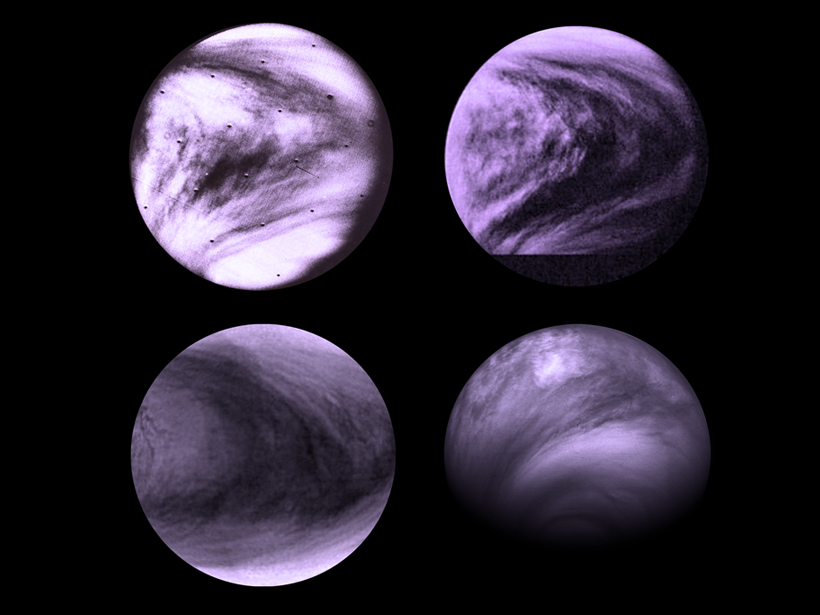
A novel model suggests that a new wave may be responsible for Venus's iconic Y pattern.
Geophysical Research Letters
Ocean Lightning Storms Are Larger Than Land Lightning Storms
A new study uses data from the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission to demonstrate that electrified storms in the tropics are 10 times larger over the ocean than those over land.
Seismic Signals Reveal Changes in Water Release from Glaciers
Seismometers could help scientists monitor elusive fluctuations in water discharge from glaciers that flow into the ocean.
Atmospheric Waves Help Cool Our Planet
A new method makes a direct estimate of the impact of atmospheric waves on water vapor concentrations in the stratosphere.
Near-Surface Aquifer Discovered on Svalbard Glacier
Arctic glacier aquifer may respond more rapidly to climate change than larger aquifers found on the Greenland ice sheet.
Magnetized Collisionless Shock Waves Measured in the Lab
Scientists create collisionless shock waves to better understand the phenomenon in nature.
New Insights into the Composition of Inner Earth
Isotopic signatures in volcanic basalts show that Earth's interior is even less uniform than scientists previously thought.
A Magmatic Seafloor Source at an Ultraslow-Spreading Ridge
An ultraslow-spreading stretch of the Southwest Indian Ridge is thicker than expected: both tectonic and volcanic processes may be feeding the growing seafloor there.
Spacecraft Records Rising-Tone Magnetosonic Waves
A rising tone in wave frequencies suggests a complicated, nonlinear series of interactions between electromagnetic sound waves and protons near the magnetic equator.
Cool Downdrafts in Large Thunderstorms Captured by Satellite
Orbiting scatterometers can reveal patterns of cool air in mesoscale convective systems.