By analyzing sediments jostled by ground shaking, researchers have shown that two impact craters near Stuttgart were created by independent asteroid impacts rather than a binary asteroid strike.
News
Trees That Live Fast, Die Young, and Mess with Climate Models
The trade-off between tree longevity and life expectancy can mean future carbon uptakes are overestimated in current global climate models.
Terrestrial Plants Flourished After the Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction
Compounds in ancient plant leaves tell the story of how an extinction event shaped our planet’s ecosystems.
Suicide Rates May Rise After Natural Disasters
Rates of suicide increased most dramatically in the second year after a disaster, after many postdisaster mental health assistance programs expire.
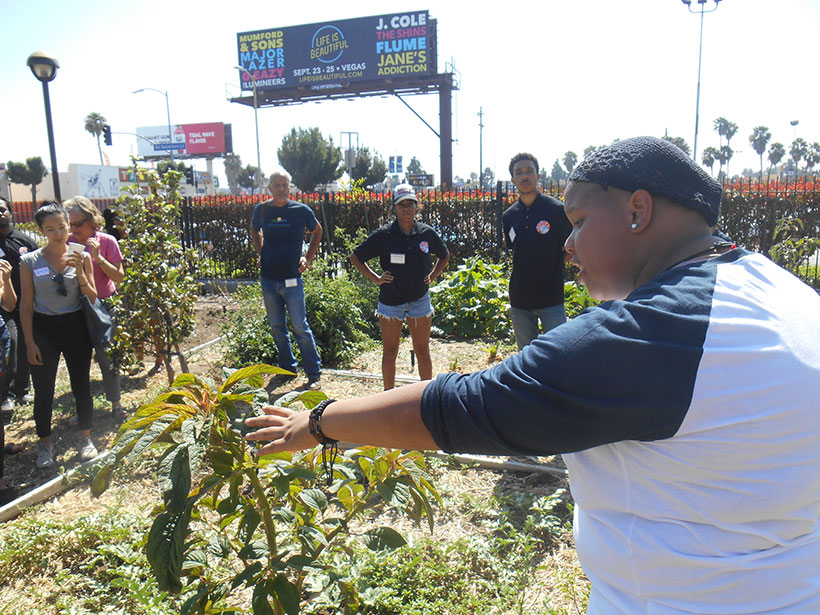
Urban Agriculture Combats Food Insecurity, Builds Community
Innovations in urban agriculture—from creative reuse of stormwater to soil rehabilitation—can help fight food insecurity and prevent further food issues.
Cover Crops, Sensors, and Food Security
Forward-Thinking Ideas for the USDA’s Agriculture Innovation Agenda
Tree Rings Reveal How Ancient Forests Were Managed
By analyzing thousands of oak timbers dating from the 4th to 21st centuries, scientists have pinpointed the advent of a forest management practice.
The Catcher in the Ice
There are three ways to extract gases from an ice core. The cleanest one, sublimation, is getting easier.
The Influence of Tidal Forces Extends to the Arctic’s Deep Sea
The Moon’s gravitational pull creates the tides, but its influence extends hundreds of meters below the sea surface too, influencing sensitive methane seeps in the seabed.
Overturning in the Pacific May Have Enabled a “Standstill” in Beringia
During the last glacial period, a vanished ocean current may have made the land bridge between Asia and the Americas into a place where humans could wait out the ice.