Scientists are using new computational tools to analyze troves of old spacecraft data to better understand one of Mercury’s unsolved mysteries.
Mercury
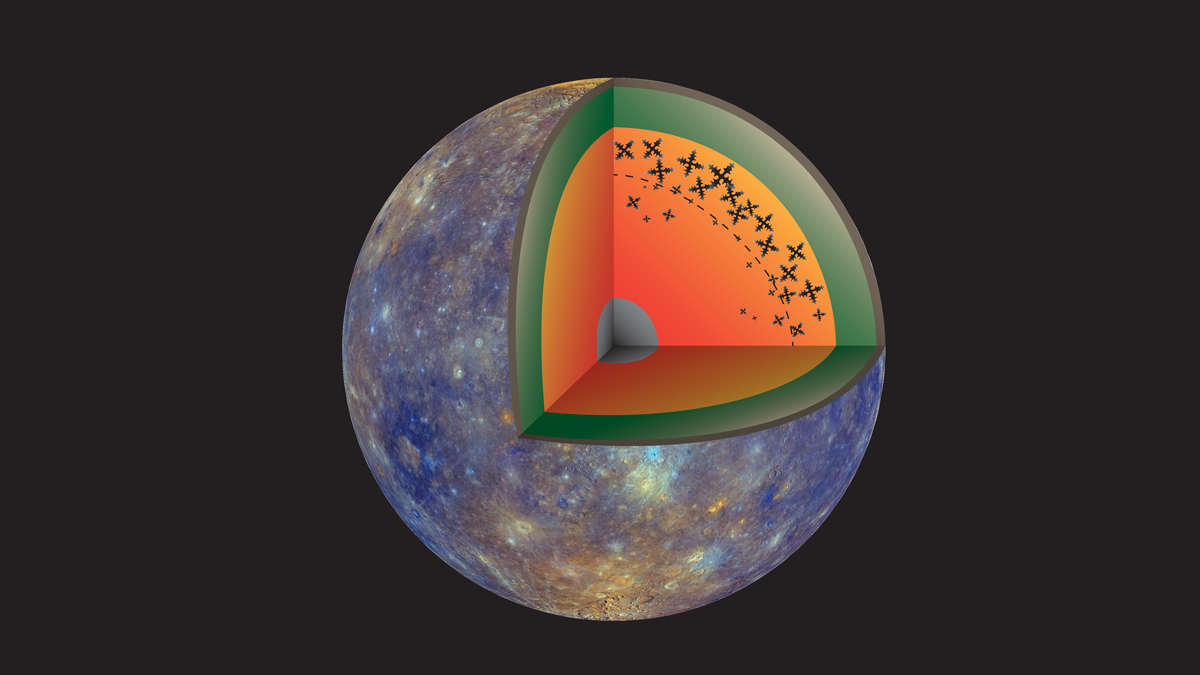
How Much Has Mercury Shrunk?
Mercury is still shrinking as it cools in the aftermath of its formation; new research narrows down estimates of just how much it has contracted.
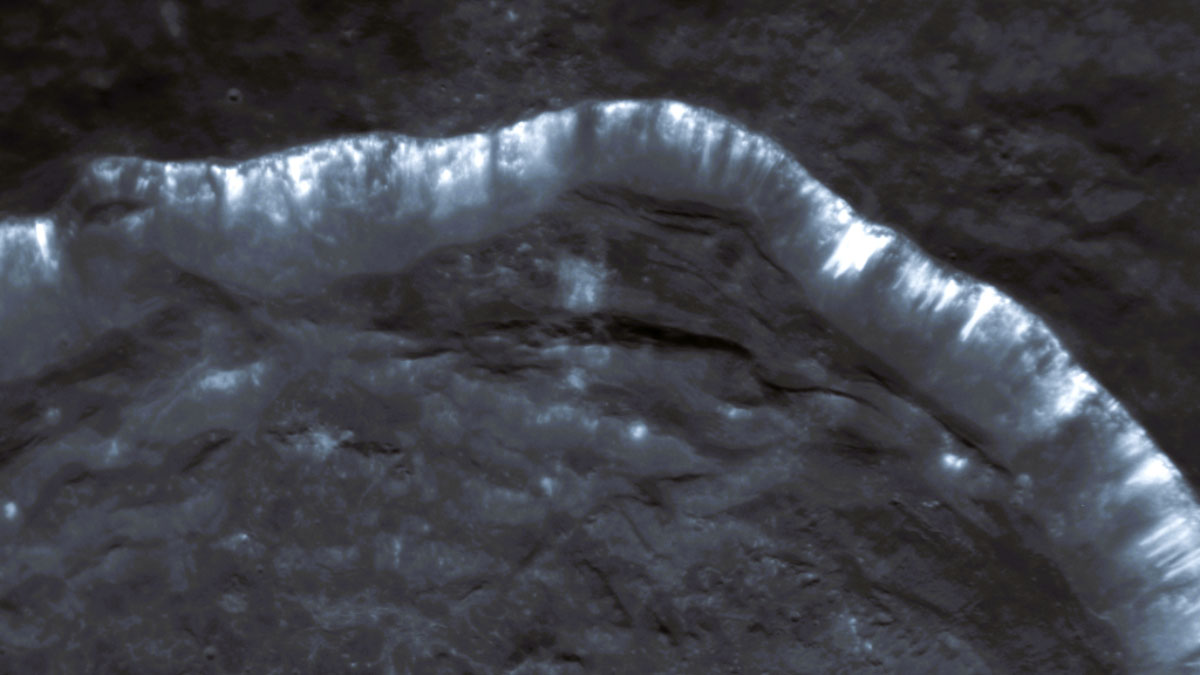
Mercury’s Hollows may be Young and Active
The first machine learning-derived global-scale survey of Mercury’s hollows suggests they are young features that may be active and will continue to evolve.
Iron Snow Ebb and Flow May Cause Magnetic Fields to Come and Go
Lab experiments find that iron crystals in planetary cores may form in bursts, causing periodic dynamos.
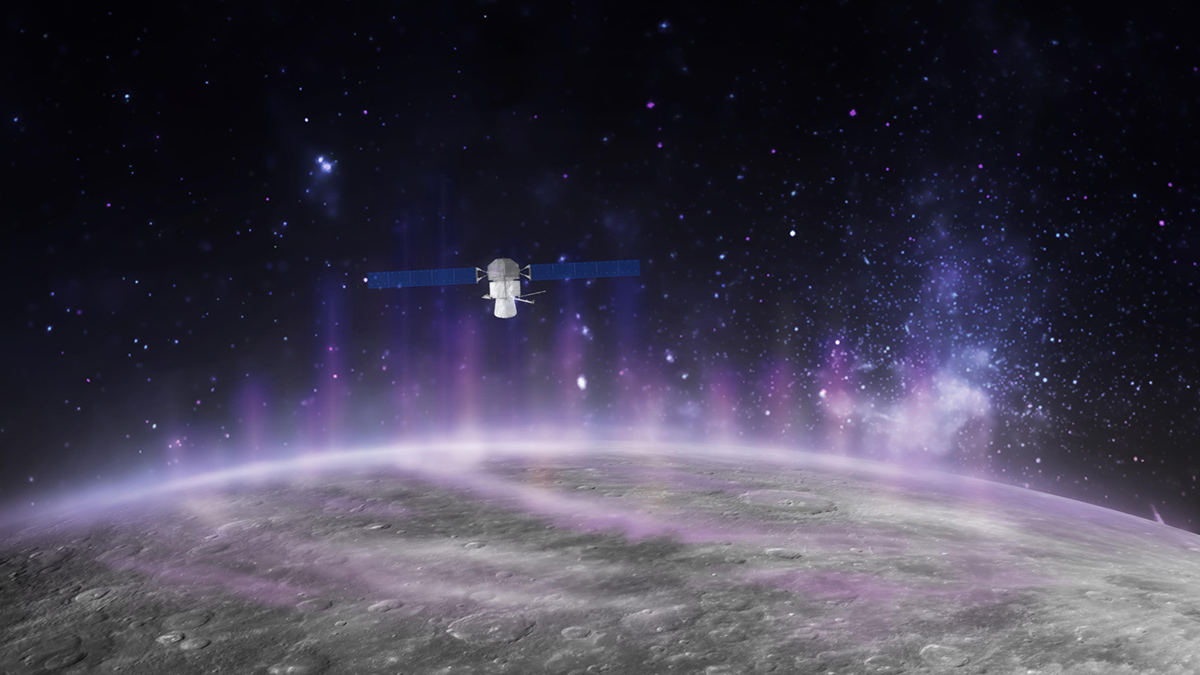
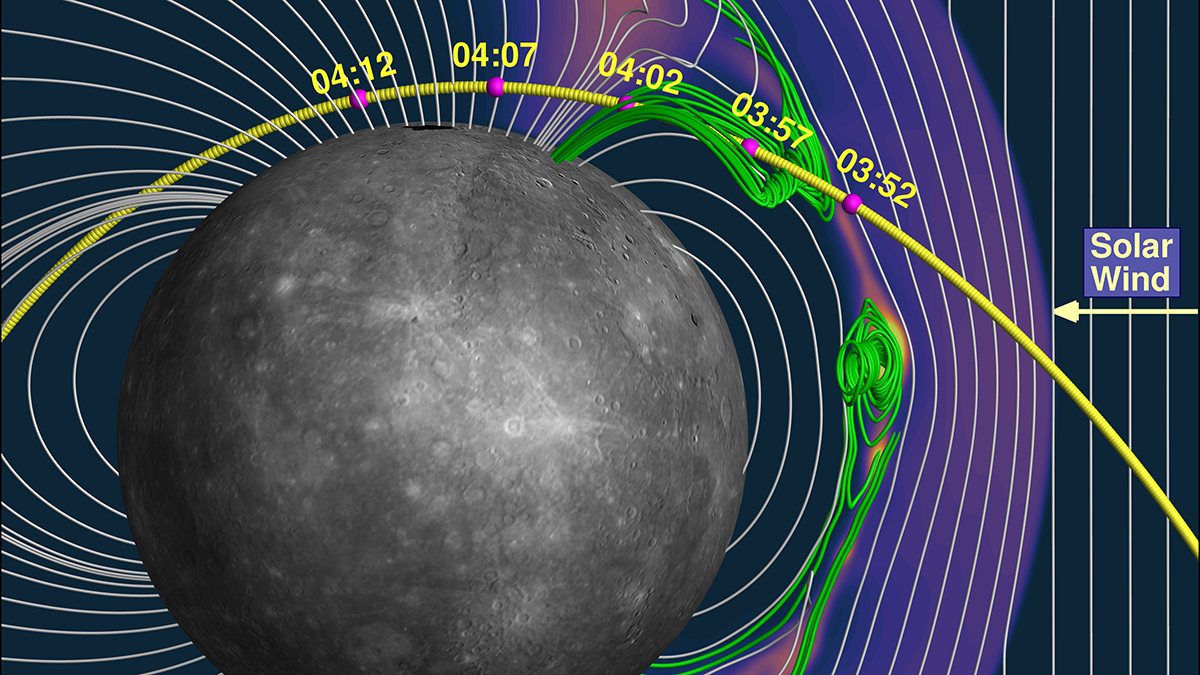
Dramatic Flyby Confirms That Mercury’s Radioactive Aurora Touches the Ground
Data collected by the BepiColombo spacecraft traces the causes of the strange aurora, which course through the planet’s weak magnetosphere.
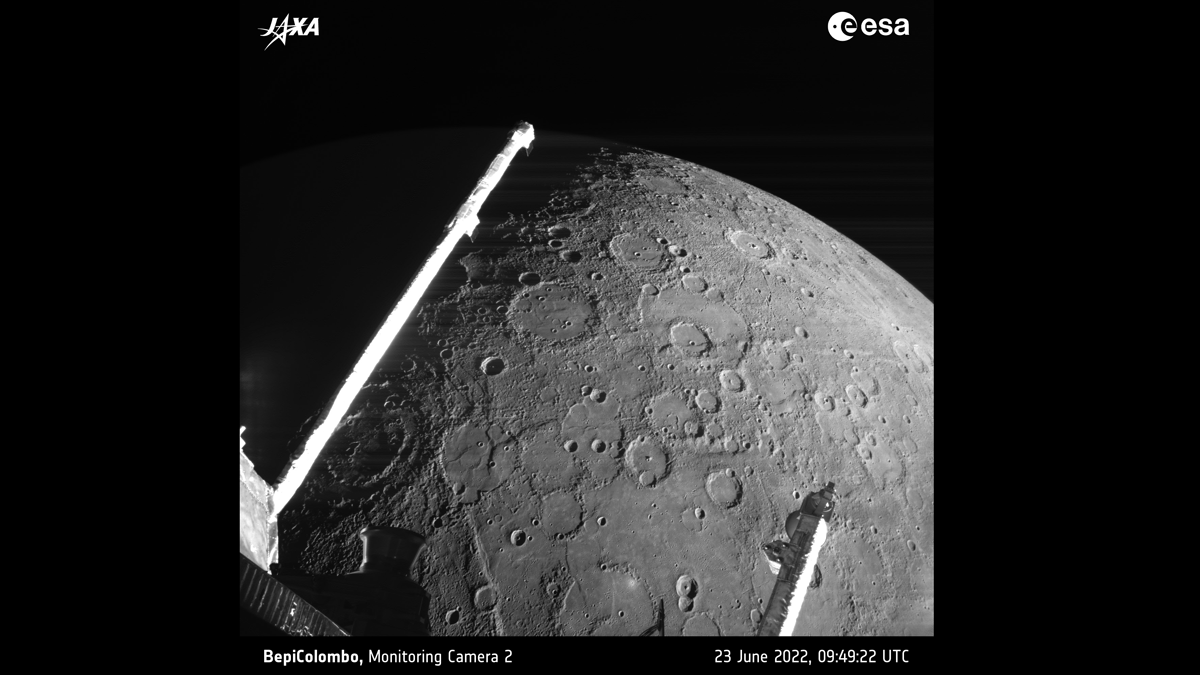
Spacecraft to Swing Past Mercury for Third Time
With each flyby, the BepiColombo mission gets another boost of energy for its eventual orbital insertion around Mercury.
Mercury Isn’t Alone in Orbit, and Scientists Don’t Know Why
A cloud of dust traces the innermost planet’s orbital path. By all accounts, it shouldn’t be there.
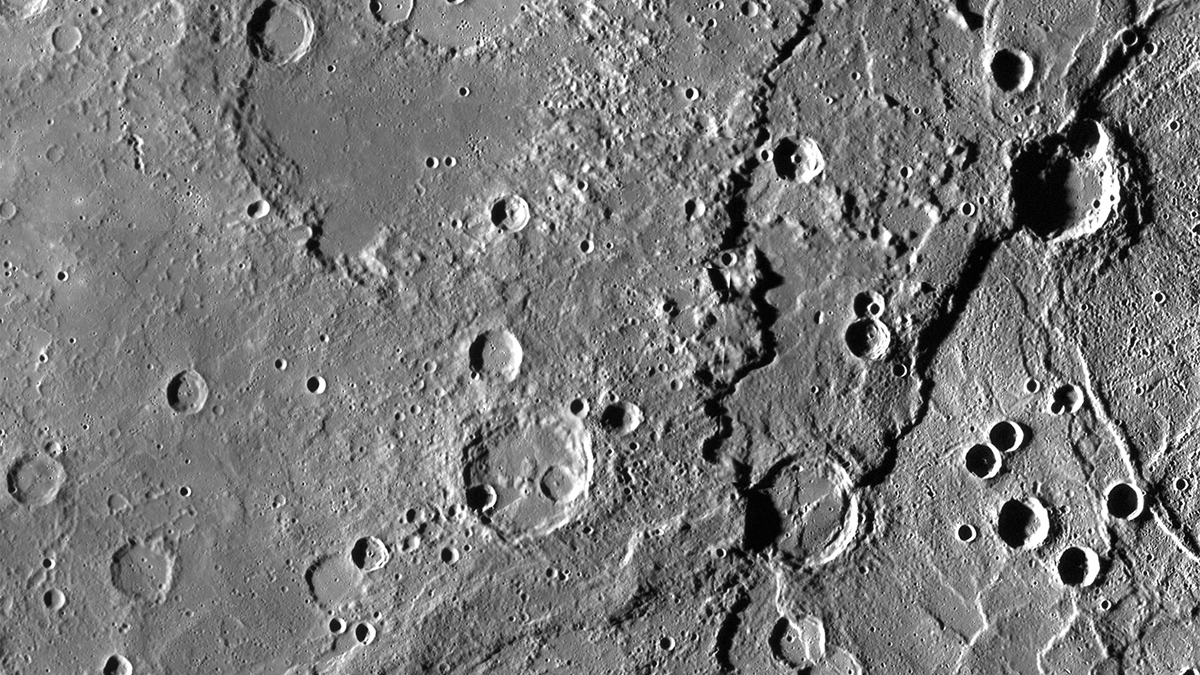
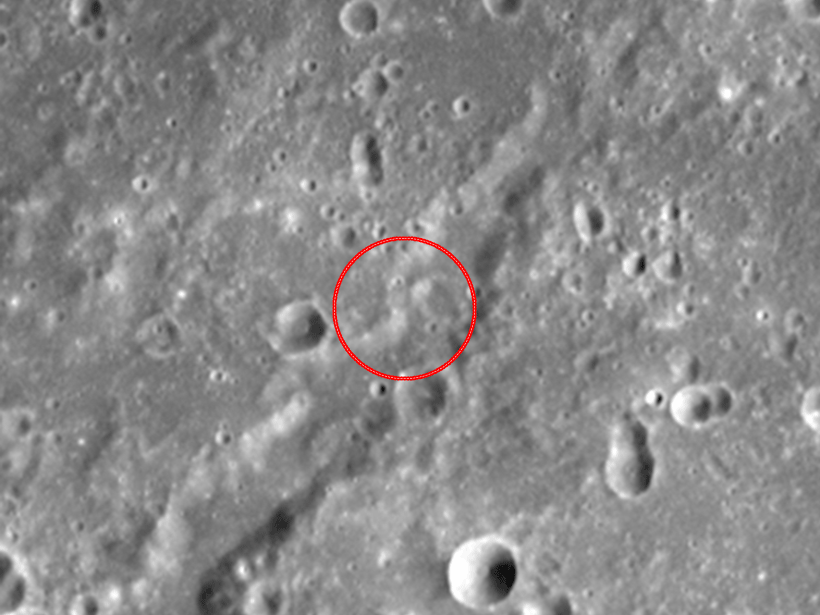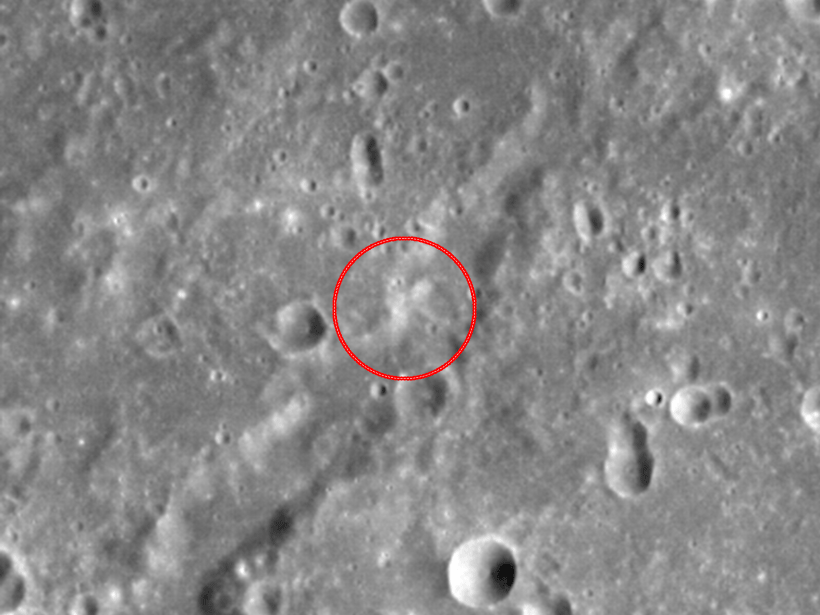
MESSENGER Reveals a More Dynamic Mercury Surface
Image pairs indicate that 99% of the planet’s surface could be altered in the next 25 million years.
Solar Wind a Major Driver of Atmospheric Sodium at Mercury
MESSENGER observations show a 50% rise in atmospheric sodium-group ions during periods of high solar wind activity.
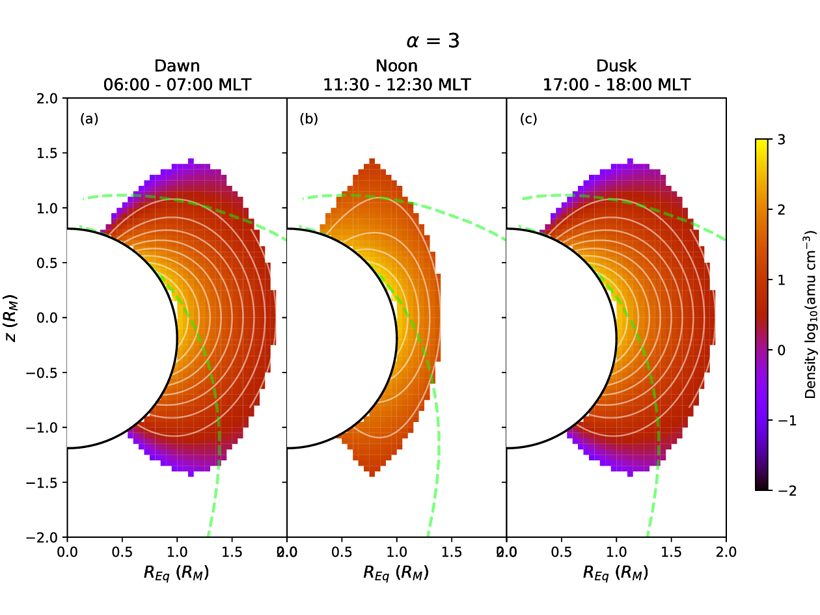
Plasma Density Distribution in Mercury’s Magnetosphere
A new measurement of plasma density distribution in Mercury’s magnetosphere obtained from observations of field line resonance events provides necessary constraint for many planetary science issues.