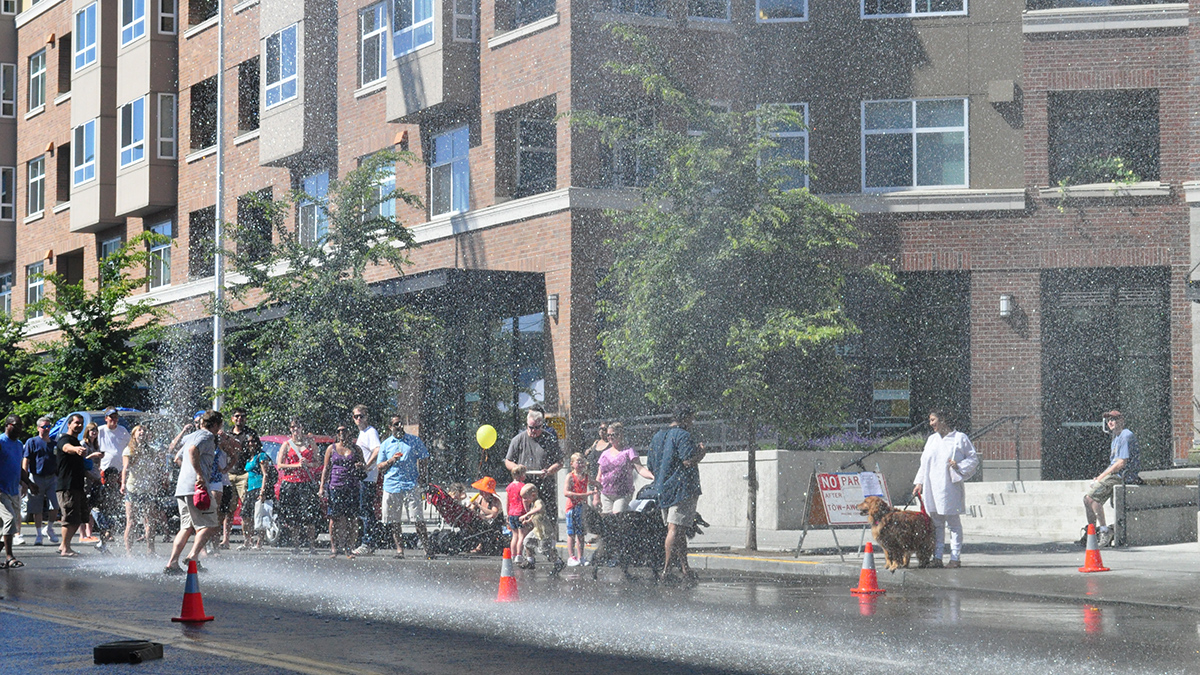New evidence from New Zealand suggests that calcium carbonate dissolution occurs not just over millennial timescales, but over annual and decadal ones too.
Sarah Stanley
Sarah Stanley, a freelance writer for Eos, has a background in environmental microbiology but covers a wide range of science stories for a variety of audiences. She has also written for PLOS, the University of Washington, Kaiser Permanente, Stanford Medicine, Gladstone Institutes, and Cancer Commons, a nonprofit that works with cancer patients.
New River Chemistry Insights May Boost Coastal Ocean Modeling
By more realistically accounting for river inputs, researchers reduced overestimation of the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by coastal waters.
Wintertime Spike in Oceanic Iron Levels Detected near Hawaii
Seasonal rainfall and runoff of sediments from the Hawaiian Islands could be responsible for the previously undetected peak.
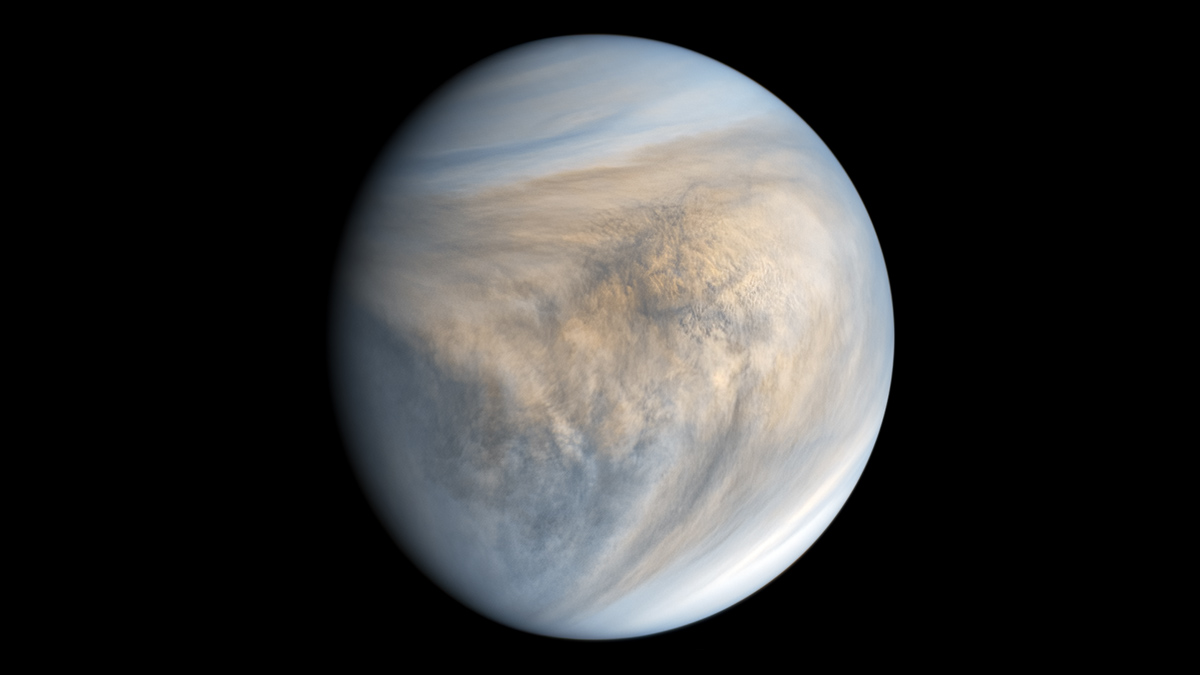
Key Driver of Extreme Winds on Venus Identified
A new study suggests that a once-daily atmospheric tidal cycle may be a bigger driver of rapid Venusian winds than previously thought.
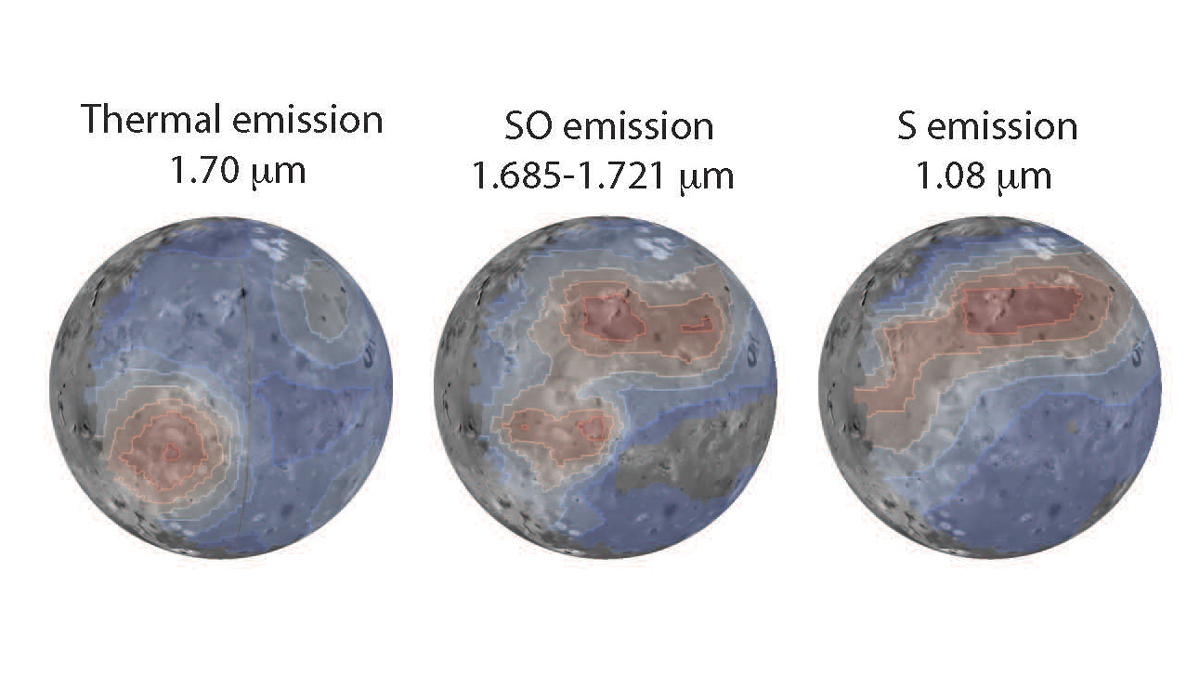
Webb Telescope Spies Io’s Volcanic Activity and Sulfurous Atmosphere
New James Webb Space Telescope images reveal cooling lava, volcanic sulfur monoxide gas, and sulfur gas emissions created by interactions between plasma and the moon’s atmosphere.
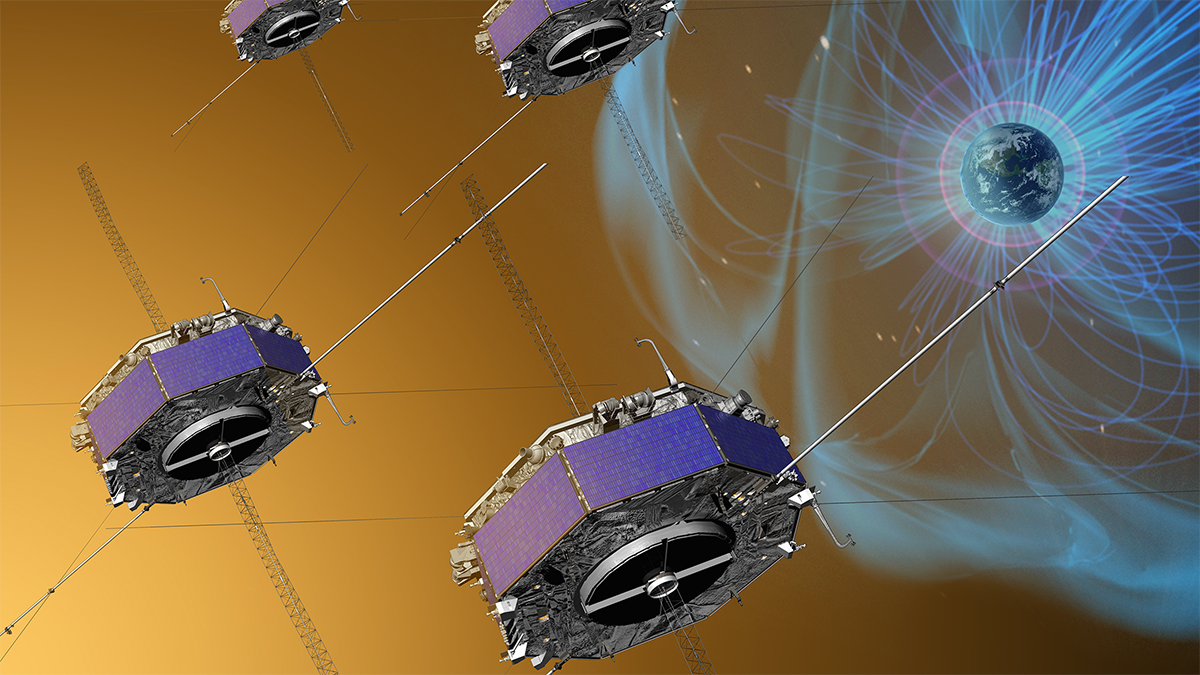
Magnetic “Switchback” Detected near Earth for First Time
Until recently, this type of zigzag shape—formed by energetic rearrangement of magnetic field lines—had been seen only near the Sun.
Unveiling What’s Under the Hood in AI Weather Models
Artificial intelligence models have improved weather forecasting, but their inner workings are largely opaque. A new approach could make their predictions more interpretable by scientists.
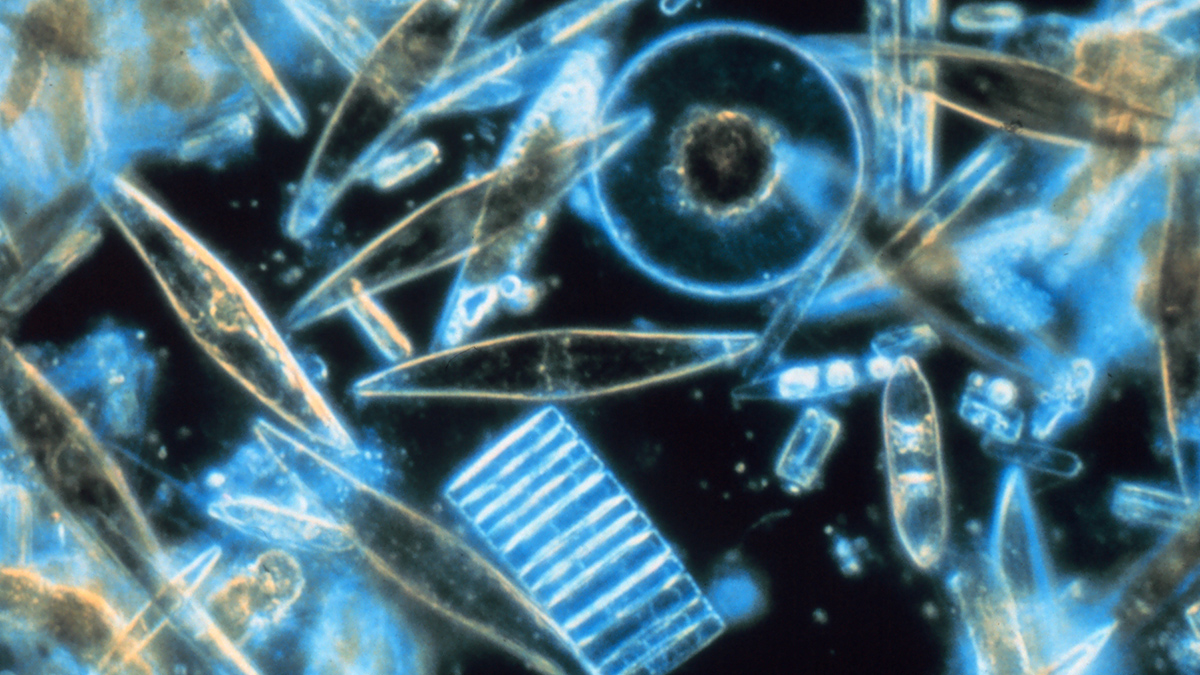
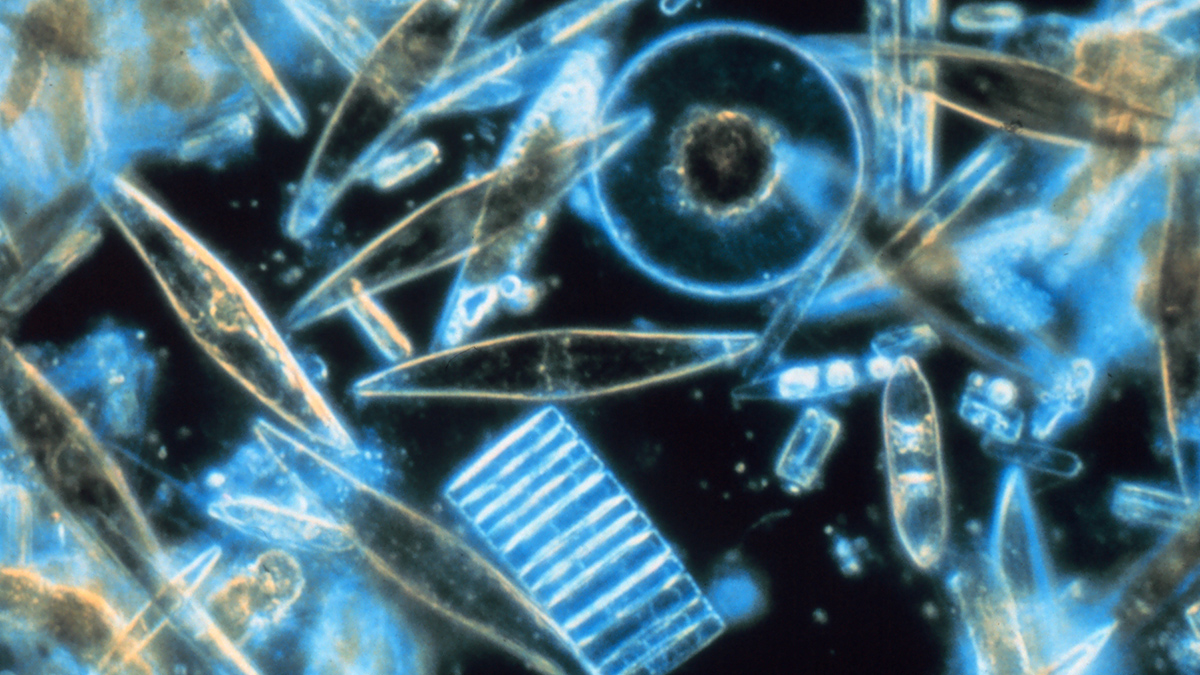
Mysteriously Bright Waters near Antarctica Explained
Shiny-shelled diatoms make a remote part of the Southern Ocean appear especially reflective in satellite imagery.
Extreme Heat in U.S. Cities Revealed at High Resolution
Data from personal weather stations power a novel way to detect urban heat islands.