New research on the energy waves caused by earthquakes provides the most detailed map to date of the subduction zone beneath Japan.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
A New Mechanism for Nitrogen Cycling in the Southern Ocean
A nitrite-oxidizing enzyme may work in reverse for some microbes in the Antarctic autumn.
Tackling the Paris Temperature Targets
The global temperature targets established in Paris in 2015 are ambitious; new research examines what it would take to achieve those targets.
How Irrigation in Asia Affects Rainfall in Africa
Up to 40% of the total rainfall in arid parts of East Africa may be caused by water vapor from farming practices in South Asia.
In the Eastern Pacific Ocean, the "Blob" Overshadows El Niño
Underwater gliders and ocean modeling reveal unexpectedly weak El Niño effects on a major West Coast current.
Your Phone, Tablet, and Computer Screens Aren't Safe from Hackers
Cables and circuitry inside your gadgets' screens act as accidental antennae that broadcast screens' contents. A new study says the industry needs to fix this security risk before hackers exploit it.
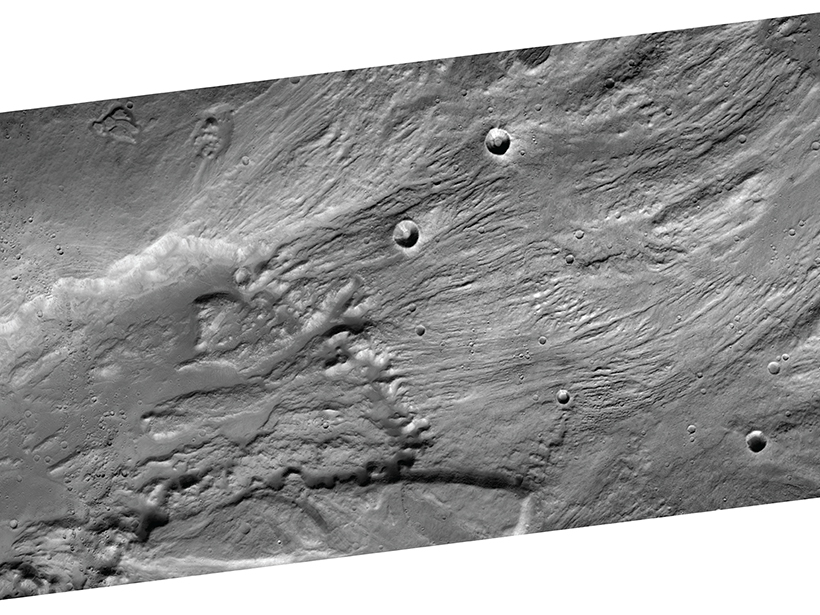
Reconstructing Catastrophic Floods on Earth and Mars
A new theoretical model suggests that ancient floods that carved canyons on Earth and Mars may have been much smaller but lasted longer than previously thought.
Volcanic Eruptions Stir an Already Complex Atmosphere
A study of Earth's atmospheric response to major volcanic eruptions seeks to reconcile contradictions between observations and climate models.
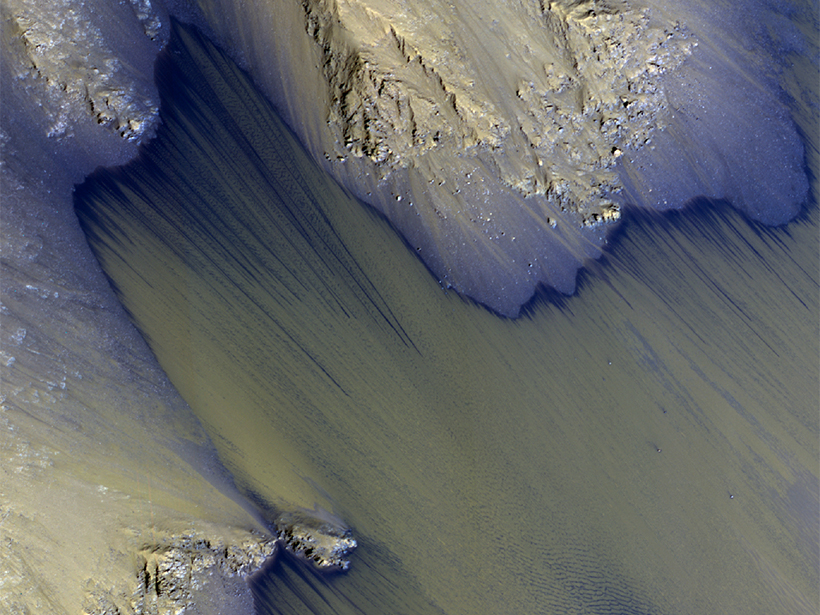
A Cluster of Water Seeps on Mars?
The discovery of dense concentrations of recurring flowlike features in two Valles Marineris chasms could aid in the search for life and influence future exploration of the Red Planet.
Revising the Displacement History of New Zealand's Alpine Fault
A reinterpretation of structural and paleomagnetic data suggests that New Zealand's Alpine Fault accommodates a far greater percentage of geologically recent plate motion than previously thought.