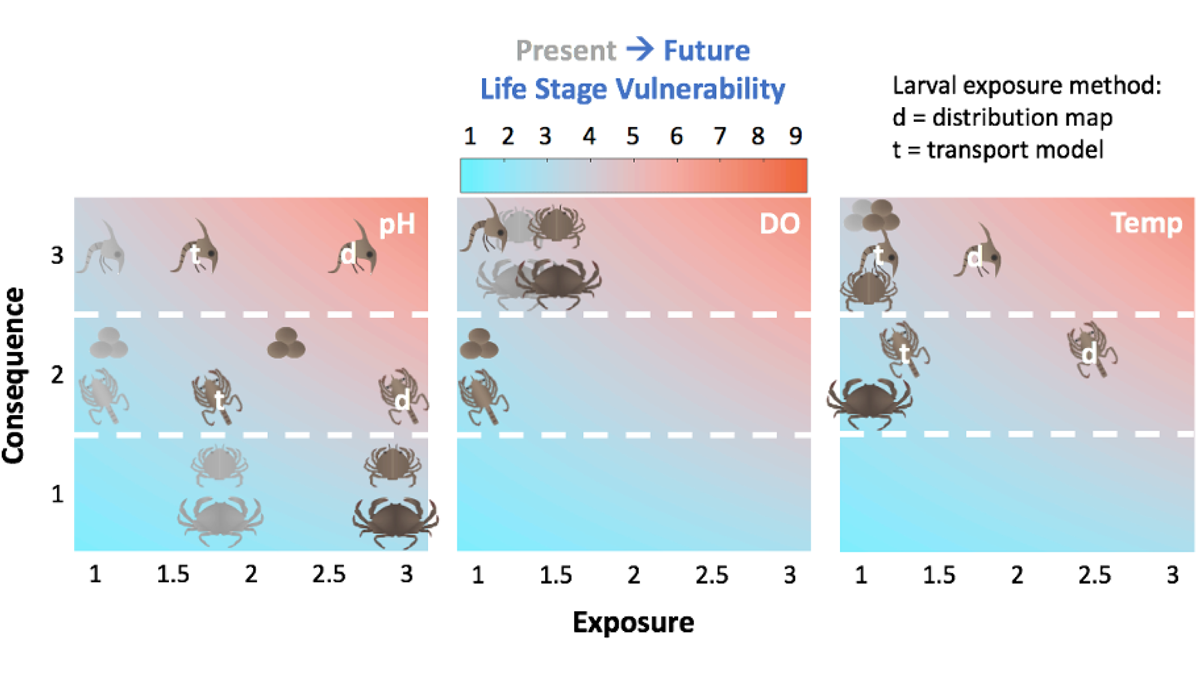
The lucrative Dungeness crab fishery is at risk because of the combined effects of projected climate-related habitat changes: lower oxygen, warming temperature, and increased acidity.
Editors’ Highlights
Simpson’s Law Role and Water Vapor Feedbacks
The choice of a fixed relative humidity leads to a simpler picture of climate feedbacks than fixing absolute humidity.
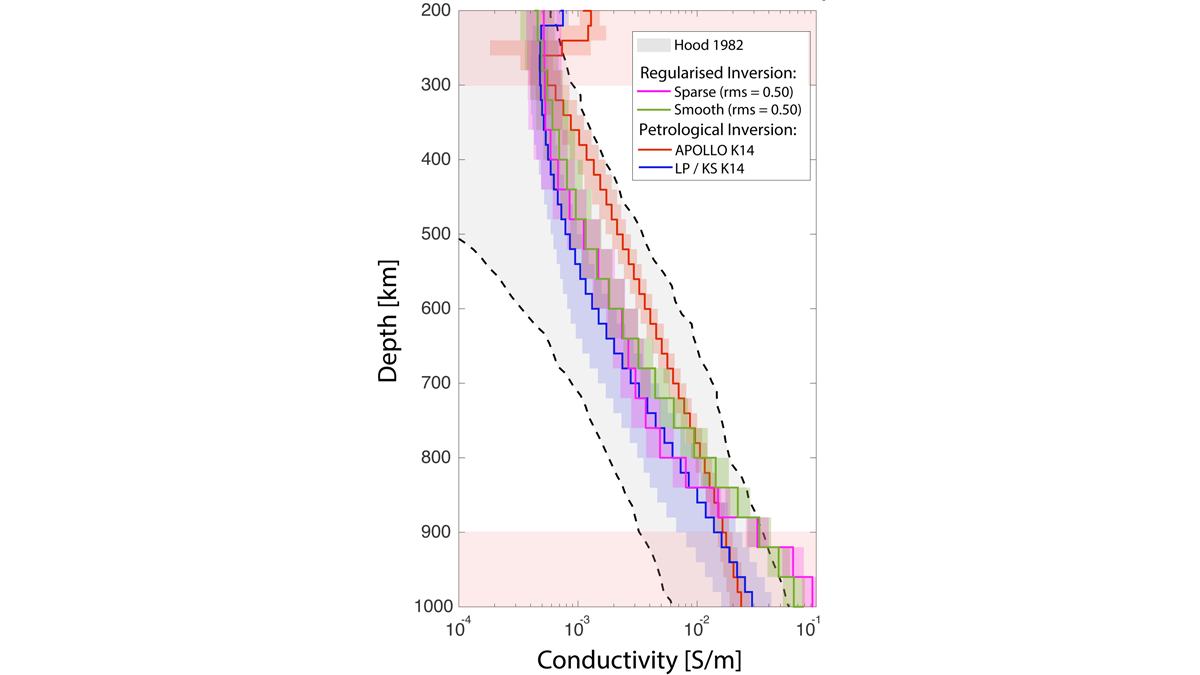
A Better Look at the Moon’s Middle Mantle
A new analysis strategy sheds new light on the electrical conductivity of the lunar mantle between 300 and 900 km depth.
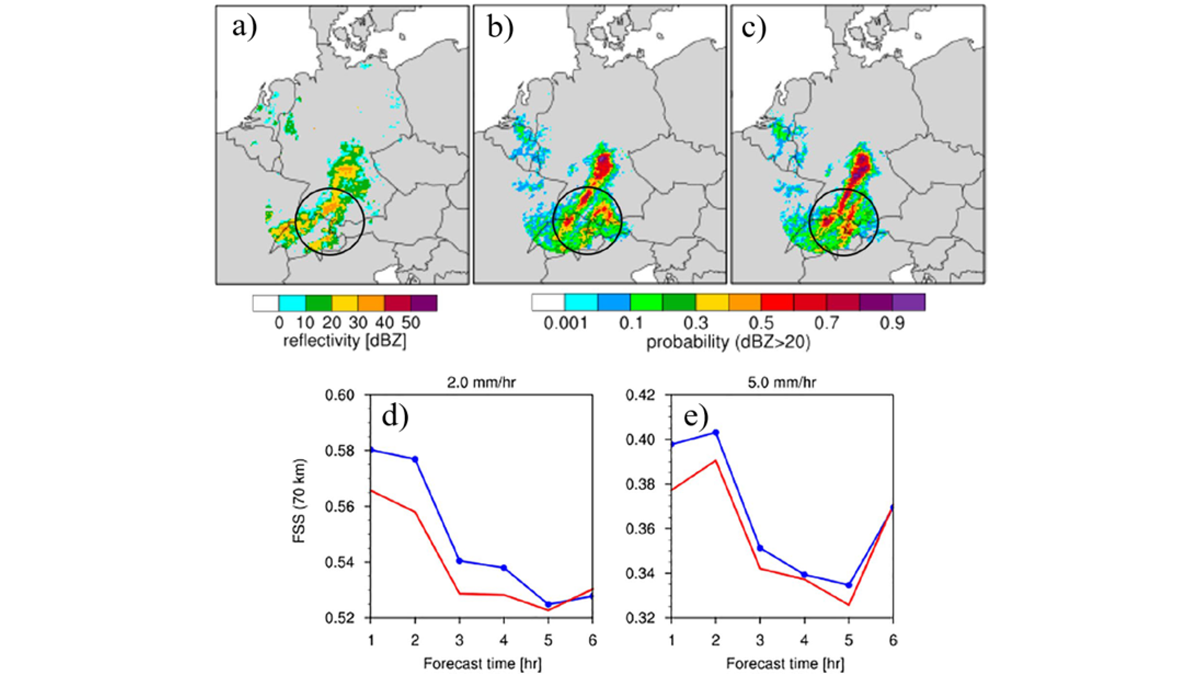
Hurricane Forecast Improvement with Better Turbulent Processes
A new look at turbulent processes has improved the prediction of hurricane rapid intensification by properly accounting for the unique environment of a hurricane eyewall.
A New Way to Represent Microphysical Uncertainty
A new way of representing microphysical uncertainty in convective-scale data assimilation reduces biases in model states and improves the accuracy of short-term precipitation forecasts.
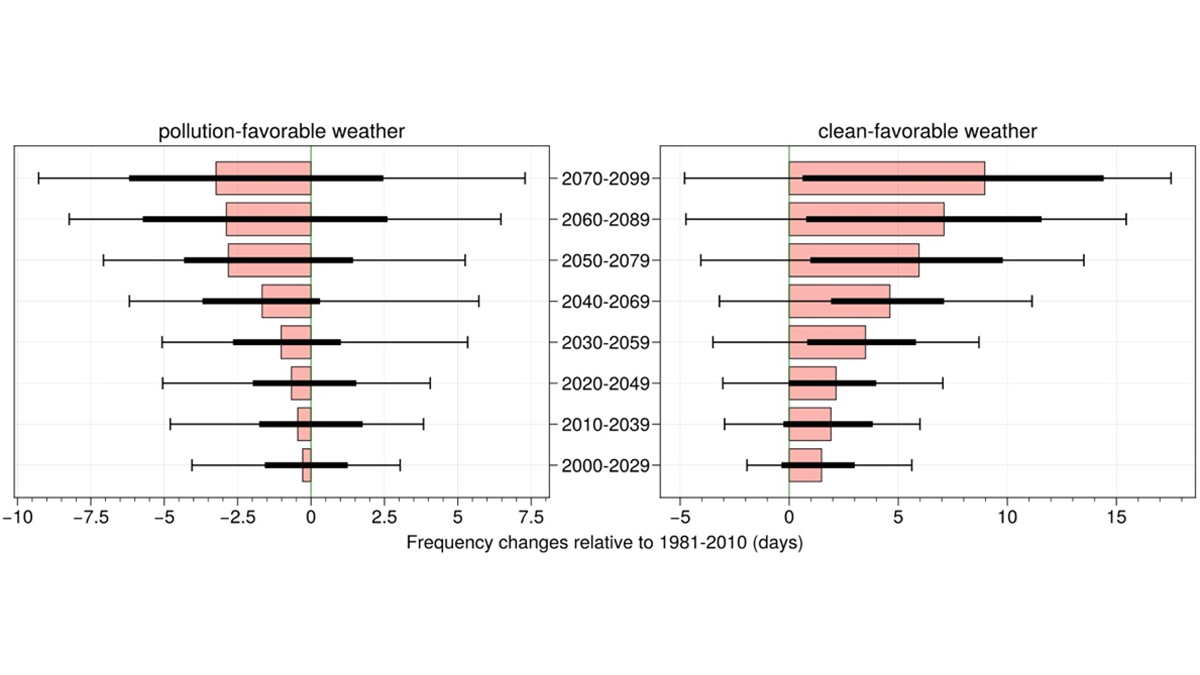
Reduced Winter PM2.5 in Northern India Under Global Warming
Global warming is projected to alleviate PM2.5 pollution in Delhi by decreasing pollution-favorable weather days and increasing clean-favorable weather days.
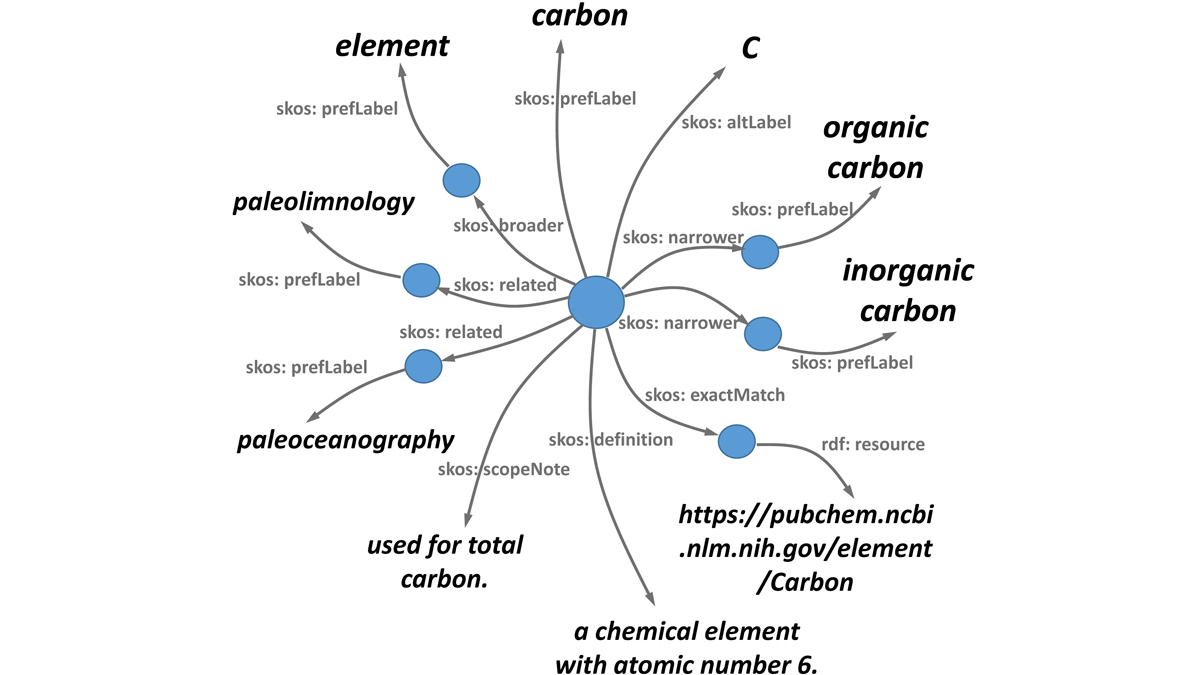
Finding the Right Words: A Common Language for Data Deposition
Discovering climate signals in the archives: how using a common language for data deposition ensures your data are found, understood and cited.
ICESat-2 Adds Estimates of Sea Level Trends to Accomplishments
The high spatial resolution and high orbit of ICESat-2 make it suited for measuring sea level close to the coast and in the polar regions, filling a gap in our sea level observational system.
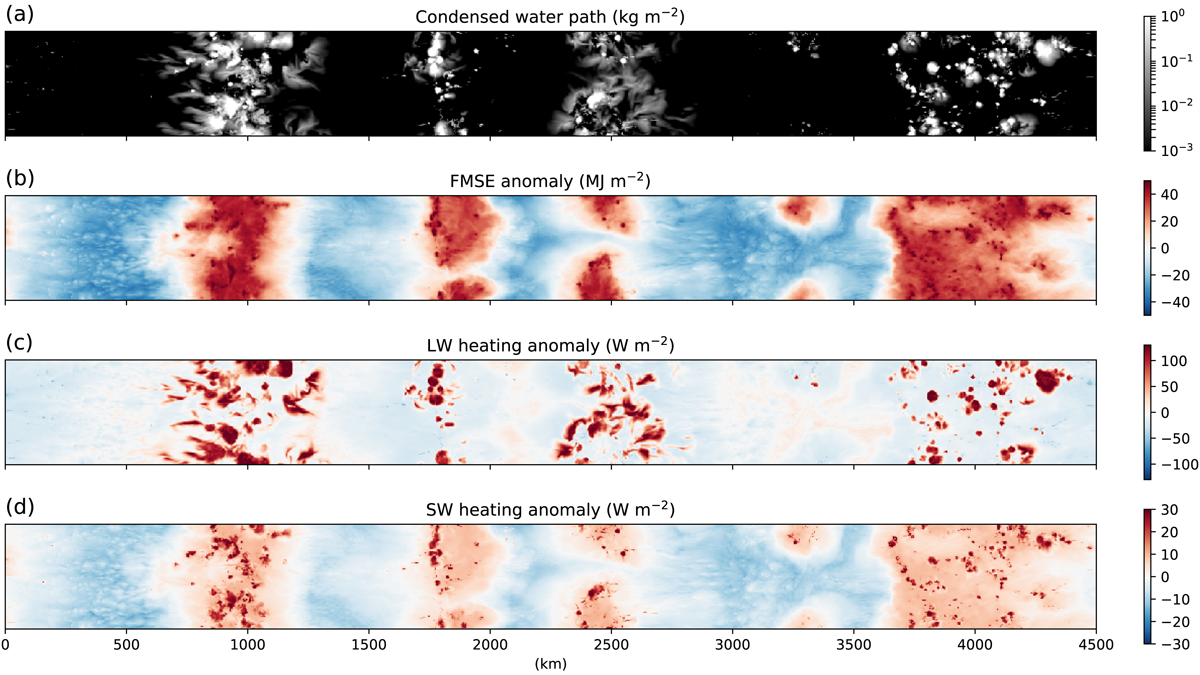
Importance of High Clouds and Moisture in Rainstorm Aggregation
A study of the impacts of radiative interactions with different cloud types on aggregation of rainstorms finds that interactions with high-clouds and water vapor are key.
AeroCom Models Improved with Aerosol and Albedo Constraints
Satellite data has been used to correct the aerosol loading and land surface albedo in several AeroCom models, which has improved shortwave flux biases between models and observations.