These chemical oddities may explain why Earth seems to be deficient in certain elements—and could prove useful in catalysts and more.
fertilizer
Fungi, Fertilizer, and Feces Could Help Astronauts Grow Plants on the Moon
A new study offers tantalizing evidence that filamentous fungi extending from roots, along with treated astronaut waste, could provide sufficient scaffolding to help plants grow in planetary regolith.
Carbon-Nutrient Ratios Drive Nitrate Removal in Mediterranean Streams
The type of organic matter, and ratio of nutrients to carbon, impact the ability of heterotrophic bacteria to effectively remove certain forms of nitrogen pollution (nitrate) from streams.
How Soil Symbionts Could Unlock Climate-Smart Agriculture
By tracing the evolutionary history of beneficial soil microbes, scientists hope to unearth a sustainable solution for producing food to feed a growing global population.
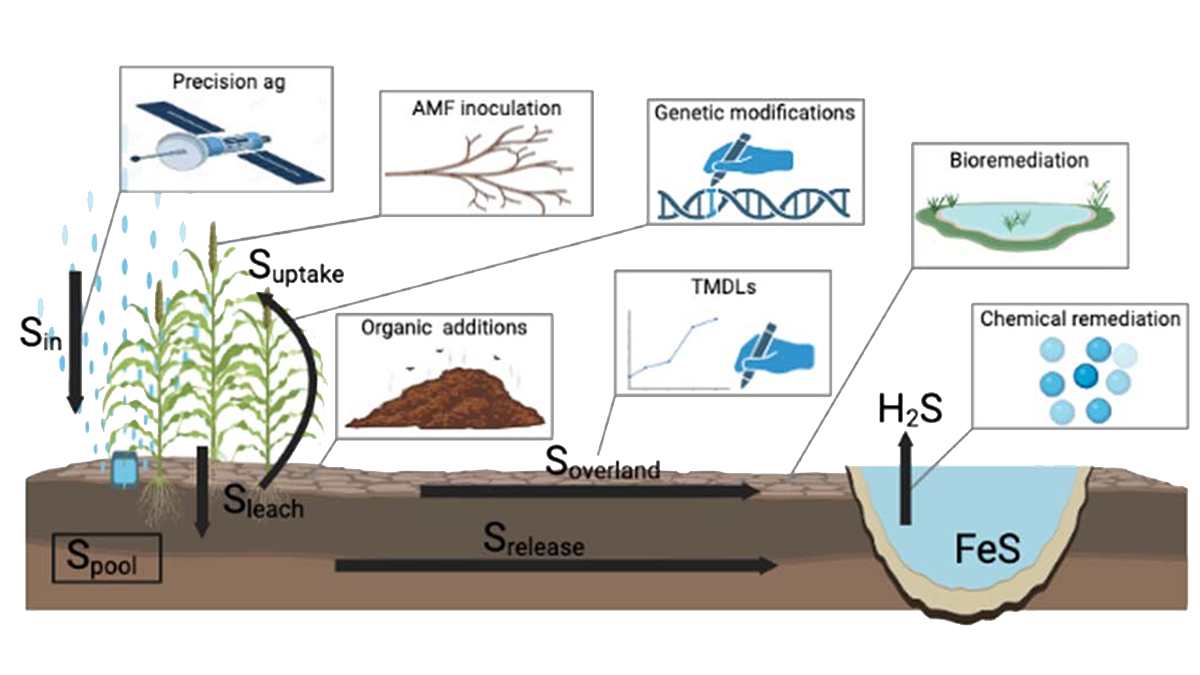
Sulfur is Demanding its Place in Crop Nutrient Budgeting
Scientists advocate for a more significant consideration of sulfur from a multidisciplinary perspective as a necessary step towards sustainable crop management.
Earth’s Critical Zone Remains a Mystery Without its People
Achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals may only be possible if human activities are central to critical zone science.
Wetlands on the Farm: Potent, Nutrient-Capturing Tools in (Relatively) Small Packages
Constructed wetlands can significantly reduce water pollution from tile-drained farms.
Traditional Fertilizers Beat Out Industrial Chemicals in Soil Health Test
New research in western India found that fertilizer based on Traditional Ecological Knowledge made soil more fertile in a head-to-head test with industrial fertilizers.
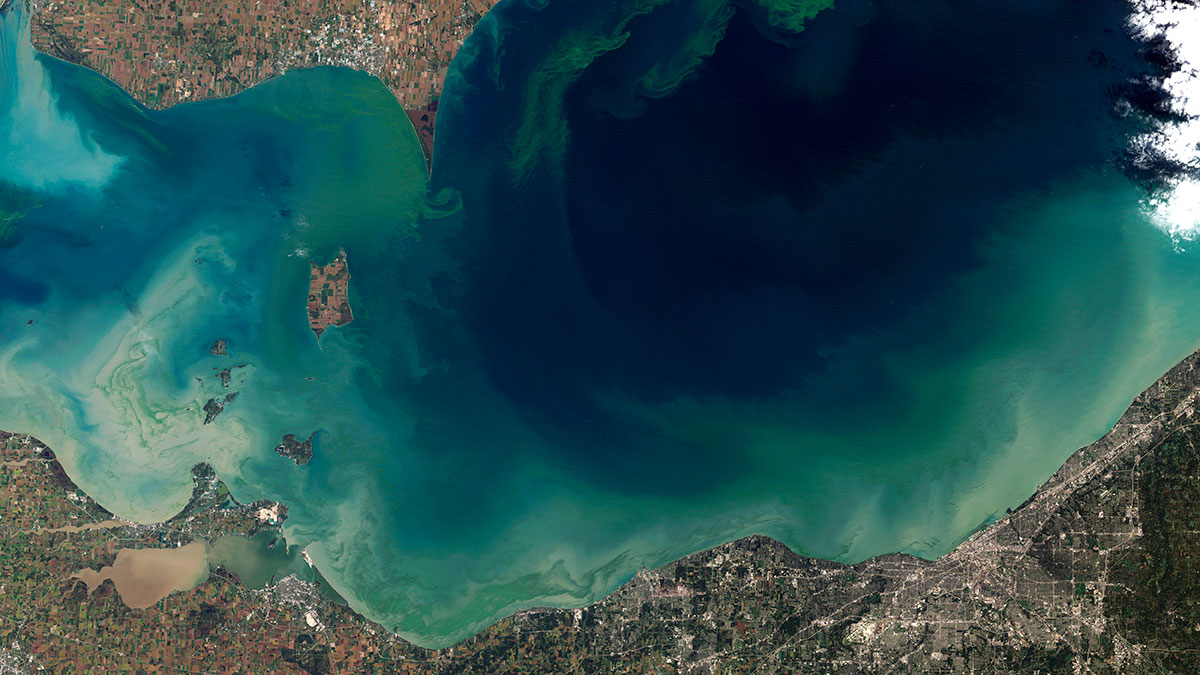
Cyanobacteria Blooms Exceed WHO Thresholds in Midwest Lakes
A study of 369 lakes across the Midwest finds that many of them, especially those close to agriculture, have high concentrations of harmful algal bloom-causing cyanobacteria.
Scientists Call for Policies to Buffer Agricultural Runoff
By reviewing 44 studies, researchers make a scientific case for regulating agricultural pollution of streams and rivers by implementing conservation practices, including riparian buffer zones.