Monitoring and forecasting the movement of volcanic clouds is key to mitigating the impacts on communities, infrastructure, and air traffic.
clouds
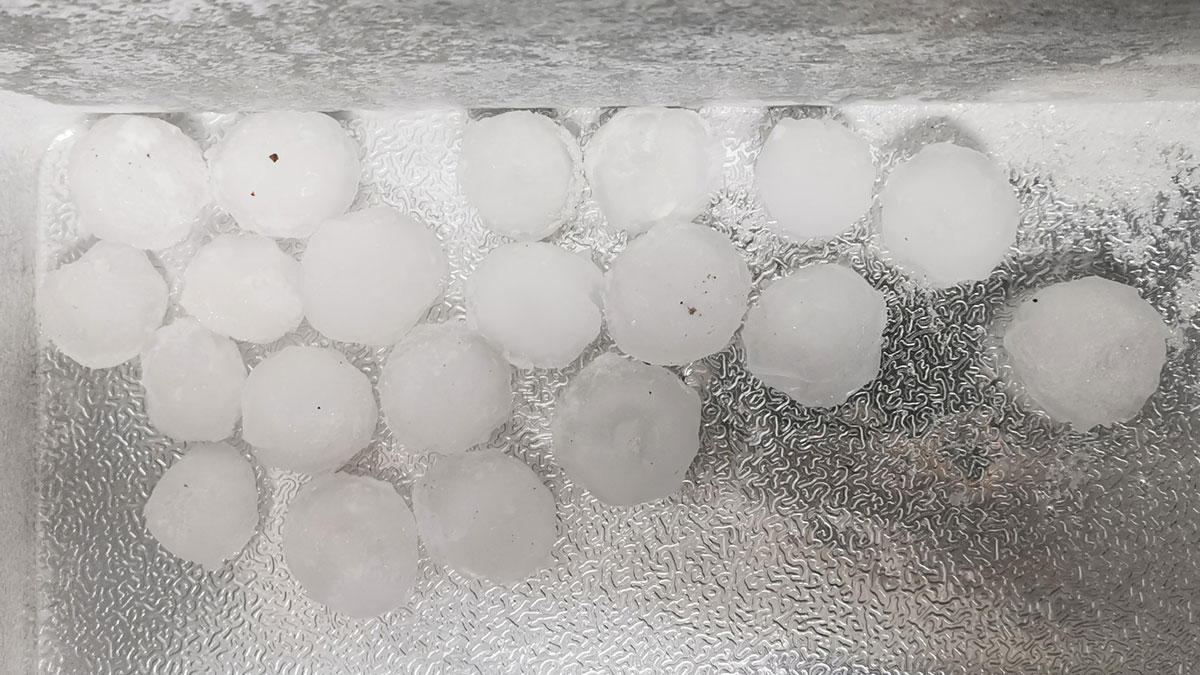
Isotopes Map Hailstones’ Paths Through Clouds
Hailstones have been said to bounce up and down through clouds as they grow. A new study found that many stones take much simpler paths.
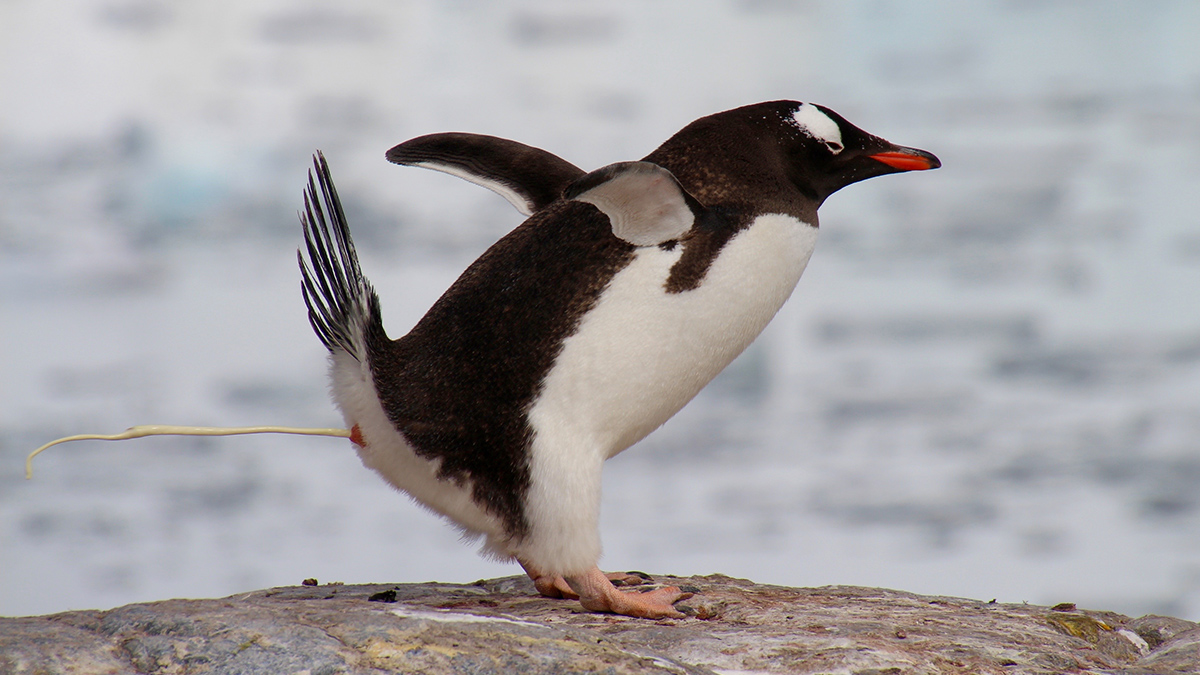
Pungent Penguin Poop Produces Polar Cloud Particles
The discovery highlights how penguins and other polar seabirds help shape their environments, even as they are under threat from climate change.
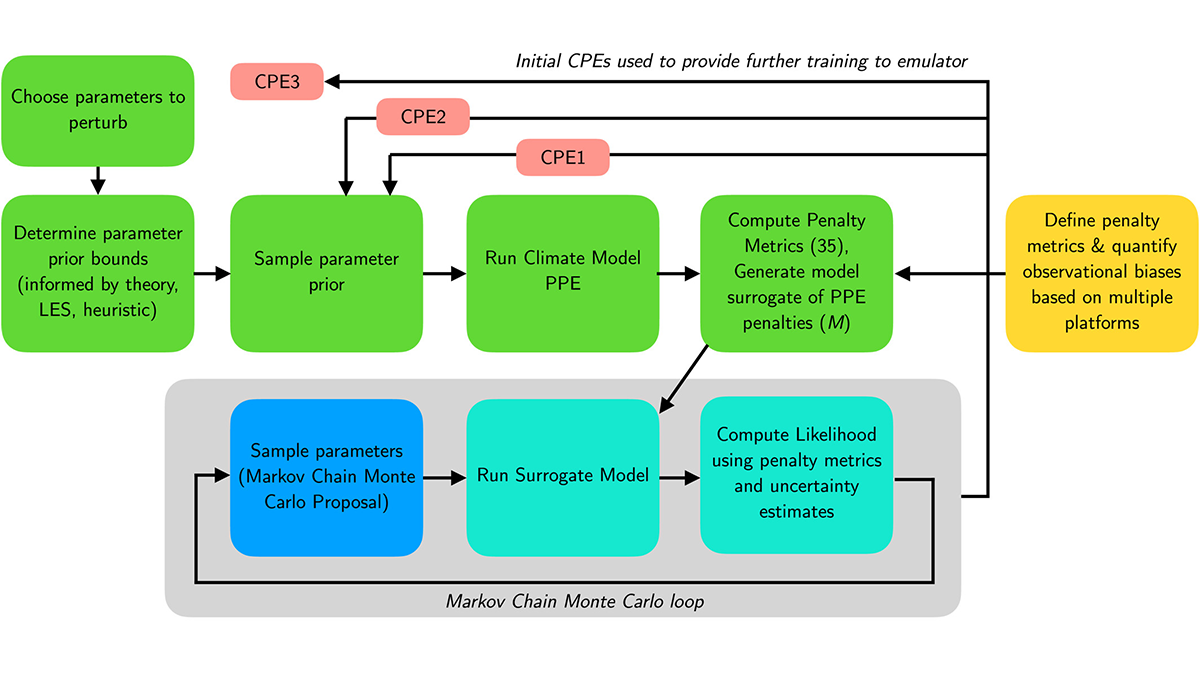
Calibrating Climate Models with Machine Learning
Using machine learning, researchers automatically calibrate a comprehensive climate model, improving simulations of difficult features and taking steps toward more reliable climate projections.
A New View of Gamma Rays from Thunderclouds
Observations from high-flying aircraft revealed that thunderclouds act as natural particle accelerators, emitting energetic electromagnetic radiation more often than scientists expected.
Machine Learning Provides a New Perspective of Low-level Clouds
Low-level clouds over the oceans, extensively studied for their role in climate change, are re-examined from a new perspective that applies machine learning to radar observations.
Tropical Congestus Clouds Explained by Water Vapor Spectroscopy
A new study demonstrates how the abundance of congestus clouds in the tropics can be explained by the water molecule’s discerning appetite for infrared radiation.
Characterizing the Space Between Clouds and Clear Sky
The area near clouds is often classified as ‘clear sky’, but a new study demonstrates the potential biases of misclassifying these transition zones and their significance for Earth’s energy budget.
Darker, Less Cloudy Earth Contributed to Record Heat
Decreases to our planet’s albedo caused by fewer low-lying clouds helped push temperatures to historic highs in 2023, according to new research.
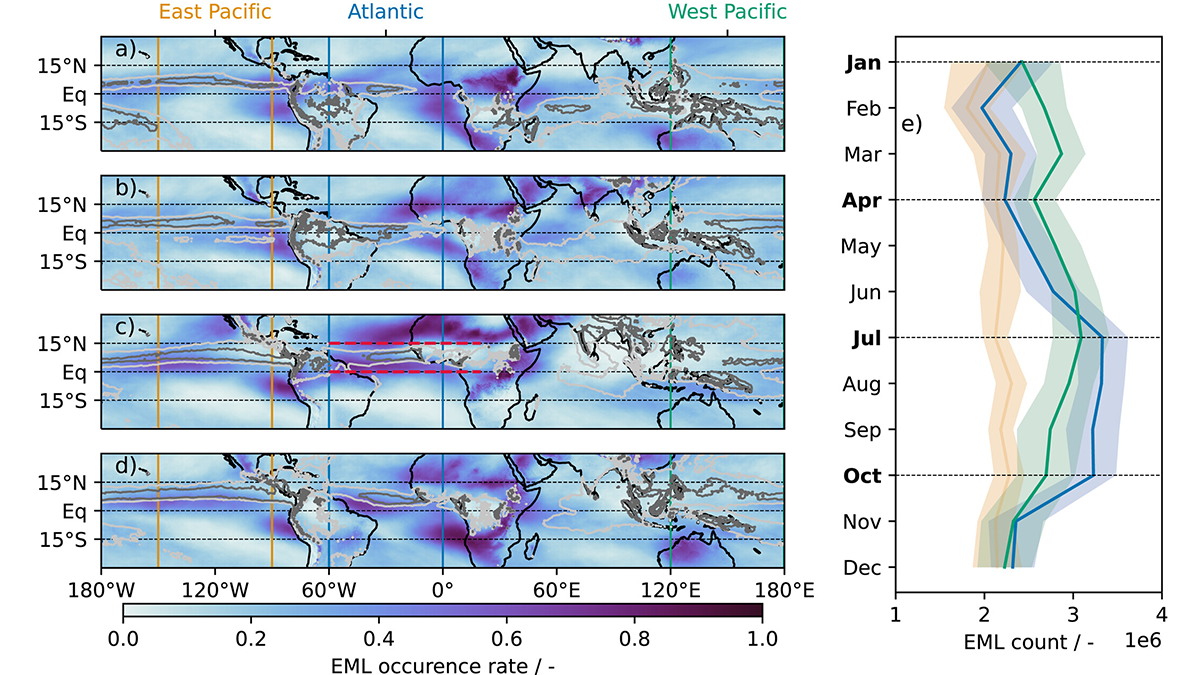
Characteristics of Moist Layers over the Tropical Atlantic
In a new study, characteristics of elevated moist layers, their seasonality, spatial distribution, structure, and the coupling of mid-tropospheric circulation and convection are examined over the tropical Atlantic.