Tiny yet stable magnetized particles created by microbes long ago could help scientists better determine the strength and orientation of ancient magnetic fields.
CC BY-NC-ND 2016
Mapping the Movement of Energy Under Japan
New research on the energy waves caused by earthquakes provides the most detailed map to date of the subduction zone beneath Japan.
Amoeba People Sing Quirky Tunes About Geoscience
A whimsical backstory identifies the musicians as aliens from the planet Crouton sent to Earth to transmit scientific information back home in song.
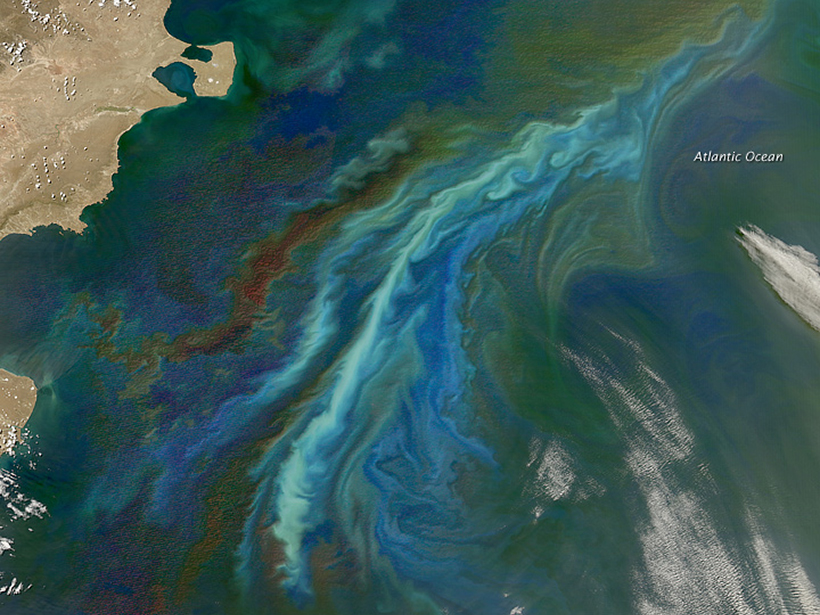
A New Mechanism for Nitrogen Cycling in the Southern Ocean
A nitrite-oxidizing enzyme may work in reverse for some microbes in the Antarctic autumn.
Tackling the Paris Temperature Targets
The global temperature targets established in Paris in 2015 are ambitious; new research examines what it would take to achieve those targets.
Tanzanian Volcanoes May Hoard Helium Ready for the Taking
Sweet spots of volcanic heat that are not too close to active eruptions may hold the world's richest reservoirs of the scientifically and medically important gas helium.
Perspectives on Climate Tipping Points
If policy makers are to make real progress, we must start meaning the same thing when we use the same words to describe climate change.
How Irrigation in Asia Affects Rainfall in Africa
Up to 40% of the total rainfall in arid parts of East Africa may be caused by water vapor from farming practices in South Asia.
In the Eastern Pacific Ocean, the "Blob" Overshadows El Niño
Underwater gliders and ocean modeling reveal unexpectedly weak El Niño effects on a major West Coast current.
Your Phone, Tablet, and Computer Screens Aren't Safe from Hackers
Cables and circuitry inside your gadgets' screens act as accidental antennae that broadcast screens' contents. A new study says the industry needs to fix this security risk before hackers exploit it.