When temperatures exceed 36°C and relative humidity passes 58%, citizens in China may experience heat stroke.
Sarah Derouin
Sarah Derouin is a freelance science journalist and editor who has been writing for Eos since 2017. She has a doctorate in geology from the University of Cincinnati and is a graduate of the Science Communication Program at University of California, Santa Cruz. Sarah has written for New Scientist, Scientific American, Popular Mechanics, Science, EARTH Magazine, and Mongabay. She was the 2018–19 Science Communication Fellow for the Geological Society of America and attended Congressional Climate Science Days. Beyond writing, Sarah was an acting associate editor for EARTH Magazine. She also worked behind the scenes as an assistant producer on Big Picture Science radio show, broadcast on more than 140 public radio stations. You can find more of her work at www.sarahderouin.com or connect with her on Twitter @Sarah_Derouin.
Short-Term Events Can Shrink the Habitable Zone in Oceans
A new study looks at habitat reduction during low-oxygen events, spurring the question, Could short-term events provide a window into the long-term health of oceans?
Impact of Climate on River Chemistry Across the United States
Findings of a new study have implications for water quality, aquatic ecosystem health, and water treatment and management as the world warms.
How Land Deformation Occurs When Fault Sections Creep
Using a physical experiment, researchers show how off-fault deformation occurs along strike-slip faults with different types of motion.
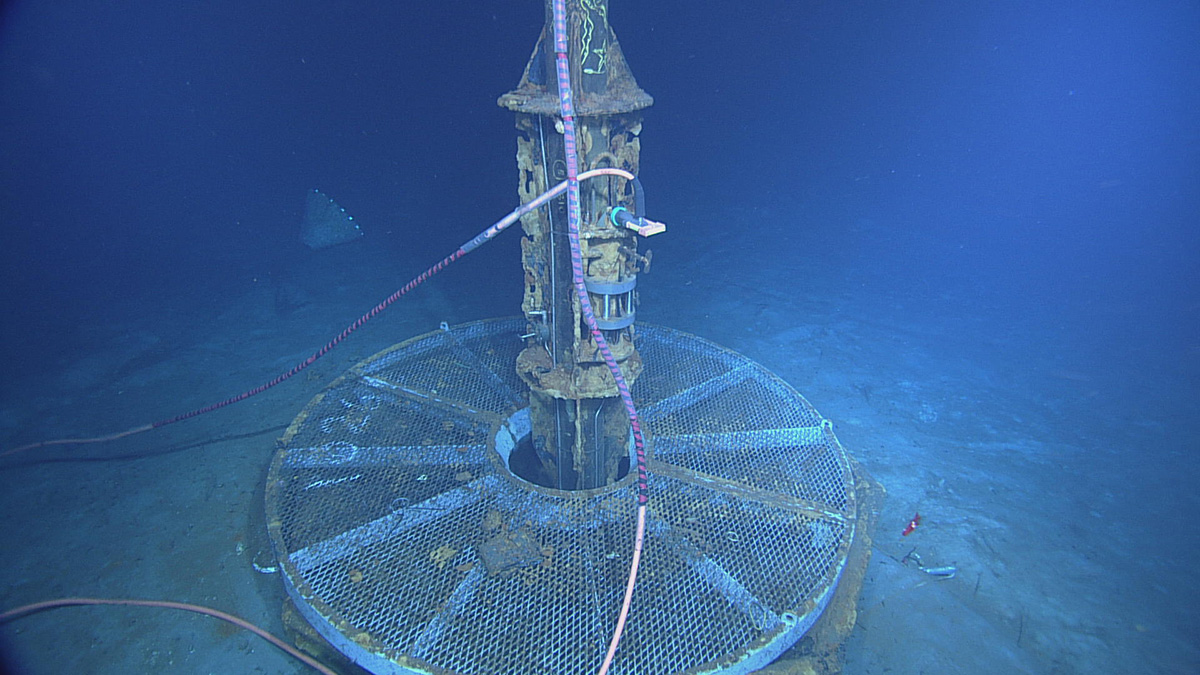
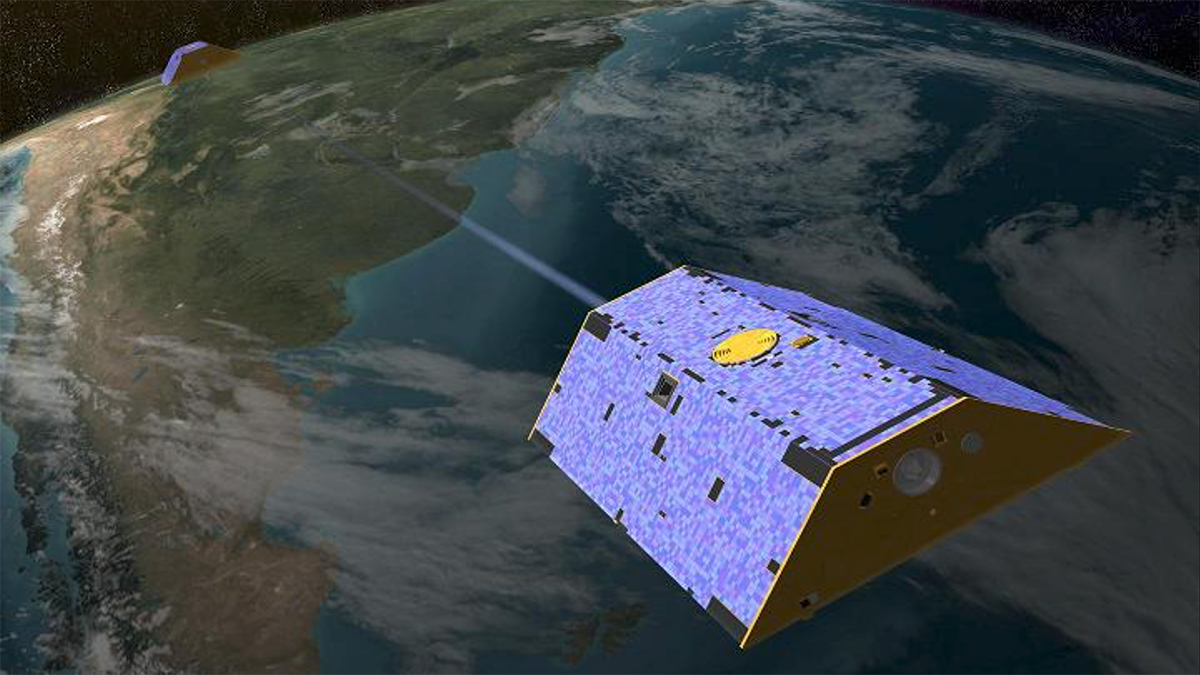
Fresh Approaches to Processing GRACE Data
Two studies showcase new methods for analyzing GRACE data that better match the land surface, producing clearer estimates of mass variations.
¿Cuánto tiempo permanecen las partículas de carbono negro en la atmósfera?
Investigadores descubren cómo el carbono negro evoluciona de partículas hidrofóbicas a sitios de nucleación de nubes, removiendo eventualmente las partículas que absorben calor del cielo.
The Seasonality of Oceanic Carbon Cycling
Scientists uncovered how seasonal changes affect the amount and rate of carbon as it moves from the ocean’s surface to its depths.
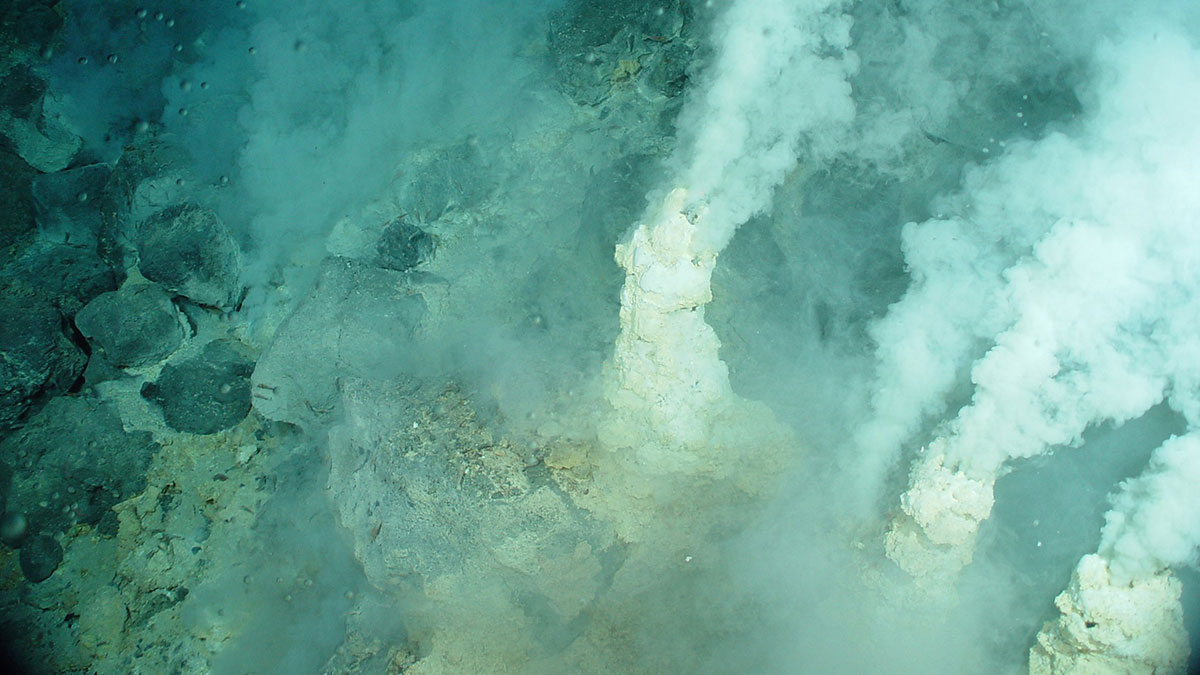
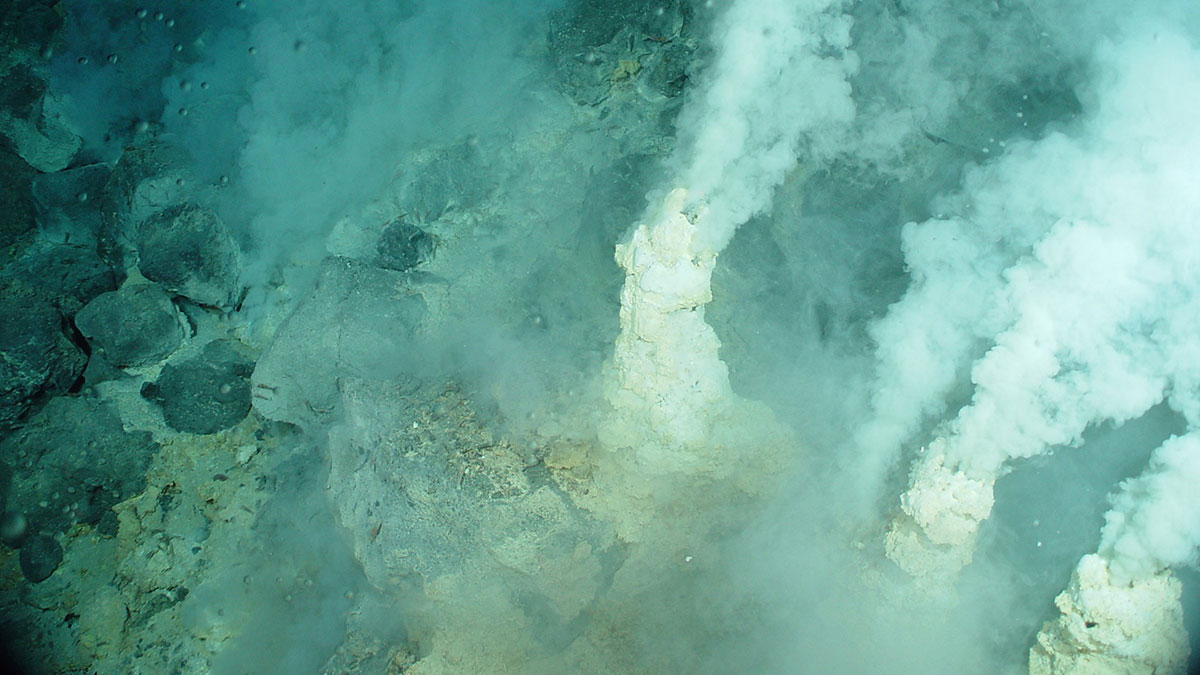
Hydrothermal Microbes Can Be Green Energy Producers
In ultramafic, reducing environments, forming microbial proteins can actually release energy.