A new model accurately reconstructs Earth’s past icehouses and indicates there’s no one driver behind them.
Nathaniel Scharping
U.S. Power Grids are Vulnerable to Extreme Weather
Different kinds of severe weather, including multiple kinds at once, have different impacts on the grid in different places.
How to Build the World’s Highest Mountain
The rocks of Mount Everest’s peak made an epic journey from seafloor to summit.
Arctic Ice Is Getting Smoother and Moving Faster
A decrease in pressure ridges over the past 3 decades is making the ice more uniform, with unclear consequences.
Tracing Metals from Earth to Water to Life in the Yellow River
The mix of metals in China’s Yellow River stays relatively similar as it moves from the upper continental crust to biological life.
Deep Beneath California’s Sierra Nevada, Earth’s Lithosphere May Be Peeling Away
Evidence for lithospheric foundering, or the process of denser material sinking into the mantle, is emerging.
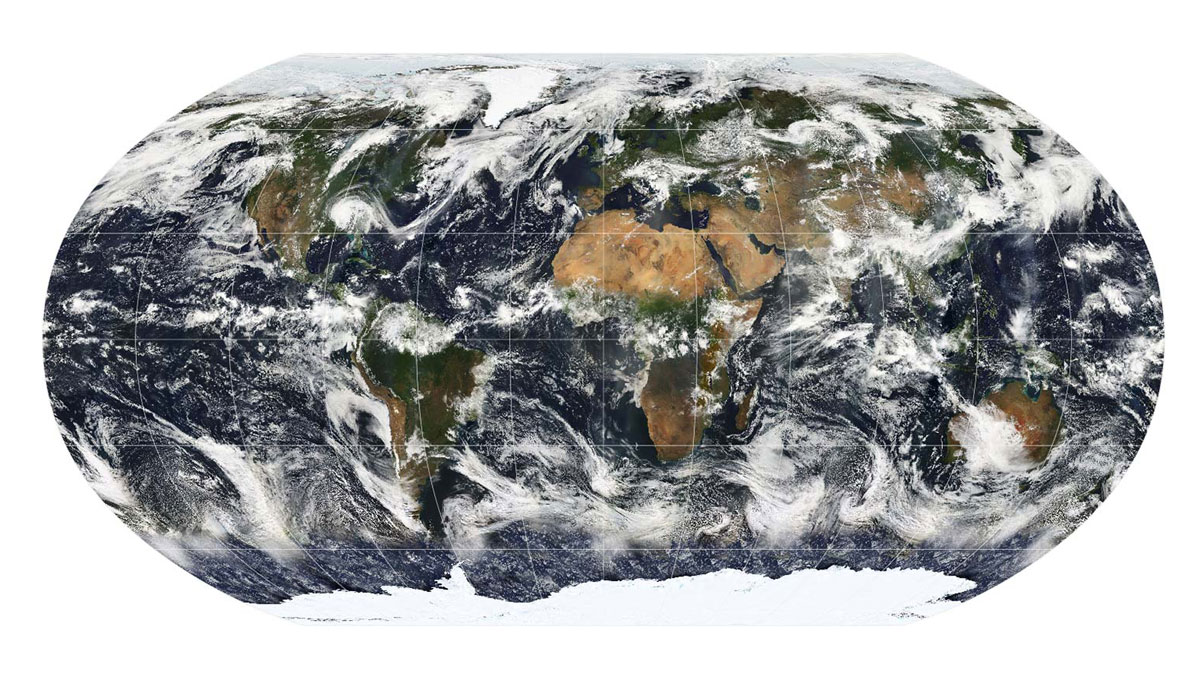
Darker, Less Cloudy Earth Contributed to Record Heat
Decreases to our planet’s albedo caused by fewer low-lying clouds helped push temperatures to historic highs in 2023, according to new research.
Bringing Climate Change’s Effects on Atmospheric Circulation to Light
A lengthening observational record is being used to test predictions and improve understanding of the mechanisms behind changing circulation.
What 92 Years of Data Say About Ice Cover
New research on Mohonk Lake in New York investigates how changing ice phenology alters temperature dynamics in lakes.
Las tormentas están tirando cada vez más árboles
La cantidad de árboles derribados por el viento ha incrementado casi cuatro veces en la región, probablemente por tormentas más fuertes.