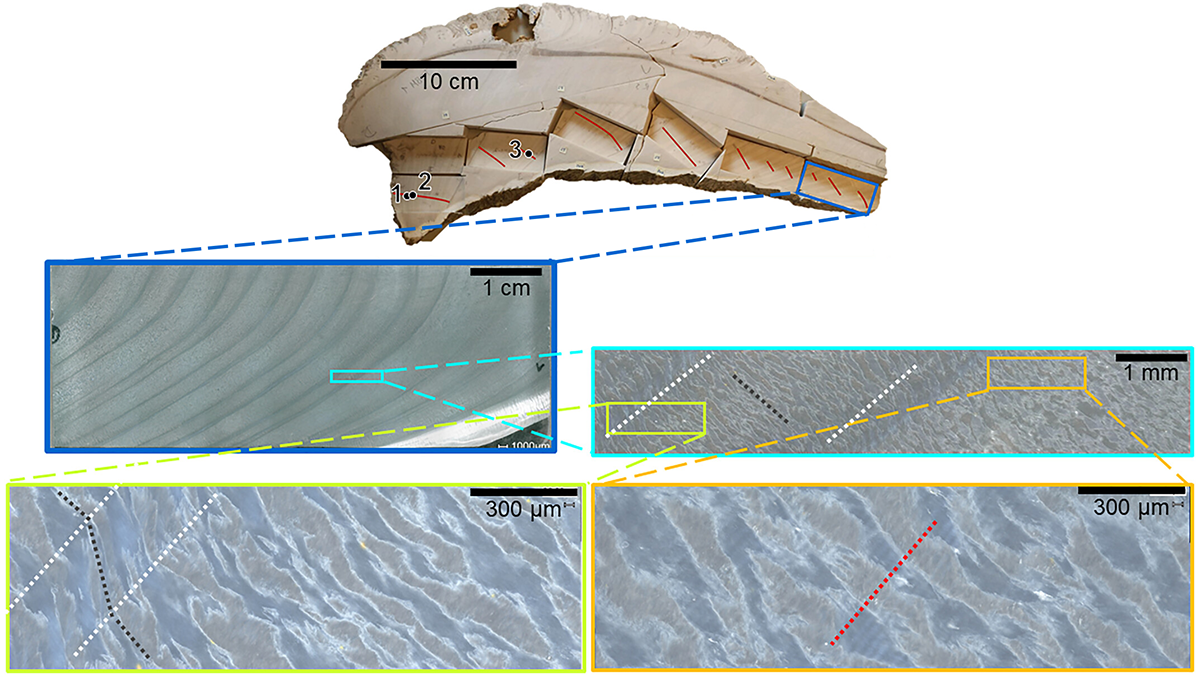
Using geochemical techniques, scientists identify daily cycles in fossilized giant clams, which permits climate reconstructions at the weather timescale.
clams
Posted inNews
“Glass Pearls” in Clamshells Point to Ancient Meteor Impact
Research suggests that the spherical structures, smaller than grains of sand, may be microtektites, but additional investigations are needed to verify their identity.
Posted inNews
Estuaries May Face Increased Parasitism as Sea Levels Rise
Researchers document how past sea levels changes affected invertebrate health in coastal environments.