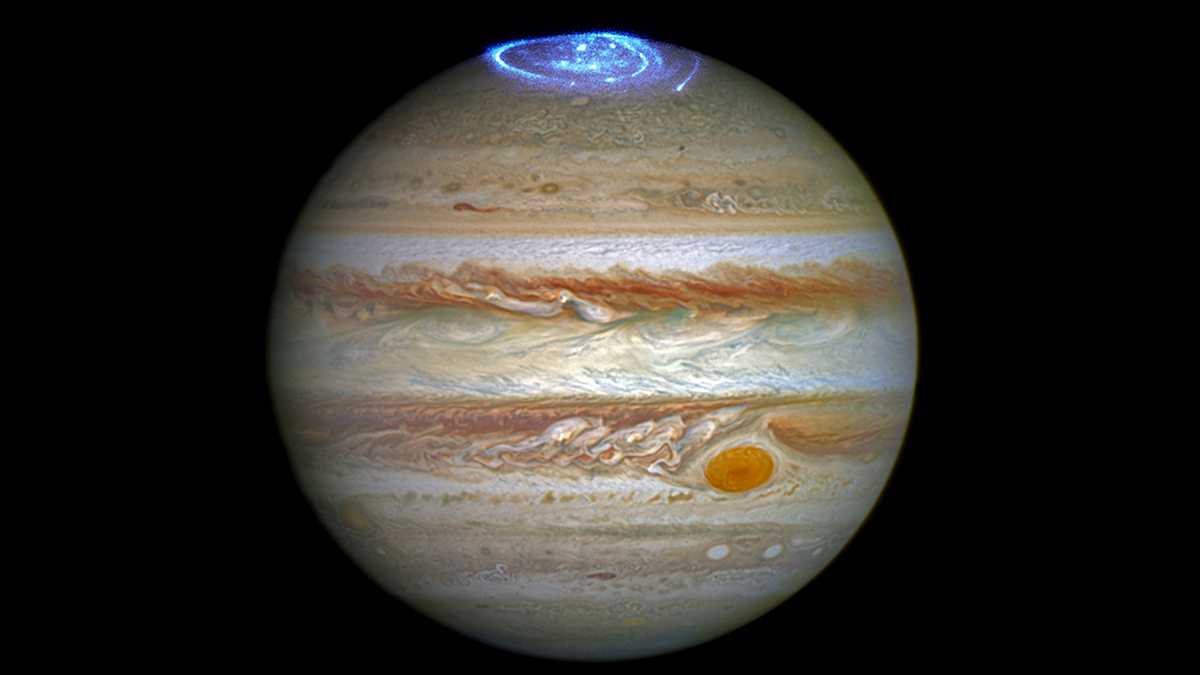
Computer simulations and data from NASA’s Juno mission reveal information about the relationship between solar wind and Jupiter’s massive magnetosphere.
Sarah Derouin
Sarah Derouin is a freelance science journalist and editor who has been writing for Eos since 2017. She has a doctorate in geology from the University of Cincinnati and is a graduate of the Science Communication Program at University of California, Santa Cruz. Sarah has written for New Scientist, Scientific American, Popular Mechanics, Science, EARTH Magazine, and Mongabay. She was the 2018–19 Science Communication Fellow for the Geological Society of America and attended Congressional Climate Science Days. Beyond writing, Sarah was an acting associate editor for EARTH Magazine. She also worked behind the scenes as an assistant producer on Big Picture Science radio show, broadcast on more than 140 public radio stations. You can find more of her work at www.sarahderouin.com or connect with her on Twitter @Sarah_Derouin.
The Secret to Mimicking Natural Faults? Plexiglass and Teflon
Researchers found an effective way to produce natural fault behavior in the laboratory.
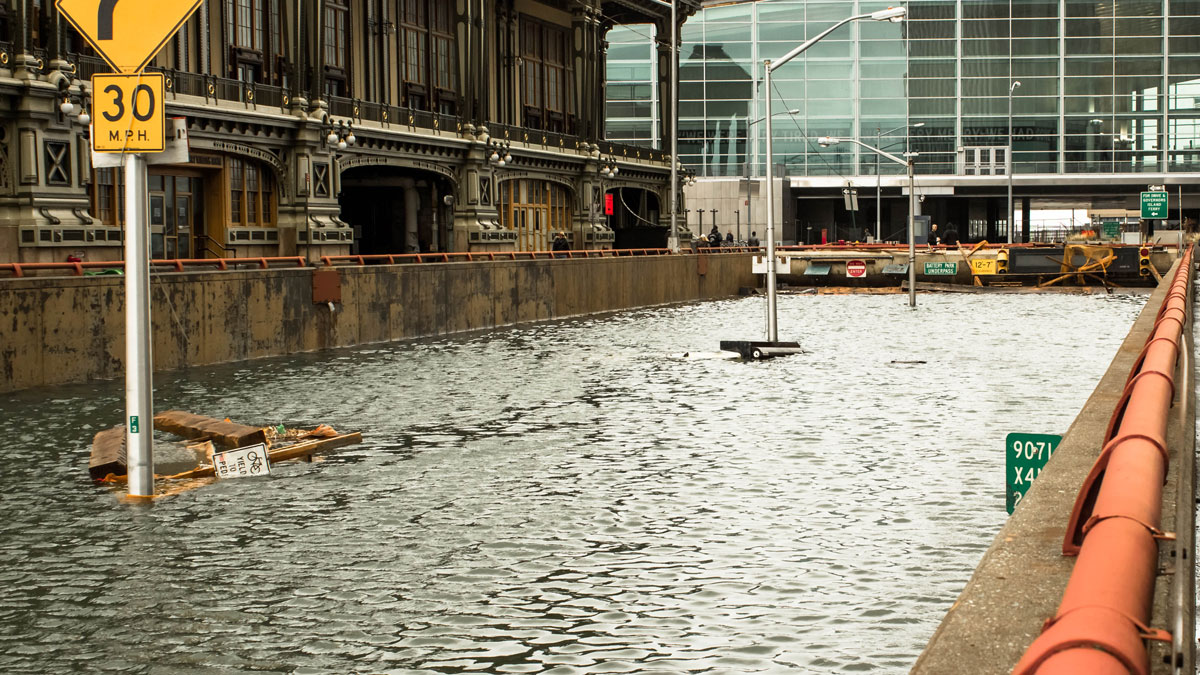
Alerting Communities to Hyperlocalized Urban Flooding
A high-accuracy, low-cost sensor network may change the way urban floods are detected and monitored.
Lakes Worldwide Need a Checkup
Lakes are facing a slew of health issues that may become chronic. Can human health care strategies help?
Source or Sink? A Review of Permafrost’s Role in the Carbon Cycle
Understanding the role of permanently frozen soil, which covers a large portion of land in the Northern Hemisphere, is crucial to reaching global climate targets.
Researchers Compare Observations Versus Modeling of Coastal Carbon Cycle
While storing carbon dioxide, the coastal ocean also releases methane and nitrous oxide. New research shows that understanding the impact of coastal oceans on climate requires more research into these fluxes and how they counteract each other.
The Nature of Mantle Flow May Depend on the Type of Slab Subducting
Researchers tease apart the links between slabs and mantle flow near subduction zones, upending some traditional views of subduction-induced mantle flow.
Uncertainty Abounds in Seeding the Sky to Fight Climate Change
Some scientists have suggested injecting solid particles such as alumina, calcite, or even diamonds into the atmosphere to temporarily limit climate warming. But new research shows there are still big unknowns.
Thunderquakes Map the Subsurface
Researchers have figured out how rumbling thunder turns to seismic waves and how this shaking could be used to reveal subsurface geology.