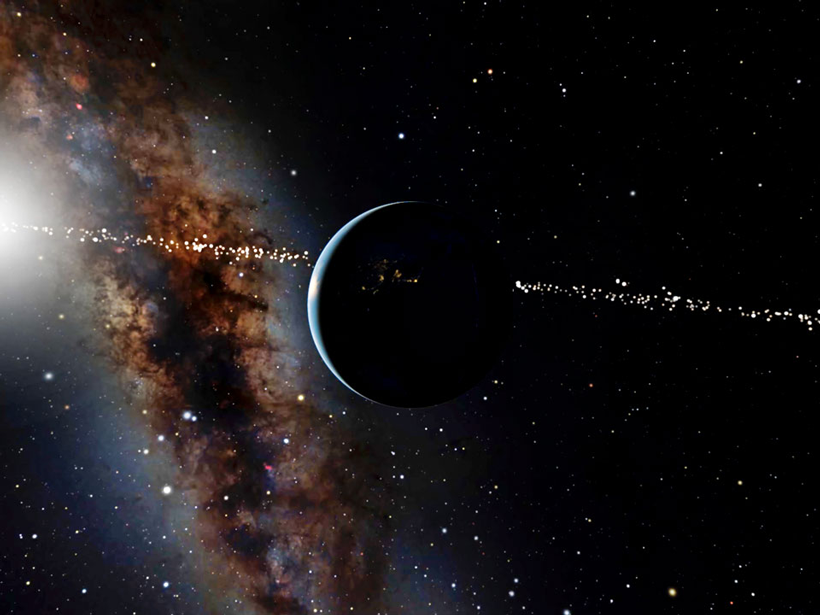
Researchers have identified more than 2,000 stars whose past, present, or future vantage points afford a view of Earth passing directly in front of the Sun, a geometry useful for pinpointing planets.
stars
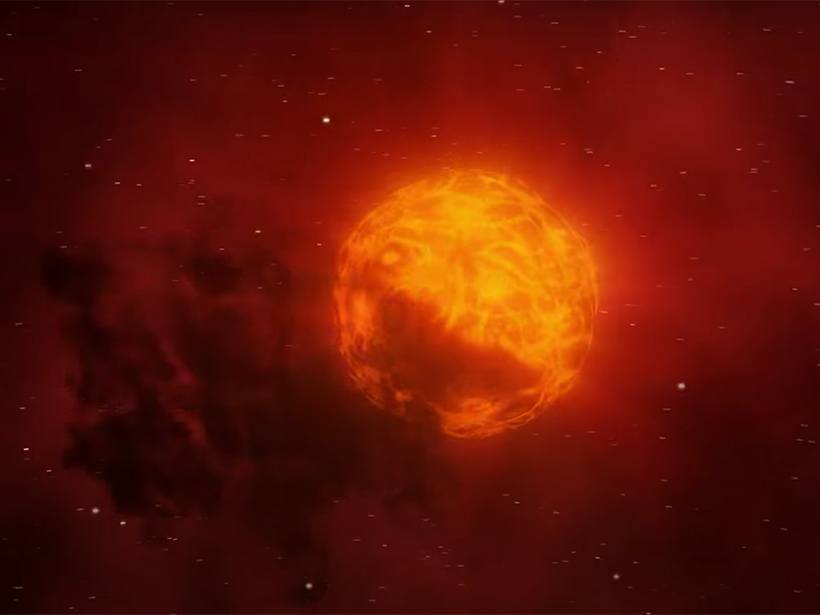
When Betelgeuse Won’t Explode, You Need a Big Telescope to Prove It
Thanks to last-minute telescope time, researchers pieced together the sequence of events that caused Betelgeuse’s Great Dimming last year.
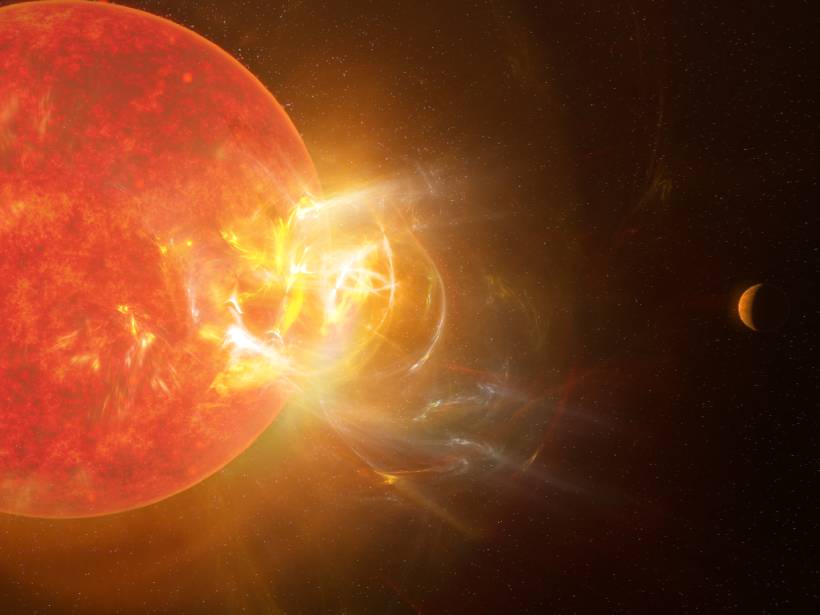
Record-Setting Flare Spotted on the Nearest Star to the Sun
Proxima Centauri recently let loose a blast of radiation, and ground- and space-based telescopes detected the record-setting event at wavelengths ranging from radio to the ultraviolet.
1.3 Million Pairs of Stars Surround the Sun
Roughly half of Sun-like stars have a stellar sibling, and a surprising fraction of those siblings are identical twins.
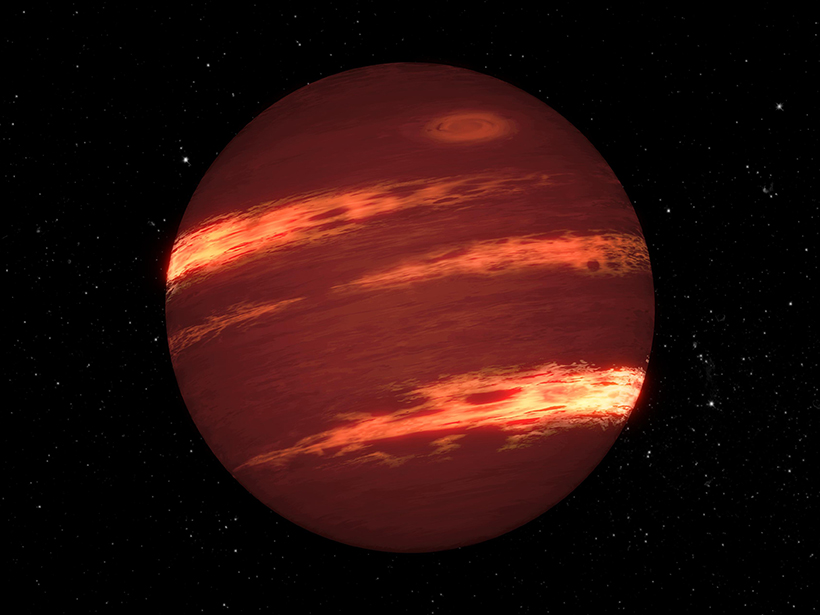
Seeing Stripes in the Atmosphere of a Brown Dwarf
A planet-hunting satellite’s observations of the nearby system Luhman 16 AB reveal bands of clouds, high-speed jets, and polar vortices.
The Closest Black Hole Is 1,000 Light-Years Away
An unseen object—probably a black hole—orbits with two normal stars in our cosmic neighborhood.
Record-Setting Winds on a Nearby Brown Dwarf
Infrared and radio observations reveal zonal winds moving faster than 2,000 kilometers per hour on a “failed star” in our celestial neighborhood.
Hot White Dwarfs May Reveal Cold Gas Giants
The gaseous atmospheres of giant planets may evaporate and accrete onto the dense surfaces of white dwarfs, providing astronomers a new way to detect hidden exoplanets.
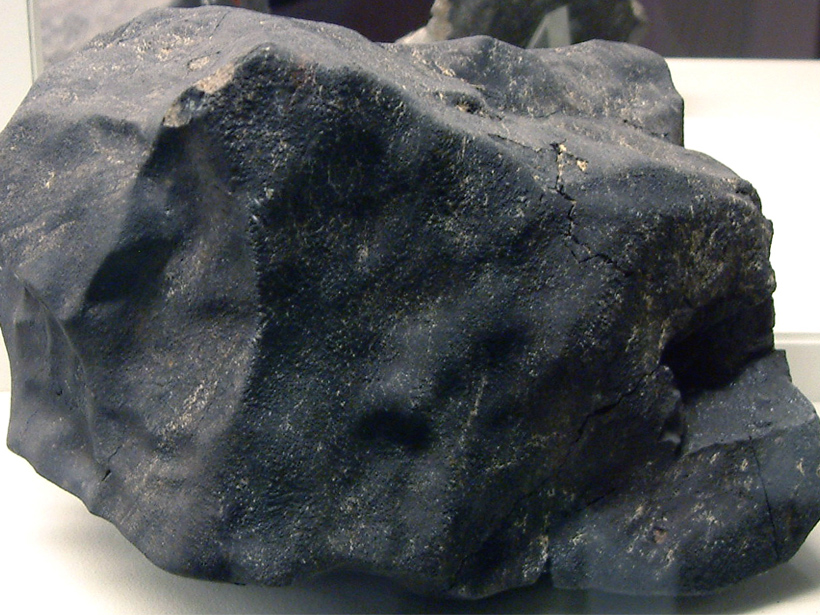
Dust Older Than the Sun Sheds Light on Galactic History
A small pile of dust grains older than the Sun brings new evidence about the rate at which stars are born in the Milky Way.
Interstellar Visitors Could Export Terrestrial Life to Other Stars
A handful of interstellar objects and long-period comets could have scooped up microorganisms from Earth and carried them to worlds around other stars.