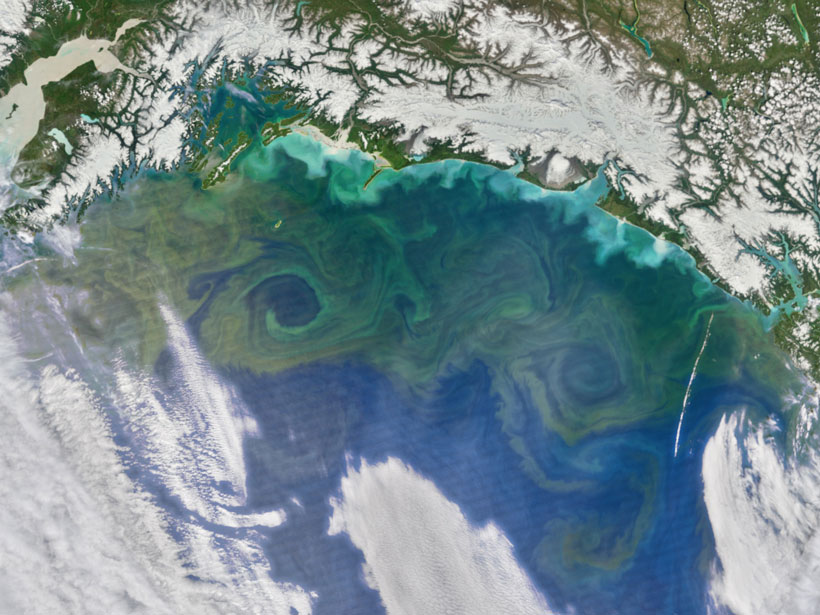
New research finds that Arctic rivers currently transport limited permafrost-derived dissolved organic carbon, which has implications for understanding the region’s changing carbon cycle—and its potential to accelerate climate change.
Terri Cook
Terri Cook is an award-winning freelance writer whose career has focused on exploring and explaining the 4.5-billion-year-history of the remarkable planet we live on. Cook, who has an M.S. degree in Earth science from the University of California, Santa Cruz, writes about geology, ecology, and the environment—as well as wine, tea, hiking, and biking—for a diverse group of publications, including Eos, Scientific American, NOVA Next, Science News, and EARTH magazine, as well as Avalon Travel and numerous other travel-related publications. Her reporting has taken her to 25 states and 20 countries scattered across 5 continents, from the depths of the Grand Canyon to the sandy Australian Outback to the mist-shrouded summit of Bali’s Mount Batur. As the coauthor of three popular guidebooks, including Hiking the Grand Canyon’s Geology and Geology Underfoot Along Colorado’s Front Range, Cook gives frequent presentations about geology and science communication. She is the recipient of a 2016 European Geosciences Union Science Journalism Fellowship and is based in beautiful Boulder, Colo.
Big Benefits from Experimental Watersheds
Scientific insights from the Agricultural Research Service’s long-term study sites underpin dozens of models and research methods that guide global land management and conservation practices.
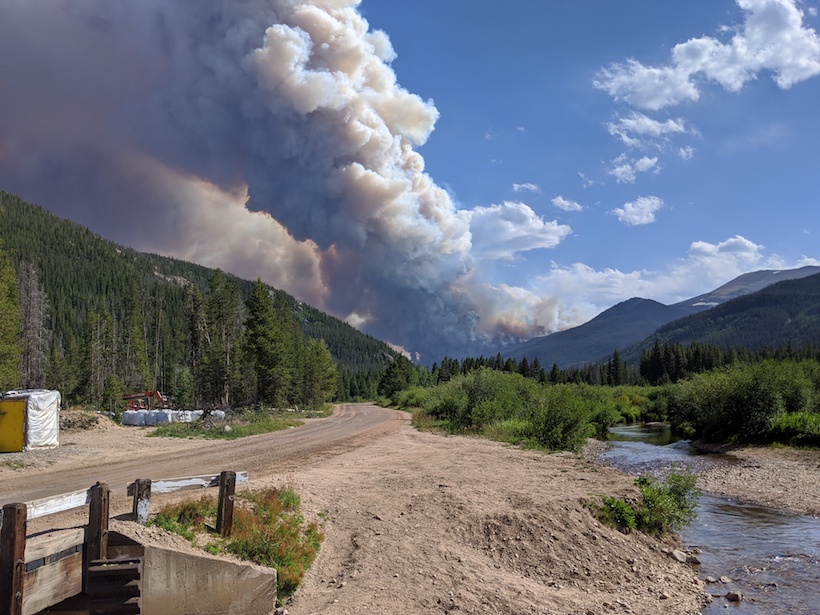
Evaluating Environmental Predictors of Western U.S. Wildfires
A new analysis highlights the importance of carefully selecting the environmental variables used to drive future changes in wildfire burn area in climate models.
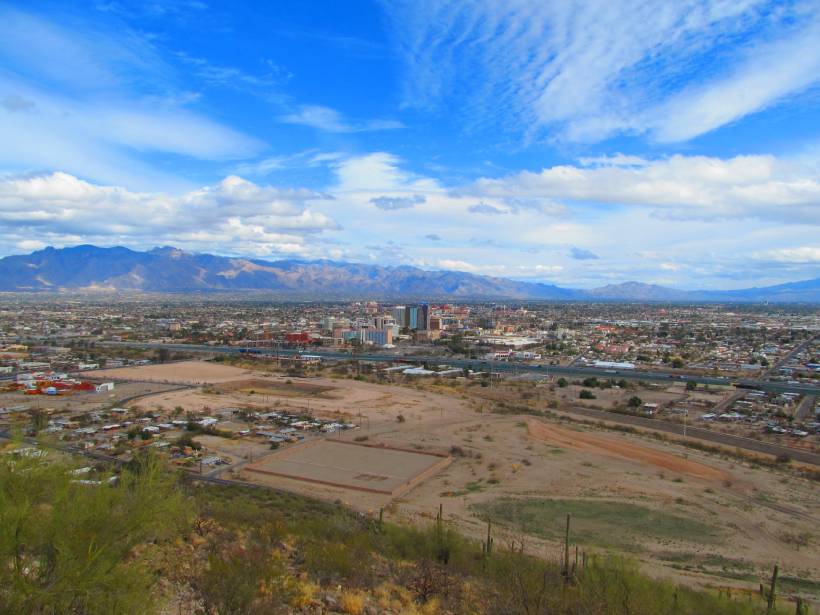
Parsing Routes to Aquifer Recharge Along Mountain Fronts
Research from the Tucson Basin indicates that tracers can be used to distinguish surface and subsurface recharge, providing crucial data to support sustainable water management in arid environments.
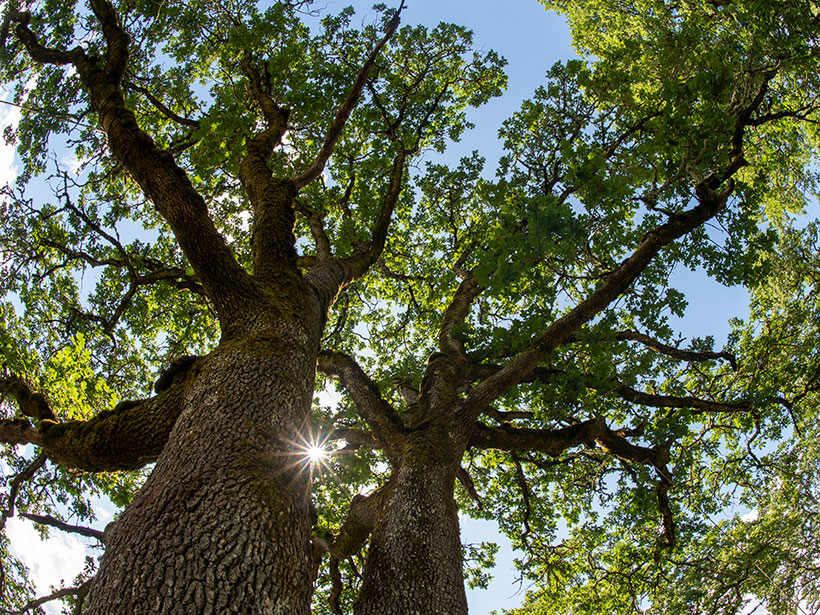
How Some Trees Survive the Summer Dry Season
Oak trees in California seasonally tap moisture in unsaturated soil and weathered bedrock, even when the groundwater table is within reach of their roots.
Autonomous Minisubmarine Measures Seawater Conditions
Forecasts of carbonate chemistry in coastal ecosystems determined from seasonal robotic measurements can improve fisheries management and help mitigate short-term ocean acidification events.
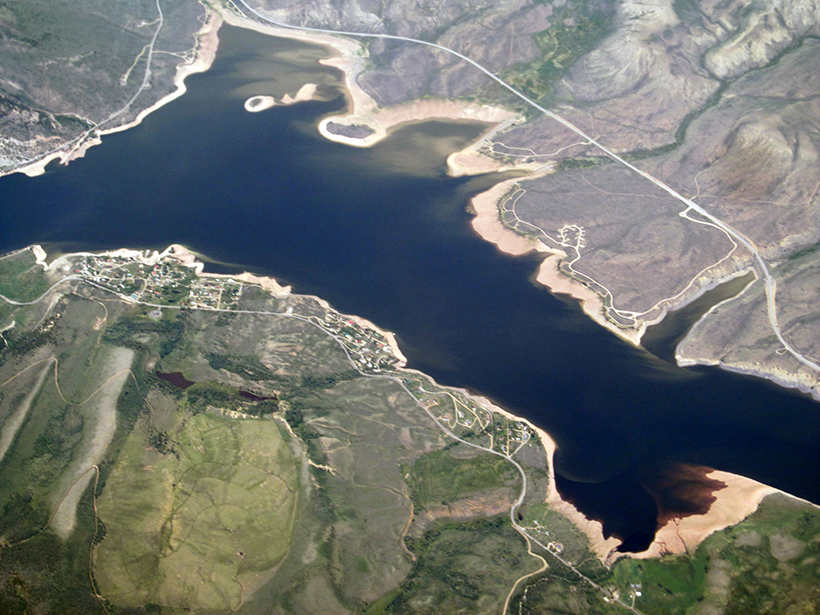
Different Models, Different Answers in Water Resource Planning
The experimental design used in climate vulnerability assessments can strongly influence the assessments’ findings and skew decisions about which factors are most important for informing adaptation.
A Promising Development for Detecting Ocean Productivity
A comparison of primary productivity measurements across the North Pacific Ocean demonstrates the potential for using autonomous instruments to discern effects of climate change on the marine food web.
A New Way to Fingerprint Drivers of Water Cycle Change
Simulations of tropical ocean convection help distinguish climate effects resulting from large-scale changes in atmospheric circulation from those resulting from higher temperatures.
Experimenting with Underwater Sediment Slides
Sediment-laden currents caused by breaching flow slides are hazardous to flood defenses and seabed infrastructure. New research shows that these phenomena must be accounted for in erosion simulations.