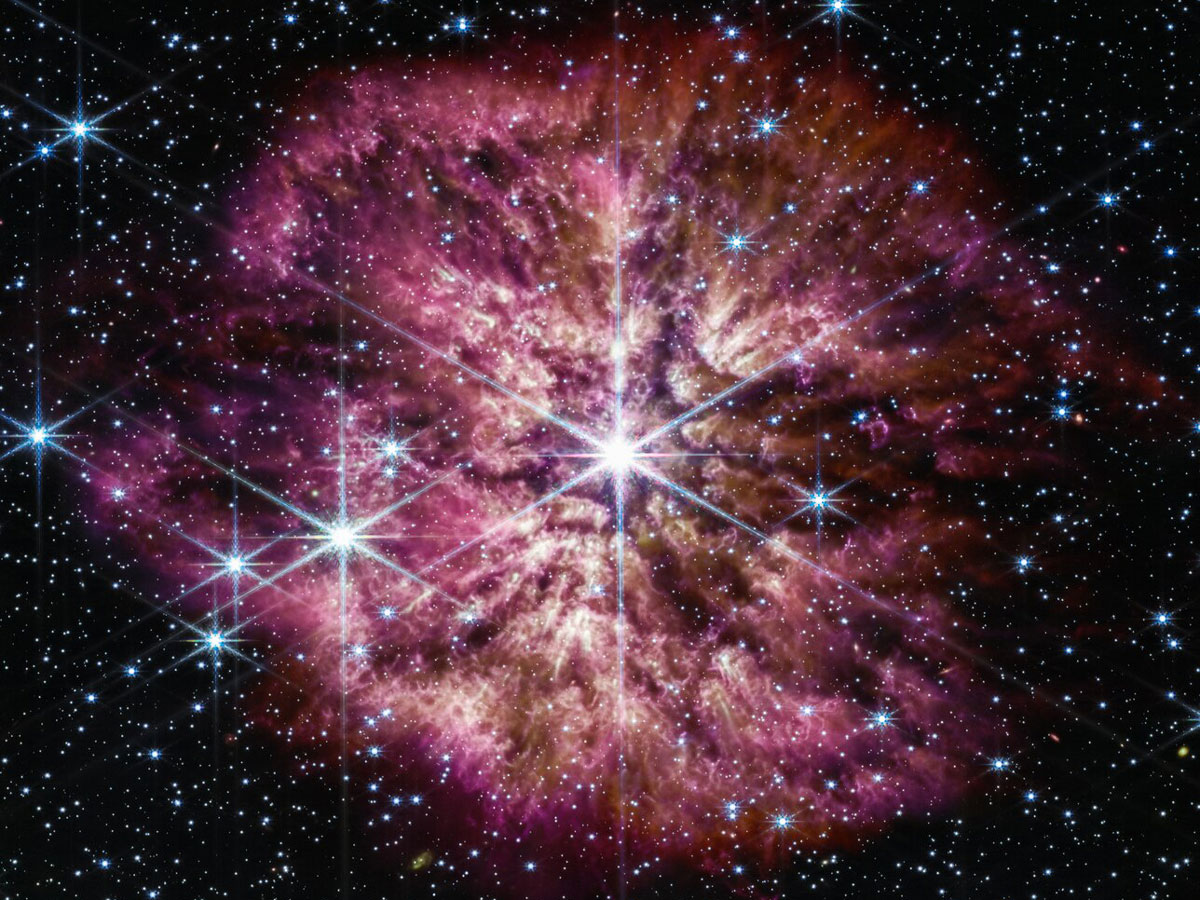
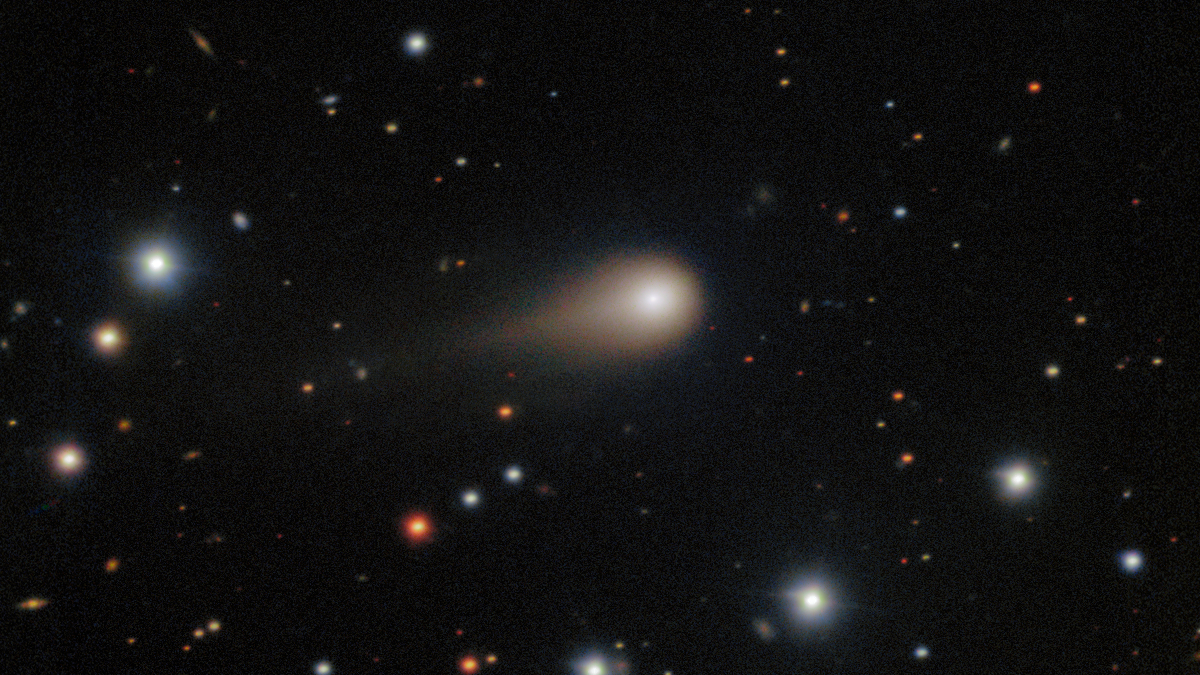
A sampling of aging Sun-like stars demonstrates that they likely eat their closest planets.
stars
Planets Might Form When Dust “Wobbles” in Just the Right Way
A liquid metal experiment has shown how magnetic rotational instability might allow dust to pool together in disks around young stars to form new worlds.
This Star Stripped Off Its Layers Long Before Exploding
A star 2 billion light-years away apparently shed most of its outer layers before exploding, providing new insights into stellar structure—and new mysteries for astronomers to solve.
Tilted Planet System? Maybe It Was Born That Way
New observations could shed light on the degree to which misalignment in a planet-forming disk contributes to skewed planetary orbits.
How an Interstellar Interloper Spurred Astronomers into Action
Valuable lessons from previous interstellar objects allowed scientists to develop a more rapid response when the third one arrived in July.
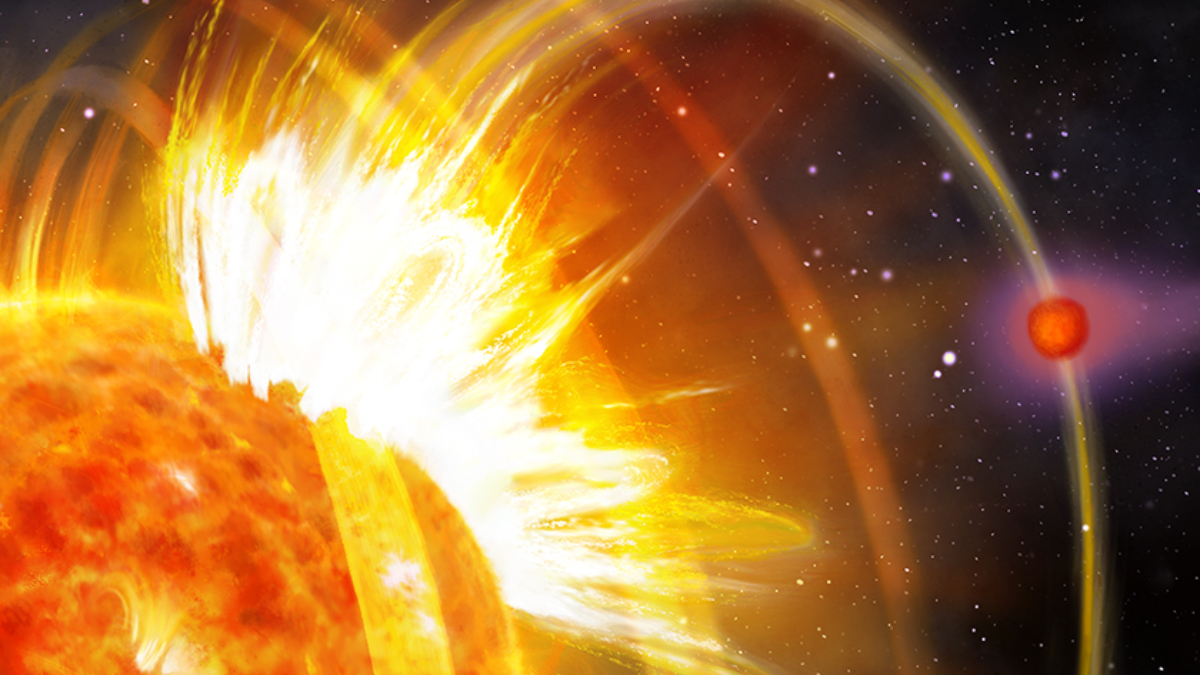
Exoplanet Triggers Stellar Flares and Hastens Its Demise
HIP 67522 b can’t stop blasting itself in the face with stellar flares, a type of magnetic interaction that scientists have spent decades looking for.
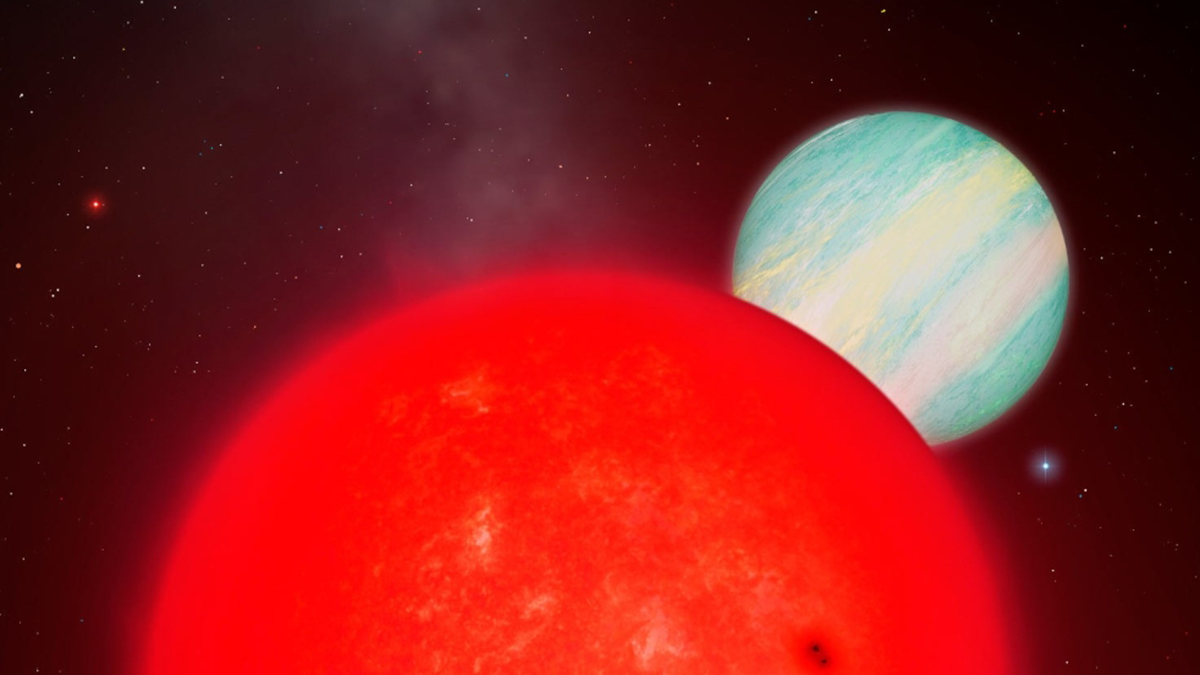
A New Exoplanet Resets the Scale
TOI-6894 b, the largest exoplanet relative to its host star yet seen, doesn’t fit the most widely accepted formation model for giant worlds.
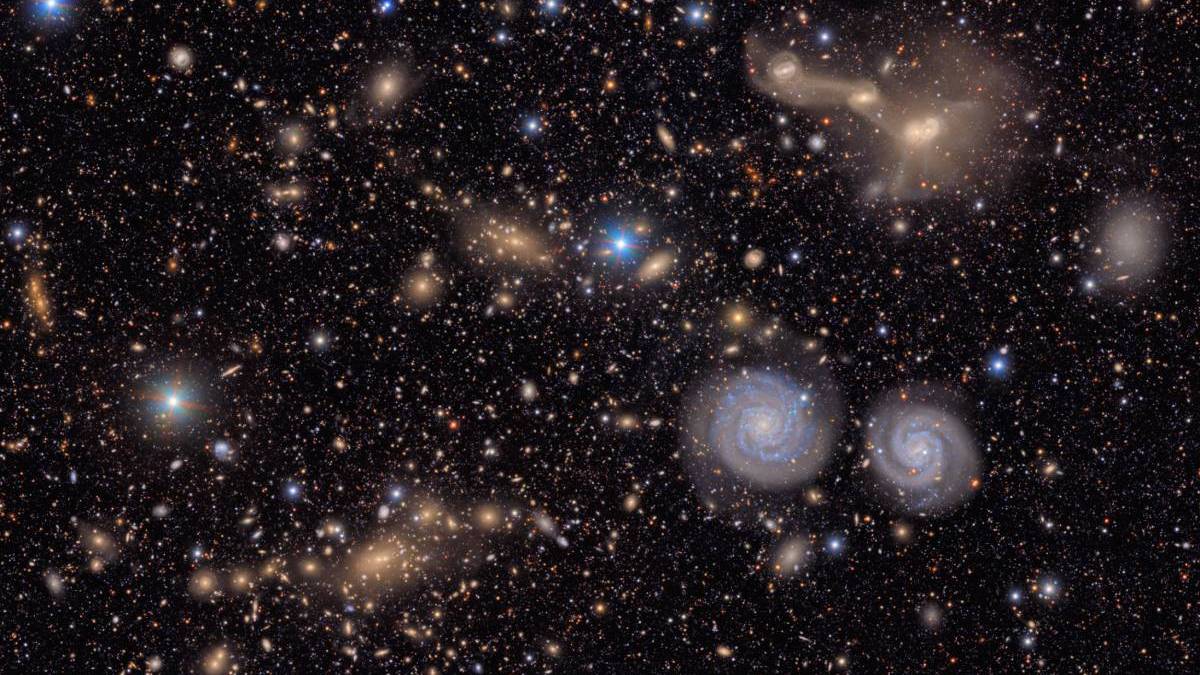
Rubin Observatory Stuns and Awes With Sprawling First Look Images
Wow. Just wow.
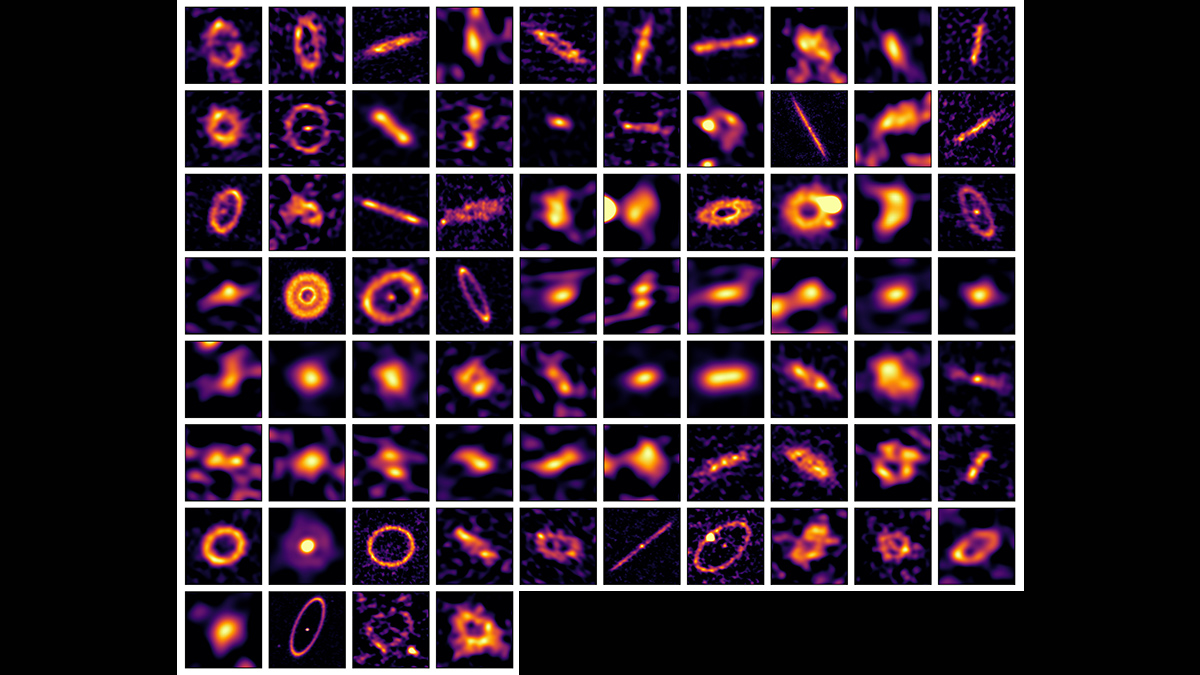
Cinturones polvorientos ofrecen una visión más clara de la formación de exoplanetas
Las observaciones en longitudes de onda milimétricas de polvo y guijarros en 74 sistemas estelares sugieren que las migraciones planetarias podrían ser más comunes de lo que pensábamos.
A Super Speedy Star May Be Streaking Through Our Galaxy
Astronomers suggest the star is towing along an exoplanet. The system could be traveling fast enough to escape the Milky Way.