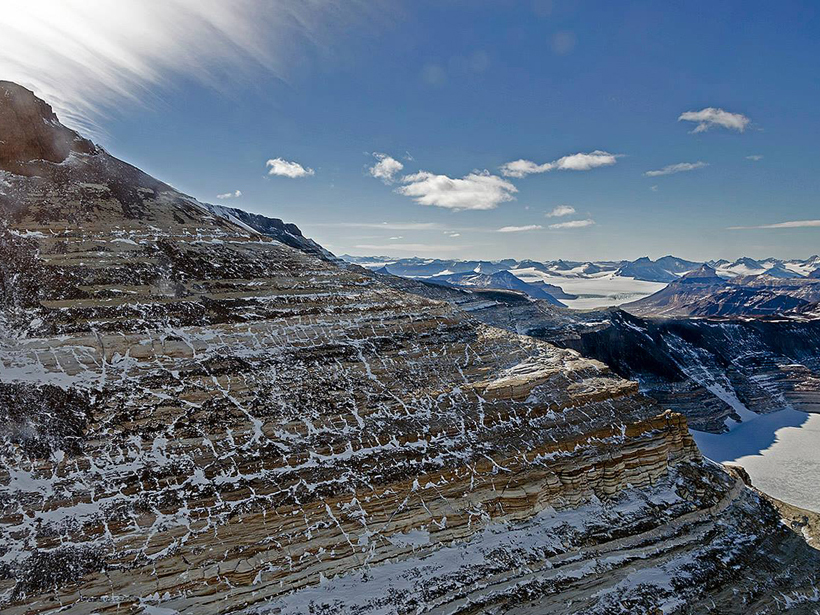
A comprehensive collection of variation in Earth's gravity could aid studies of the Antarctic geoid and of Antarctica's geology and ice sheet dynamics.
Sarah Stanley
Sarah Stanley, a freelance writer for Eos, has a background in environmental microbiology but covers a wide range of science stories for a variety of audiences. She has also written for PLOS, the University of Washington, Kaiser Permanente, Stanford Medicine, Gladstone Institutes, and Cancer Commons, a nonprofit that works with cancer patients.
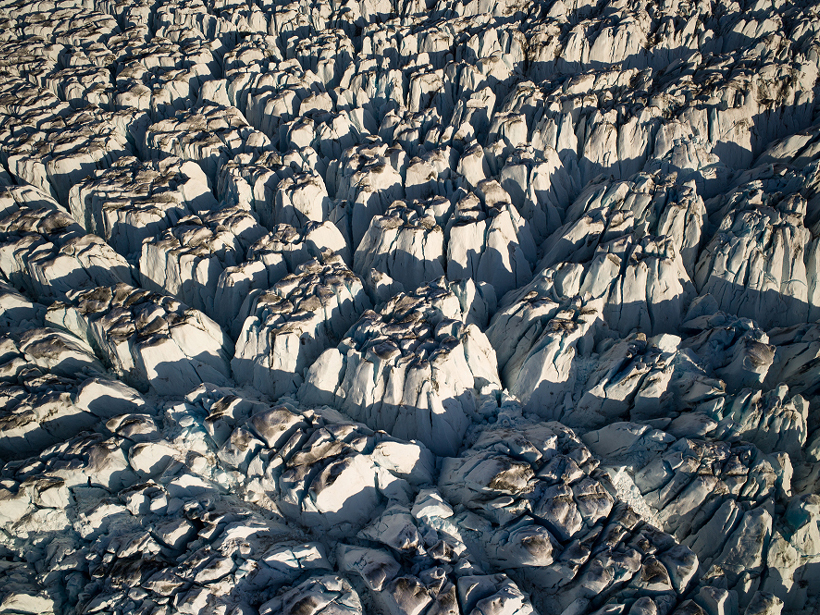
Recent Studies Crack Open New Views of Glacial Crevasses
Scientists review 60 years of direct and remote observations of crevasses and the models used to simulate them.
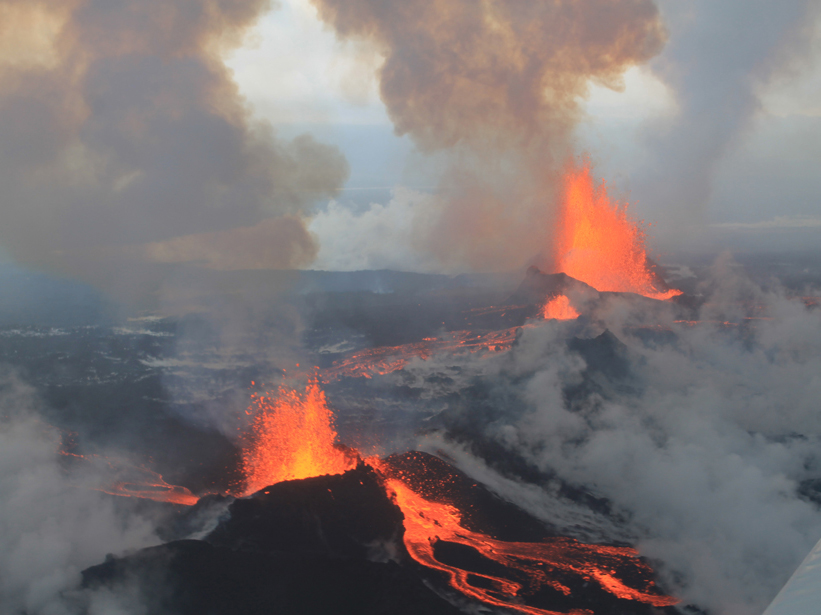
Icelandic Eruption Caused Record-Breaking Sulfur Dioxide Release
Satellite and ground-based data reveal sulfur dioxide flux, trace element release, and preeruption magma movement.
What Causes the Strange Pulses in Saturn's Magnetosphere?
A new model shows that a spiral wave may explain why many phenomena in the gas giant's magnetosphere undergo periodic cycles.
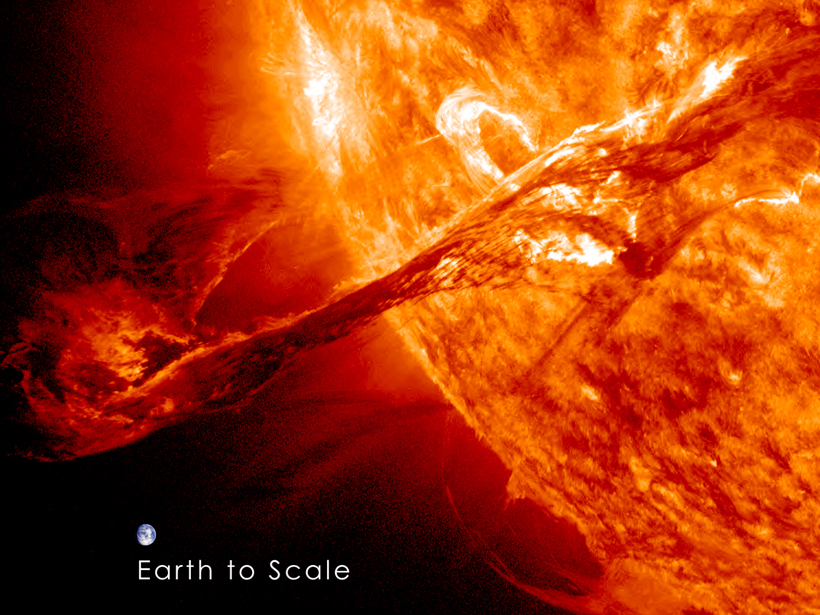
New Solar Wind Model Could Improve Space Weather Forecasts
Real-world data drive a simulation that successfully predicts Sun structures and interplanetary solar wind dynamics.
An Unprecedented View of Biogeochemistry off India's West Coast
Yearlong study reveals seasonal changes in oxygen levels, nutrient availability, and plankton growth.
New Weather Satellite Captures Sea Surface Temperatures
A new algorithm improves the accuracy of Pacific and Indian Ocean surface temperature measurements by the Japanese geostationary satellite Himawari-8.
Detecting Black Carbon in the Arctic Atmosphere
Measurements of light-absorbing carbon particles made during an Arctic research expedition could improve understanding of their effects on the Arctic climate.
Distant Rains Contributed to La Niña Ocean Warming Event
Unusually low salinity intensified a warm-water current off the coast of Western Australia in 2010–2011.
New Model Predicts Big Solar Proton Storms
Forecasts of dangerous solar events could buy time for astronauts en route to the Moon or Mars.