Un proyecto de ley en el Congreso Brasileño permitiría la expansión minera en territorios Indígenas. Una nueva investigación demuestra cómo esto podría afectar radicalmente a los pueblos aislados.
News
Evidence of Drought Provides Clues to a Viking Mystery
A persistent drying trend, not plunging temperatures, may have played a role in the unexplained disappearance of Norse settlers from Greenland, according to researchers.
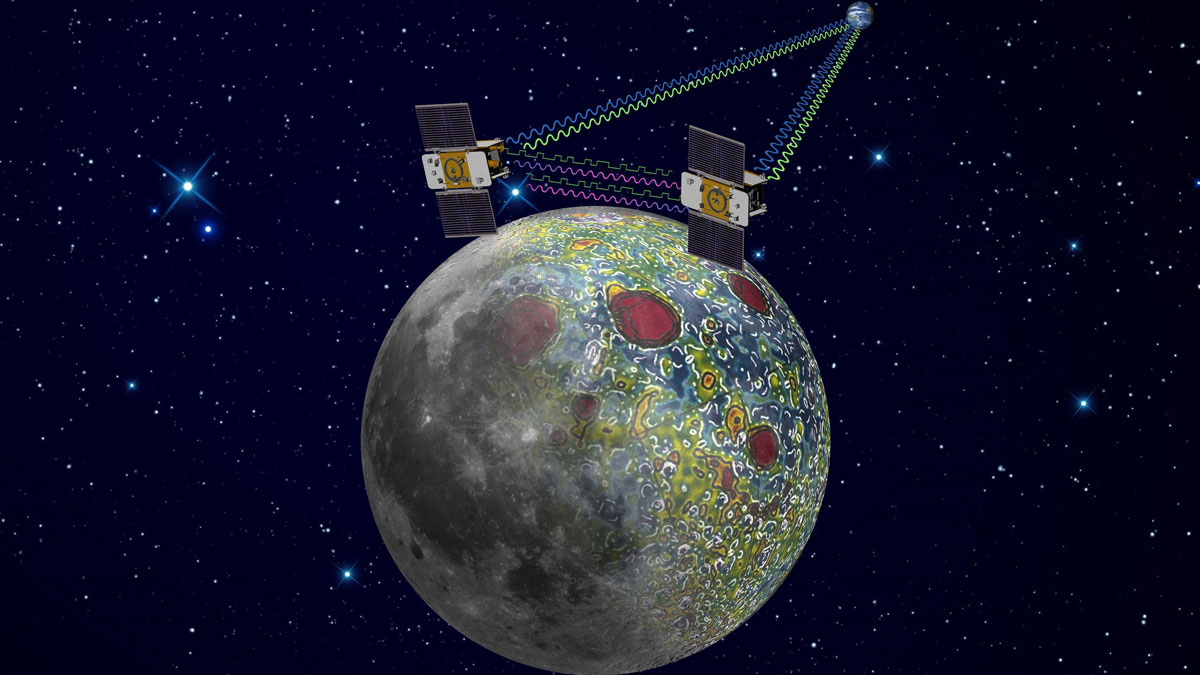
Moon’s Porosity Changes Cratering History, Study Says
Gravity field measurements from decade-old lunar orbiter provide a proxy for counting craters.
Martian Glaciers May Have Carved Its Valleys
Networks of valleys provide puzzling hints of running water on the surface of the Red Planet. New research suggests that some tributaries could have formed from icy sheets thousands of meters thick.
A Spike in Wildfires Contributed to the End-Permian Extinction
An upward trend in fossilized charcoal indicates that wildfires may have contributed to extinctions during the Great Dying.
Scientists Bring Forests into the Internet of Things
Armed with $10.5 million in funding, researchers will deploy novel sensors for real-time data assimilation and modeling of how changes in climate are affecting woodlands.
Maui Endures More Drought and Drier Streams
Drought continues to threaten Maui’s native land-based and marine ecosystems, water resources, and traditional ways of life. But conservationists have hope—and ways to fight back.
Should Inhaled Anesthetics Be Swapped for IVs?
Using intravenous anesthetics instead of volatile ones could help curb greenhouse gas emissions, but there are challenges to making the switch.
Groundwater May Fix as Much Carbon as Some Ocean Surface Waters
Microbes from wells as deep as 90 meters created organic carbon at a rate that overlaps with some nutrient-poor spots in the ocean.
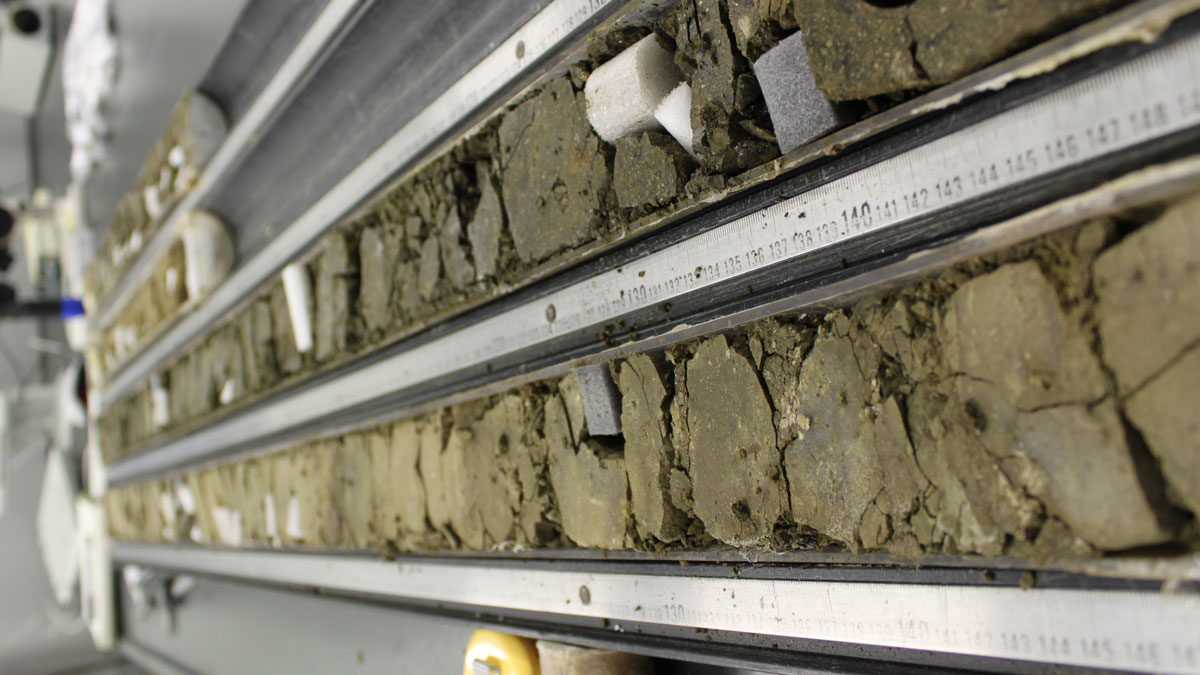
Stretching Crust Explains Earth’s 170,000-Year-Long Heat Wave
During a brief period in Earth’s past, a massive emission of carbon abruptly raised global temperatures, acidified oceans, and stamped out species. New data may help explain how it happened.