研究人员对沉积物岩心进行了采样,发现磁铁矿丰富的地方也存在产甲烷细菌。
Rachel Fritts
Rachel Fritts is a science writer specializing in ecology, sustainability, and Earth science. Her work has appeared in a number of publications, including Ars Technica, Science News, Science, Mongabay, and Hakai Magazine. She also writes scripts about evolution for the PBS Digital Studios channel Eons. Rachel is currently completing a master’s degree in science writing at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Microbes Likely Form Magnetite in the South China Sea
Researchers sampled sediment cores and found that where magnetite was abundant, methane-producing bacteria were as well.
Investigadores desarrollan el primer presupuesto integral de gases de efecto invernadero de México
Un nuevo estudio profundiza en dos décadas de datos para crear una cuantificación integral de fuentes de carbono, metano y óxido de nitrógeno que podrían ayudar a guiar las políticas climáticas.
Cómo los movimientos del manto dan forma a la superficie terrestre
Dos nuevos conjuntos de datos ayudan a los investigadores a separar las influencias de la tectónica de placas y el movimiento del manto en la topografía de la superficie.
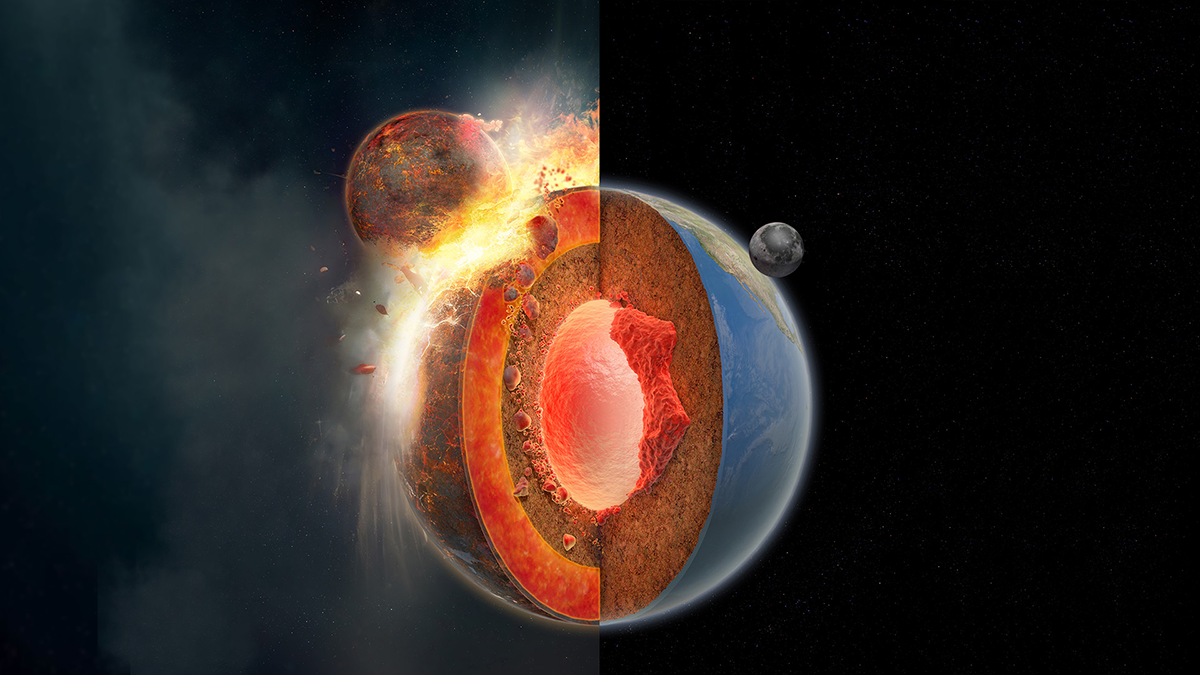
Earth’s Subduction May Have Been Triggered by the Same Event That Formed the Moon
The giant impact that formed the Moon may also have led to extrastrong mantle plumes that enabled the first subduction event, kick-starting Earth’s unique system of sliding plates.
How Mantle Movements Shape Earth’s Surface
Two new data sets help researchers tease apart the influences of plate tectonics and mantle movement on surface topography.
A Better Way to Predict Arctic Riverbank Erosion
Permafrost thaw might cause Arctic riverbanks to erode more quickly. But a new study shows why these erosion rates aren’t as dramatic as some scientists feared.
Africa’s Carbon Sink Capacity Is Shrinking
A new estimate of Africa’s greenhouse gas budget from 2010 to 2019 shows increasing emissions from cropland expansion, livestock, and fossil fuel use—meaning the continent may have transitioned from an overall carbon sink to a slight carbon source.
Sea Otters’ Appetite for Crab Is Helping Strengthen Estuary Banks
Apex predators can have a powerful impact on coastal erosion rates by keeping grazer populations down, but their influence has been largely overlooked.
Researchers Develop Mexico’s First Comprehensive Greenhouse Gas Budget
A new study delves into 2 decades of data to create a comprehensive quantification of carbon, methane, and nitrous oxide sources and sinks that could help guide climate policy.