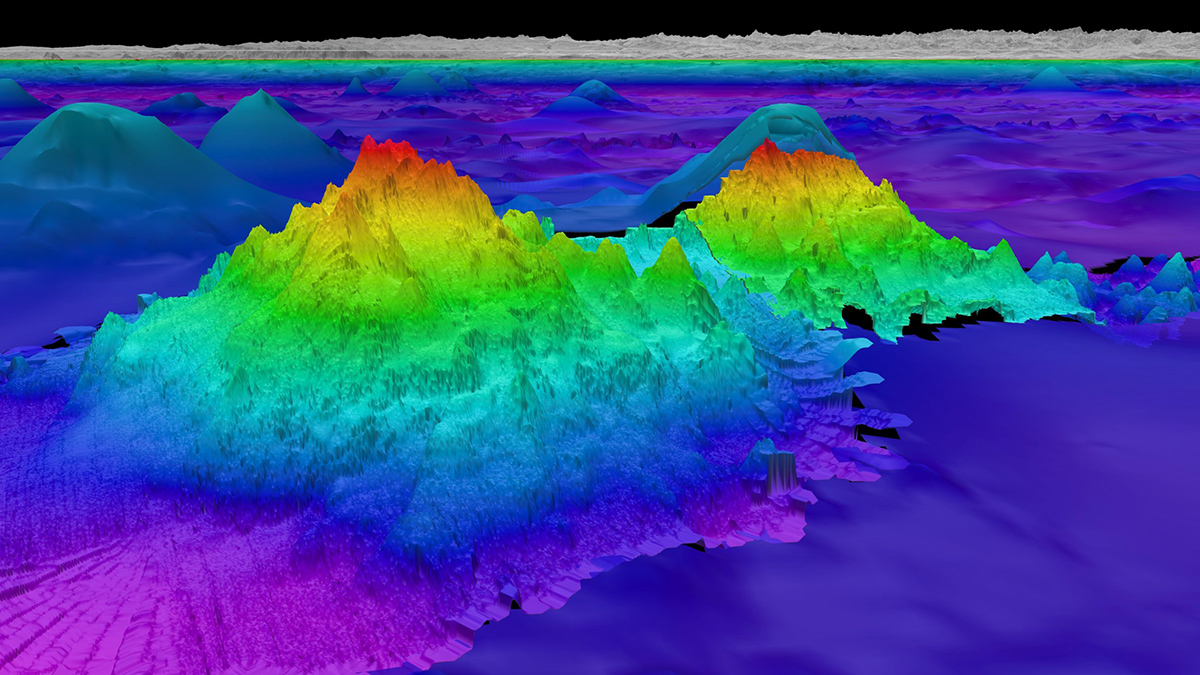
Seamounts may play a significant role in ocean turbulence and the upwelling of deep waters.
Tim Hornyak
Tim Hornyak (www.timhornyak.com) is a Canadian writer based in Tokyo, Japan, who has worked in journalism for more than 20 years. He has written extensively about travel, food, technology, science, culture, and business in Japan, as well as Japanese inventors, roboticists, and Nobel Prize–winning scientists. Tim’s writing has appeared in media including The New York Times, Nature, Science, Scientific American, CNBC, CNET, Eos, The Japan Times, and IDG News. He is the author of Loving the Machine: The Art and Science of Japanese Robots and has contributed to several Lonely Planet travel guidebooks. His favorite robot is Astro Boy, but he firmly believes that the greatest Japanese invention of all time is the onsen (hot spring). He has lived in Tokyo for more than 15 years.
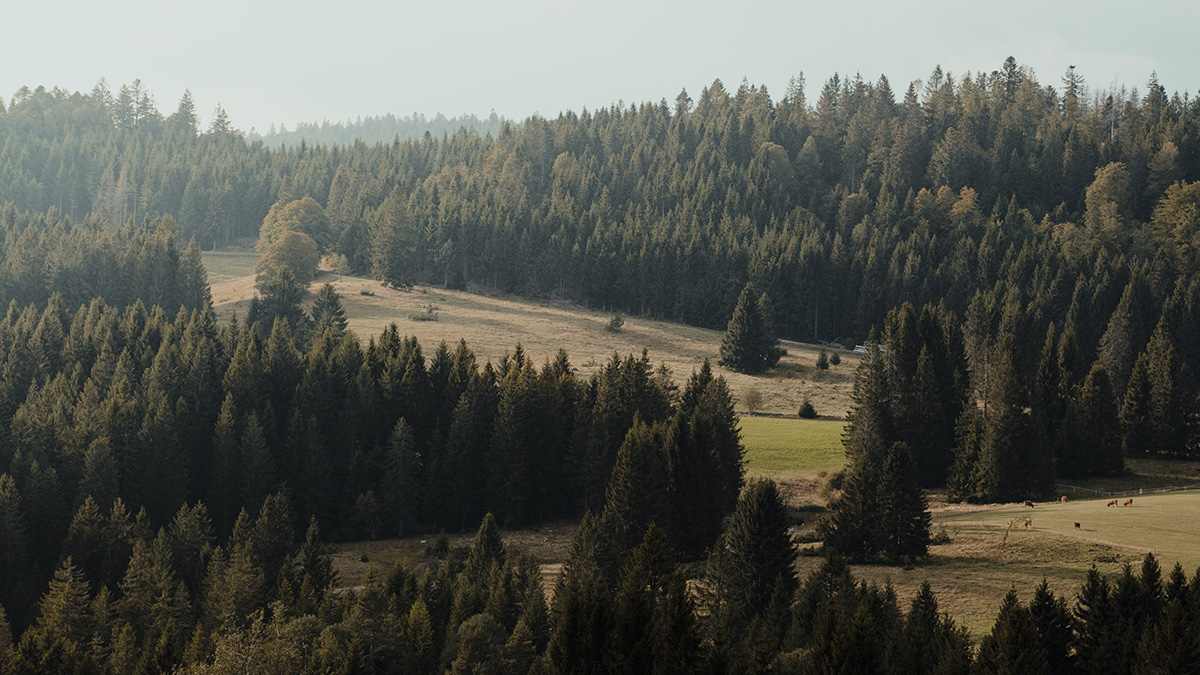
Wissenschaft verknüpft den Wald mit dem Internet der Dinge
Ausgestattet mit rund 10,5 Mio. Euro an Forschungsgeldern werden Forschende neuartige Sensoren zum Einsatz bringen, die der Assimilation von Daten in Echtzeit und der Erstellung von Modellen dienen, die die Auswirkung von Klimaveränderungen auf Waldgebiete abbilden.
New Seafloor Map Only 25% Done, with 6 Years to Go
Beneath the waves, the vast majority of the ocean is unknown. Seabed 2030 is using cutting-edge technologies to fill in the bathymetric blanks and fully map the seafloor.
Mounds of Ancient Ocean Floor May Be Hiding Deep in Earth
A mysterious seismic feature at the bottom of Earth’s mantle is more widespread than previously thought.
Godzilla Gets a Forever Home on the Ocean Floor
The world’s largest oceanic core complex is named after the reptilian monster from Japanese science fiction. Parts of the seabed feature were recently christened with the beast’s anatomy.
Could Jupiter’s Heat Waves Help Solve a Planetary Energy Crisis?
Infrared observations reveal that Jupiter’s upper atmosphere is much warmer than models predict. The discovery may be a clue to finding missing heat sources in other giant planets.
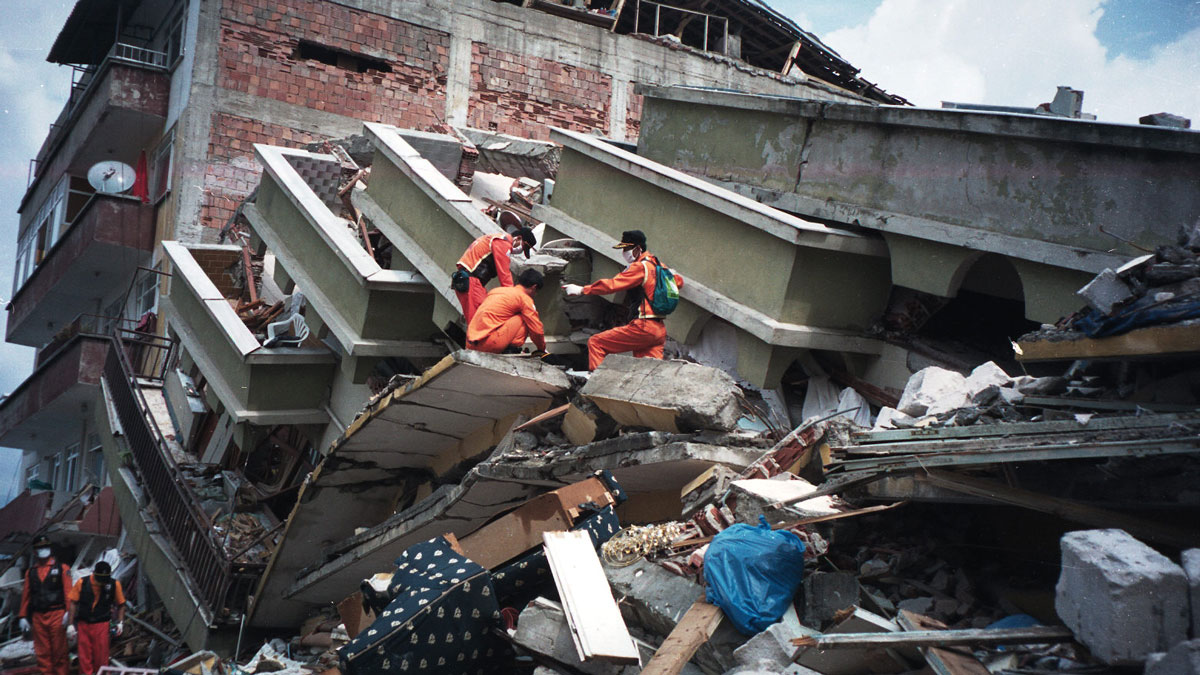
¿Tienen los terremotos y las placas tectónicas una relación bidireccional?
Un terremoto catastrófico en Turquía que sucedió en 1999 cambió el movimiento de la placa de Anatolia, según un estudio que podría modificar los fundamentos de modelamiento de los terremotos.
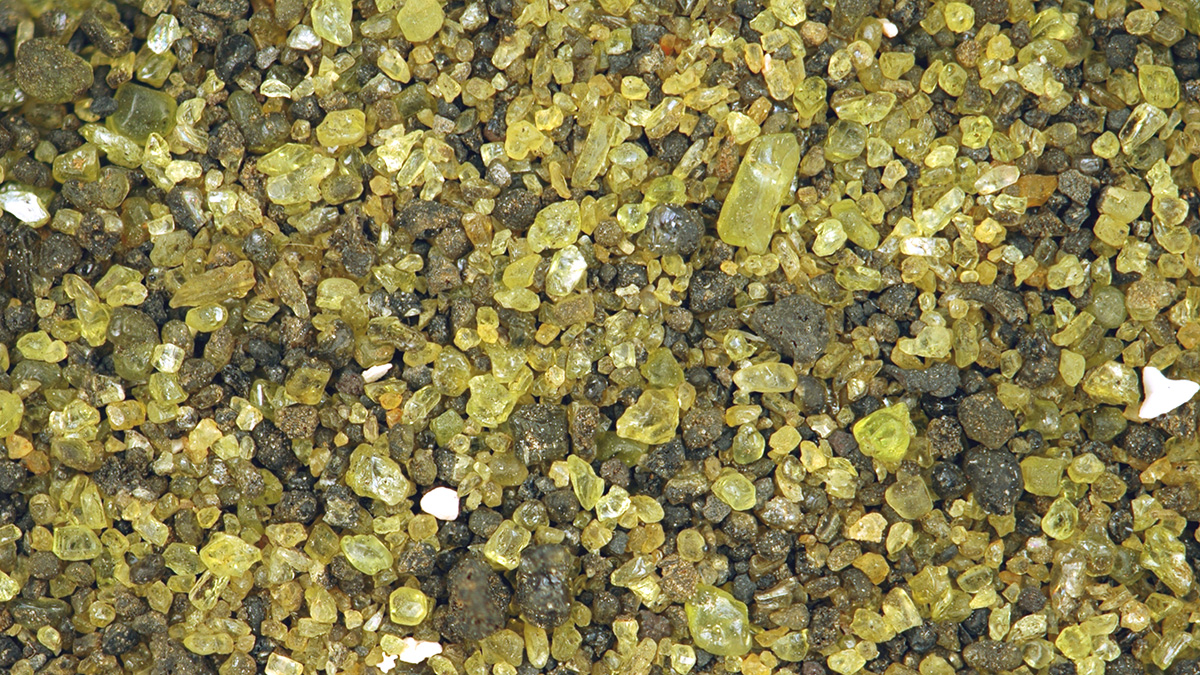
Can These Rocks Help Rein in Climate Change?
Spreading olivine on beaches could accelerate ocean uptake of carbon dioxide and potentially limit climate change. The concept and execution still face some scrutiny from scientists.
Scientists Bring Forests into the Internet of Things
Armed with $10.5 million in funding, researchers will deploy novel sensors for real-time data assimilation and modeling of how changes in climate are affecting woodlands.
Muography Array Under Tokyo Bay Spots Meteotsunami Waves
A new study shows how muons can be used to study tide and wave phenomena, helping secure coastal communities.