Modeling Earth’s near-space environment and its electrical currents is challenging. A new study compares how four different models stack up against observations.
L. Crane
Leah Crane, a Research Spotlight writer for Eos.org, is a freelance science writer focusing on physics and space. She holds a bachelor’s degree from Carleton College in physics and astronomy.
How Geomagnetic Storms Light Up the Geocorona
After geomagnetic storms, Earth’s corona abruptly increases in hydrogen density. For the first time, serendipitous observations have allowed researchers to investigate why.
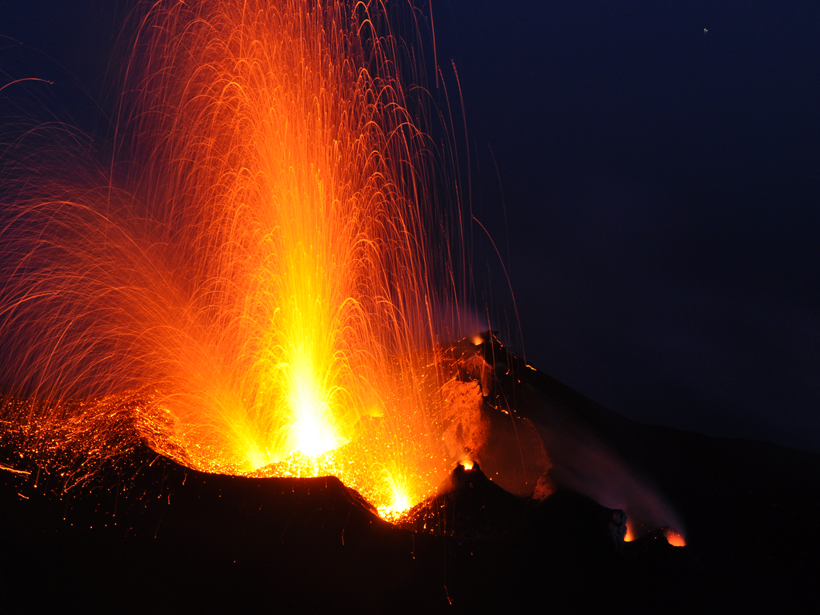
Tracking Volcanic Bombs in Three Dimensions
A new method allows researchers to precisely track in three dimensions bits of fragmented magma as they are expelled in explosive volcanic eruptions.
Polar Interlopers in the Aurora
A new study suggests that poleward boundary intensifications in the aurora are caused by fast flows of plasma from the poles into the auroral oval.
When Lower-Atmosphere Waves Invade the Upper Atmosphere
A review of the literature shows that weather nearer Earth's surface could produce up to 35% of the ionosphere's variability.
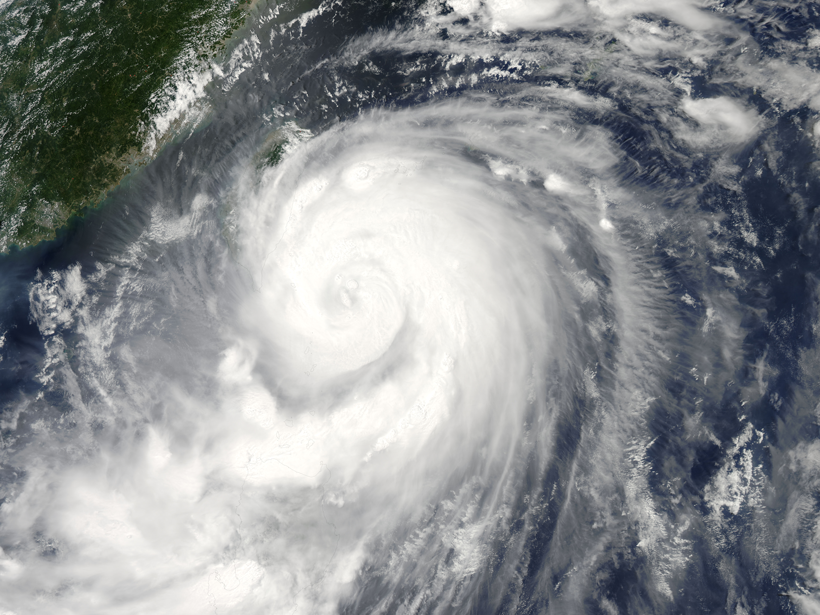
Reading Raindrops: Microphysics in Typhoon Matmo
Quantitative predictions about tropical storms require an understanding of even their smallest physical processes. A new study observes unusual microphysics in 2014's Typhoon Matmo.
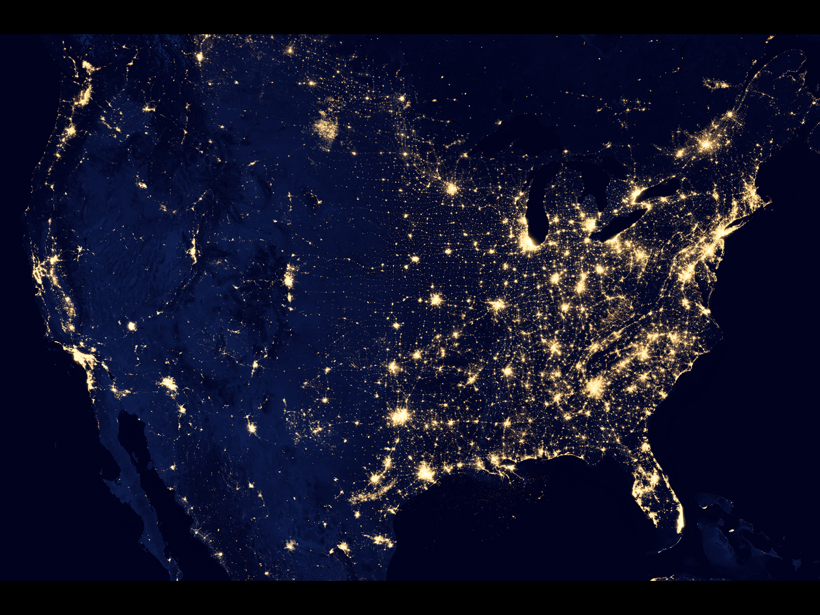
Mapping Geoelectric Hazards Across the United States
Variations in Earth’s magnetic field can induce electric fields in the ground, driving damaging currents through our power grids.
Earthquakes Could Funnel Radio Waves to Dark Zones in Mountains
By being coupled with a layer of mobile electrical charges on the Earth's surface, radio waves could travel over the ground to areas that would normally be unreachable, like behind a mountain.
Tide Gauge Records May Underestimate 20th Century Sea Level Rise
Tide gauges can help measure sea level change, but their limited locations and short records make it hard to pinpoint trends. Now researchers are evaluating the instruments' limitations.
Mapping Water and Heat Deep Under Long Valley Caldera
Researchers use electrical resistivity to find the heat source and reservoir feeding Long Valley Caldera's labyrinthine hydrothermal system.