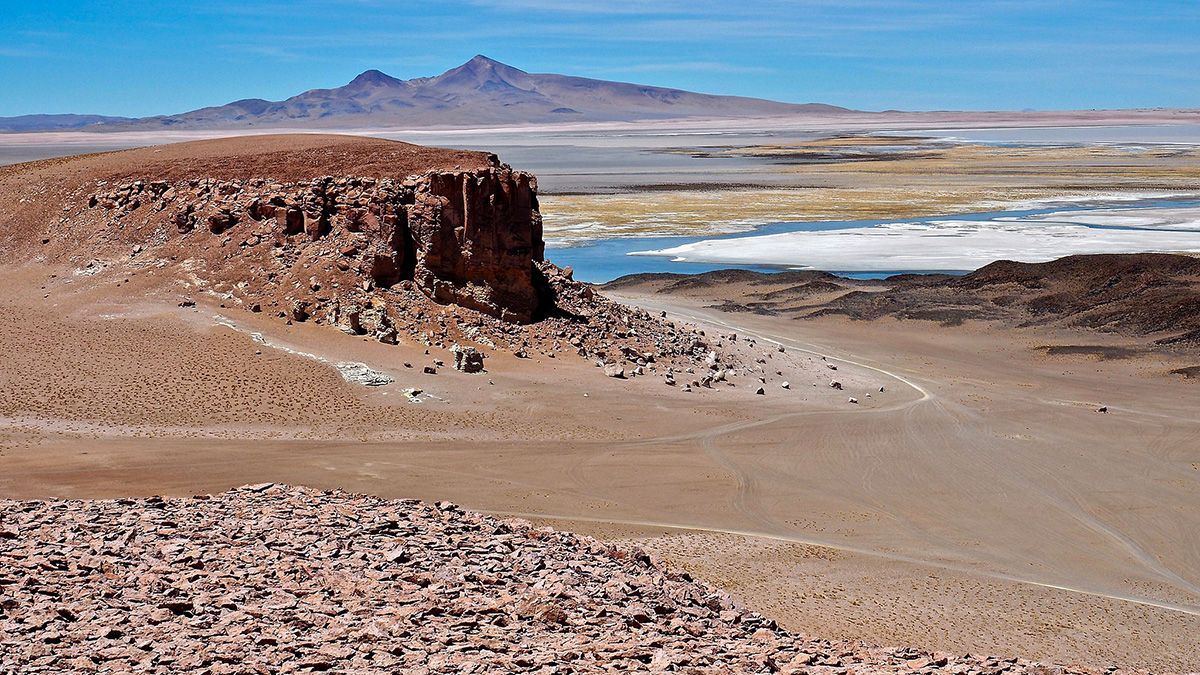
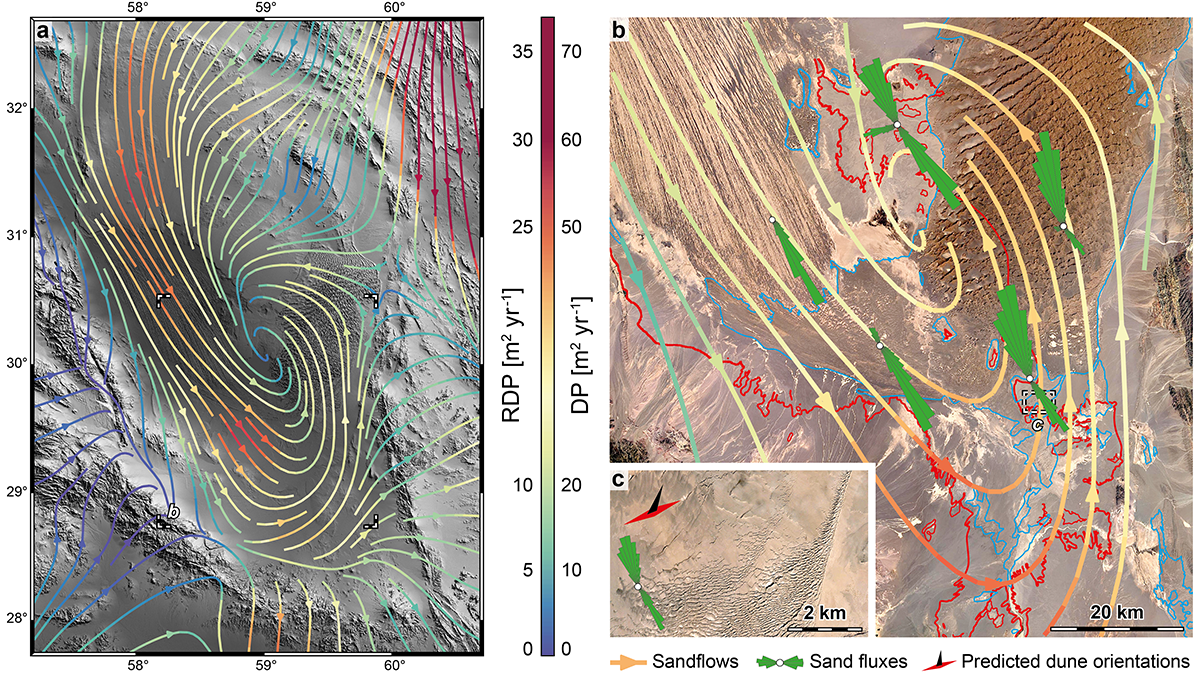
The Lut Desert in Iran is an exceptional natural laboratory to study how wind moves sediment across the landscape. A new study quantifies erosional and depositional sediment fluxes of the desert.
deserts
Iodine-Laden Desert Dust Is Eating at Ozone Pollution
In a happy accident, scientists found a potential solution to an atmospheric chemistry mystery. Their findings could be a missing piece in the iodine cycle and in atmospheric models.
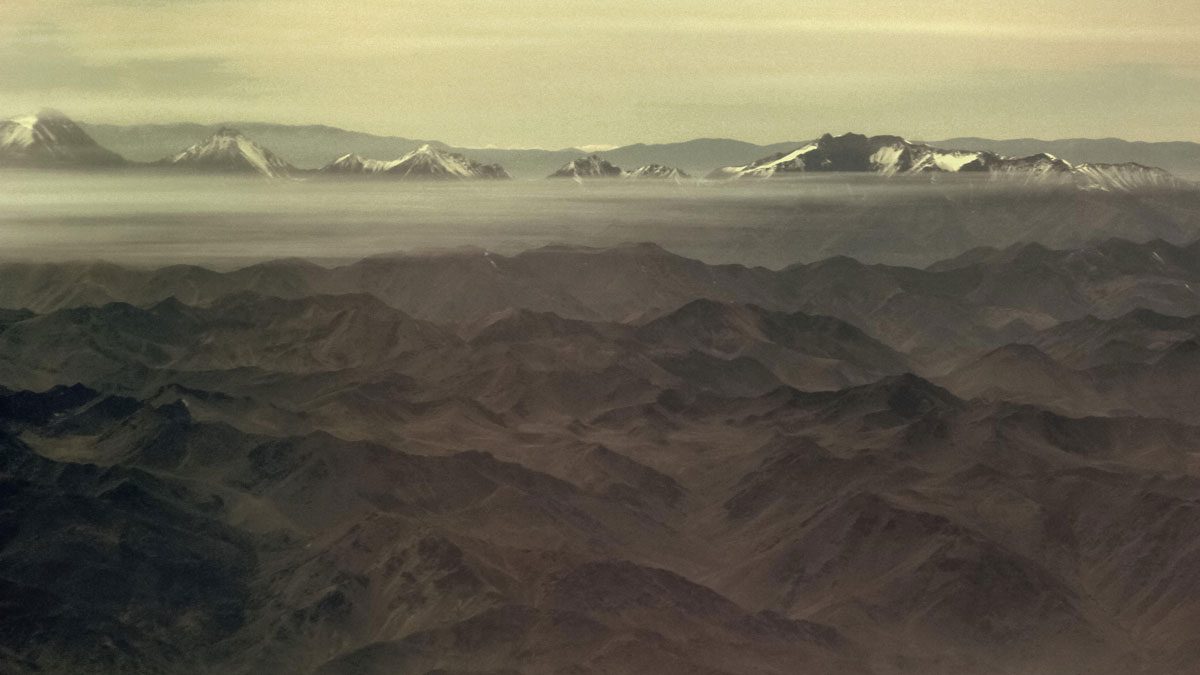
Understanding Rare Rain Events in the Driest Desert on Earth
A new study reveals the atmospheric paths of storm events that can deliver a decade’s worth of rain in a few hours to the Atacama Desert.
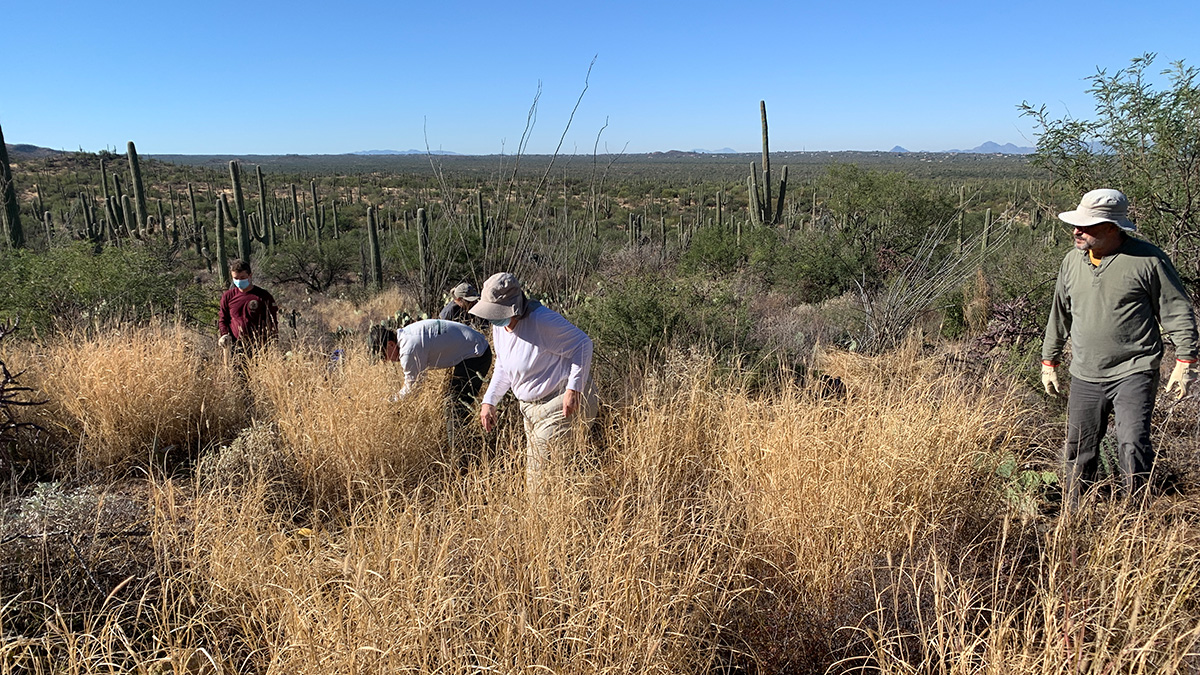
Invasive Plants and Climate Change Will Alter Desert Landscapes
In experiments conducted in Biosphere 2, invasive buffelgrass weathers higher temperatures and drought conditions better than its native brethren.
Biocrust “Probiotics” Can Aid Dryland Restoration Efforts
Bacteria can speed up the growth of biocrust-forming organisms in nurseries, providing more material for restoration of degraded dryland soil.
Dunes Dance to a New Rhythm in Climate Change
Dunes may morph or creep in new directions in a warming world.
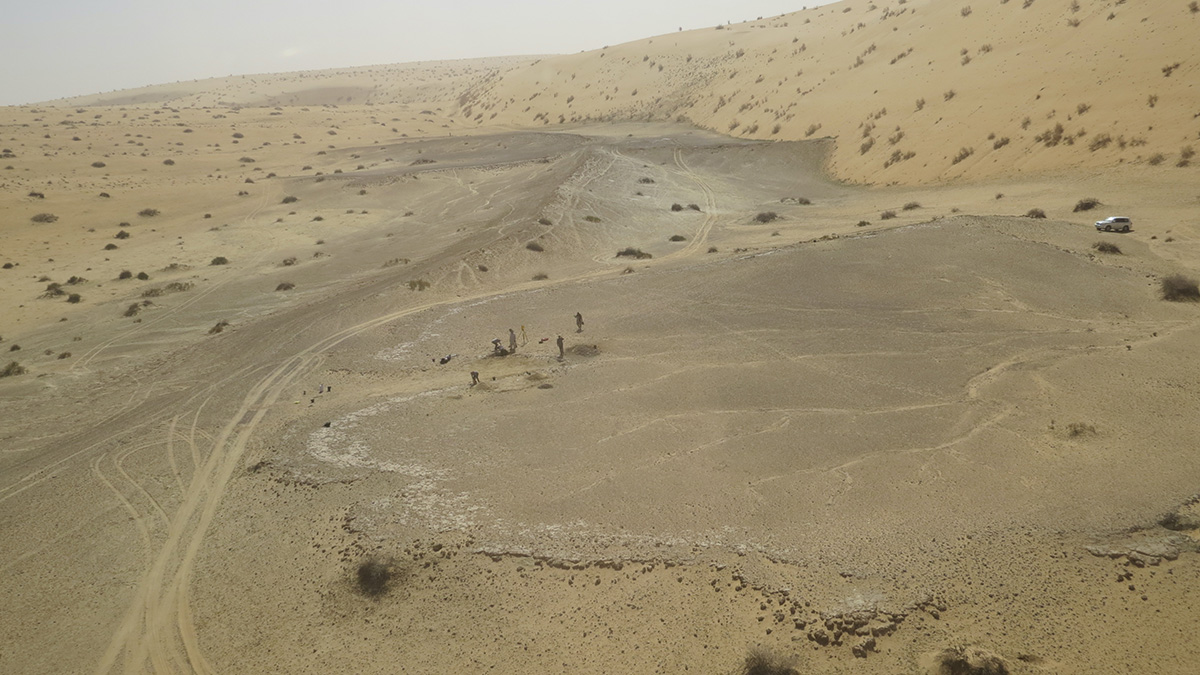
Greener, Wetter Arabia Was a Crossroads of Early Human Migration
Hand axes, hippo bones, and a stack of ancient lake beds show that arid Arabia experienced intervals of humid weather, spurring pulses of human migration over the past 400,000 years.
Desert Life Conjures Organic Carbon from Thin Air
Without water, photosynthesis shuts down. To survive dry spells, desert microbes scavenge traces of hydrogen from the air and burn it for energy. Some even use hydrogen to fuel carbon fixation.
A Reminder of a Desert’s Past, Before Dingo Removal
A fence spans Australia’s Strzelecki Desert, keeping dingoes out of the southern side. Drone and satellite technology have illustrated how removing this top predator changes vegetation growth.
Network Connects Indigenous Knowledges in the Arctic and U.S. Southwest
Indigenous Peoples from the Arctic and the U.S. Southwest have joined together to tackle issues of food sovereignty in two environmental extremes. Their bond led to a swift response to COVID-19.