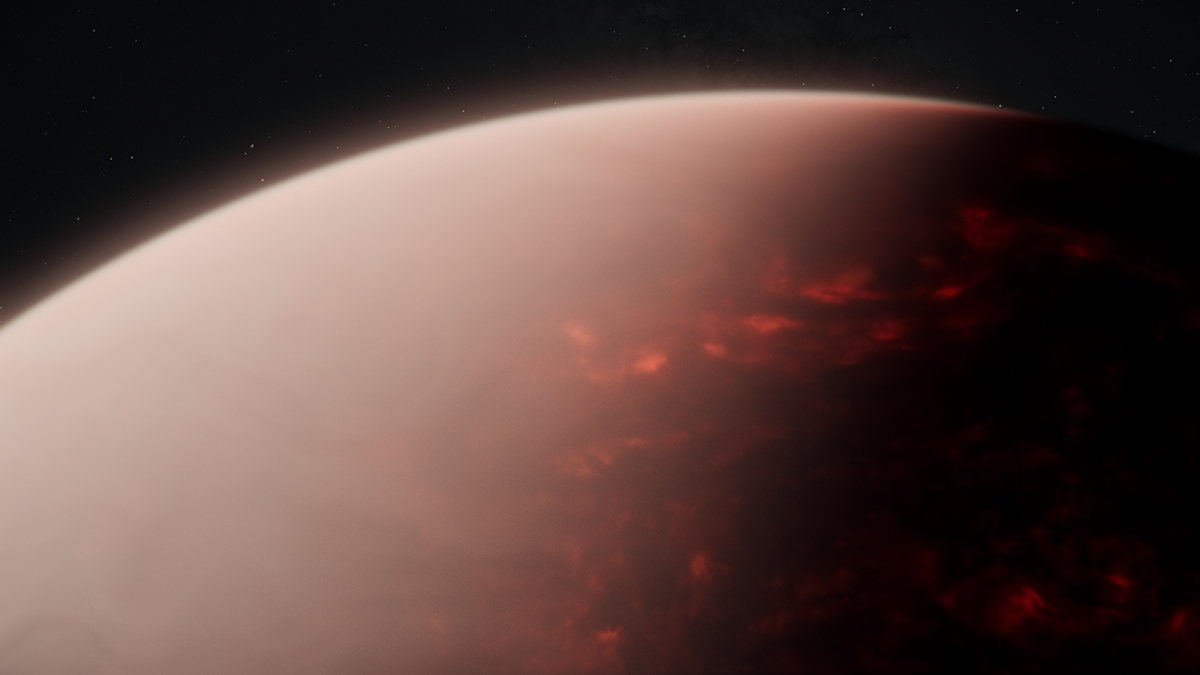
TOI-561 b, an exoplanet roughly 275 light-years away, seems to have a thick atmosphere despite being wildly irradiated by its host star.
News
After Sackett, a Wisconsin-Sized Wetland Area Is Vulnerable
An analysis of wetland legal frameworks shows how water rules could leave millions of hectares without meaningful protections.
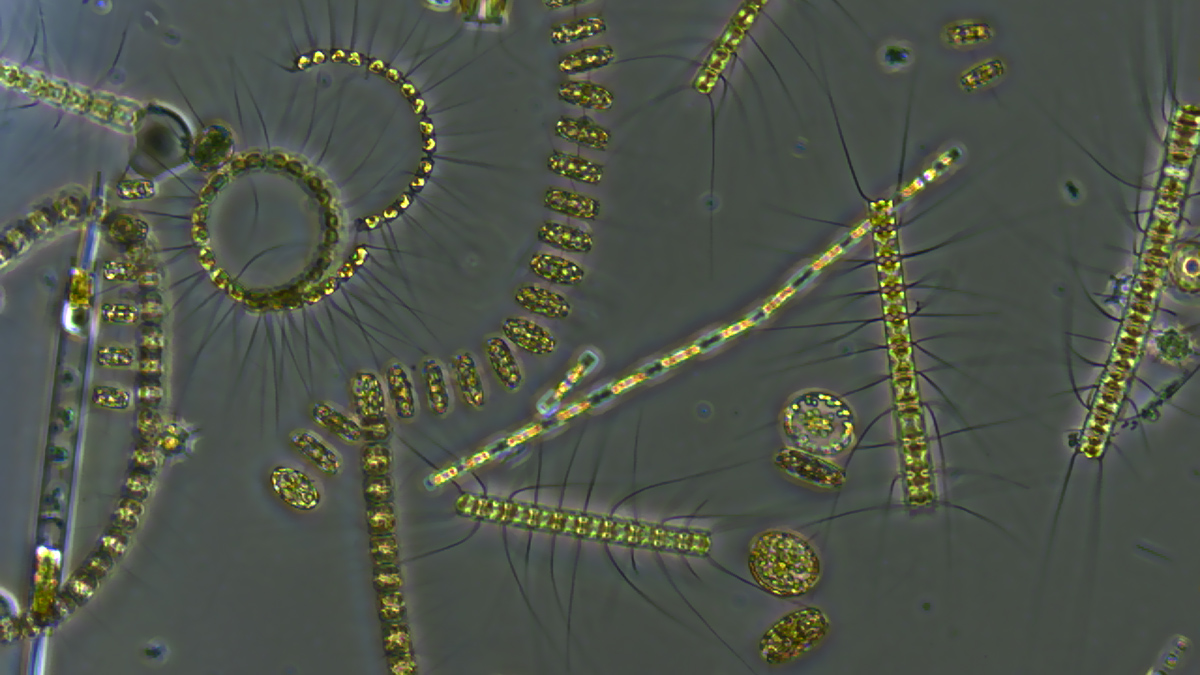
Las olas de calor marinas lentifican el flujo de carbono de los océanos
Cuando el plancton se encuentra en agua caliente, la materia orgánica se estanca en la superficie e interrumpe el transporte de carbono hacia el fondo océanico.
Our Favorite Science Stories of 2025
What Earth and space science stories stood out this year?
Democracy and Education Increase Women’s Belief in Climate Change
The finding, which focuses on lower-income countries, could help inform plans to shrink the global climate knowledge gender gap.
Blending Science and Indigenous Knowledge to Tell an Estuary’s Story
A new study of nutrient levels in soil cores supports oral Indigenous history, informing future estuary restoration efforts.
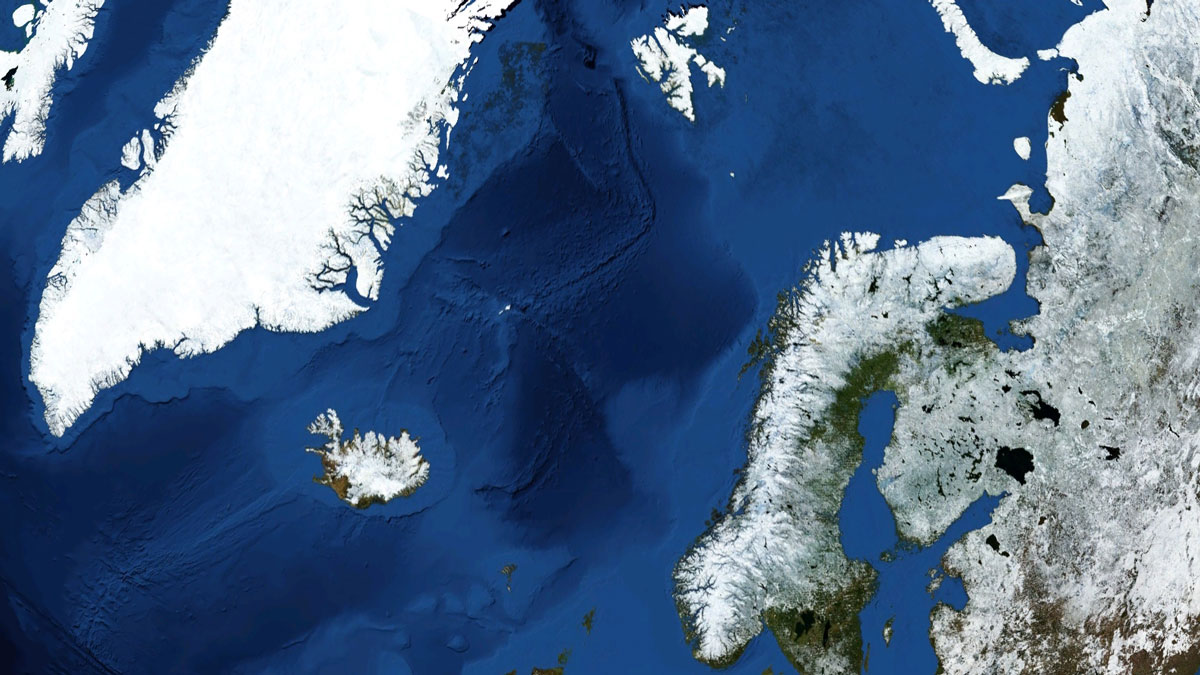
New Eyes on One of the Planet’s Largest Submarine Landslides
Researchers have mapped the ancient Stad Slide off the coast of Norway to better understand what triggered it, and the hunt is on for the tsunami it might have unleashed.
What Okinawan Sailor Songs Might Teach Us About the Climate
New work bridges the worlds of Ryukyuan classical music and the geosciences.
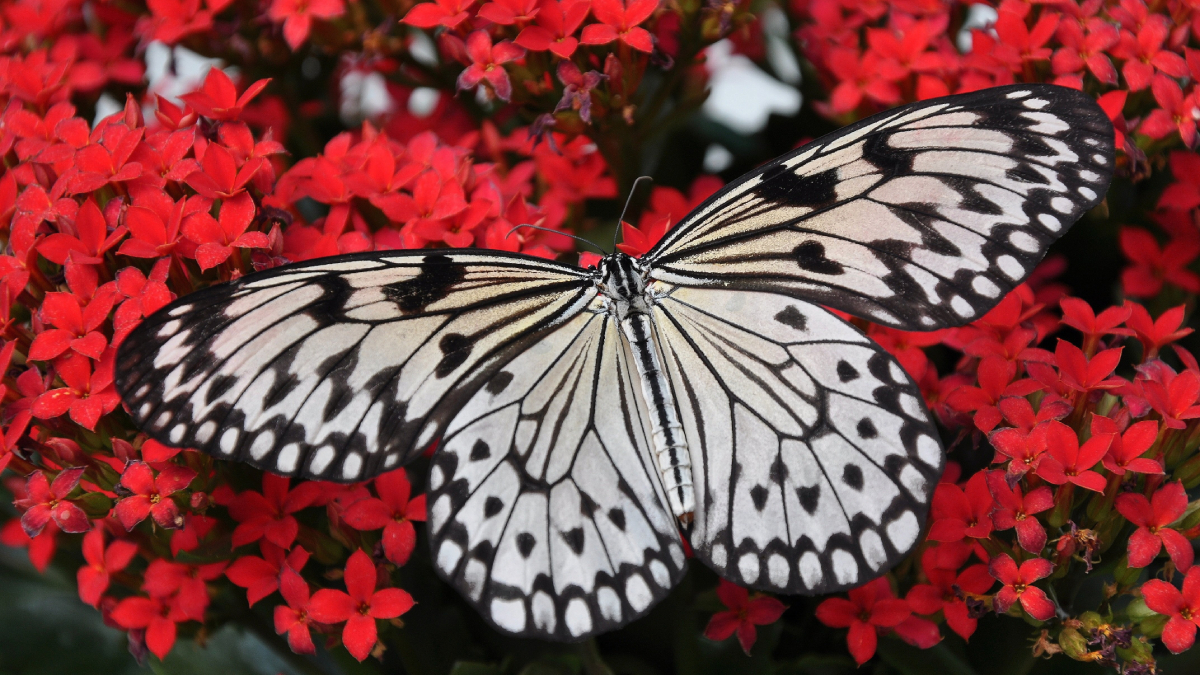
Climate Change Could Drive Butterflies and Plants Apart
Insects and the plants they depend on are migrating in response to climate change, but not always in the same way.
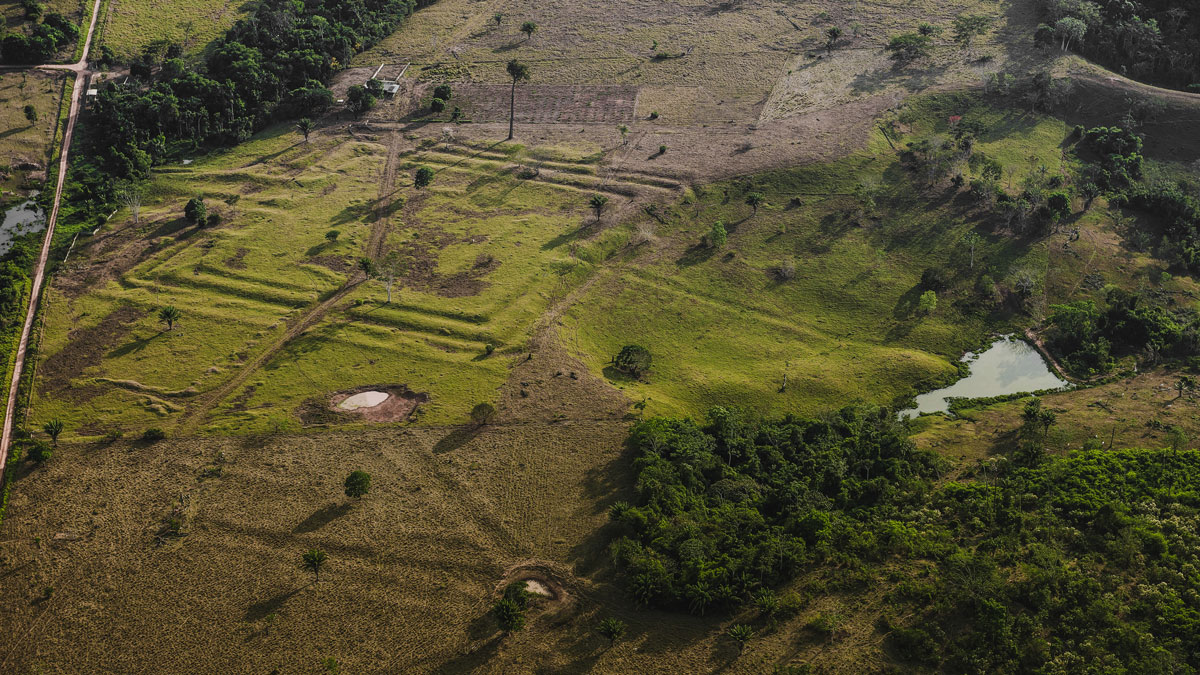
How Ancient Indigenous Societies Made Today’s Amazon More Resilient
Portions of the forest managed by pre-Columbian populations hold higher biomass and are more able to withstand climate change.