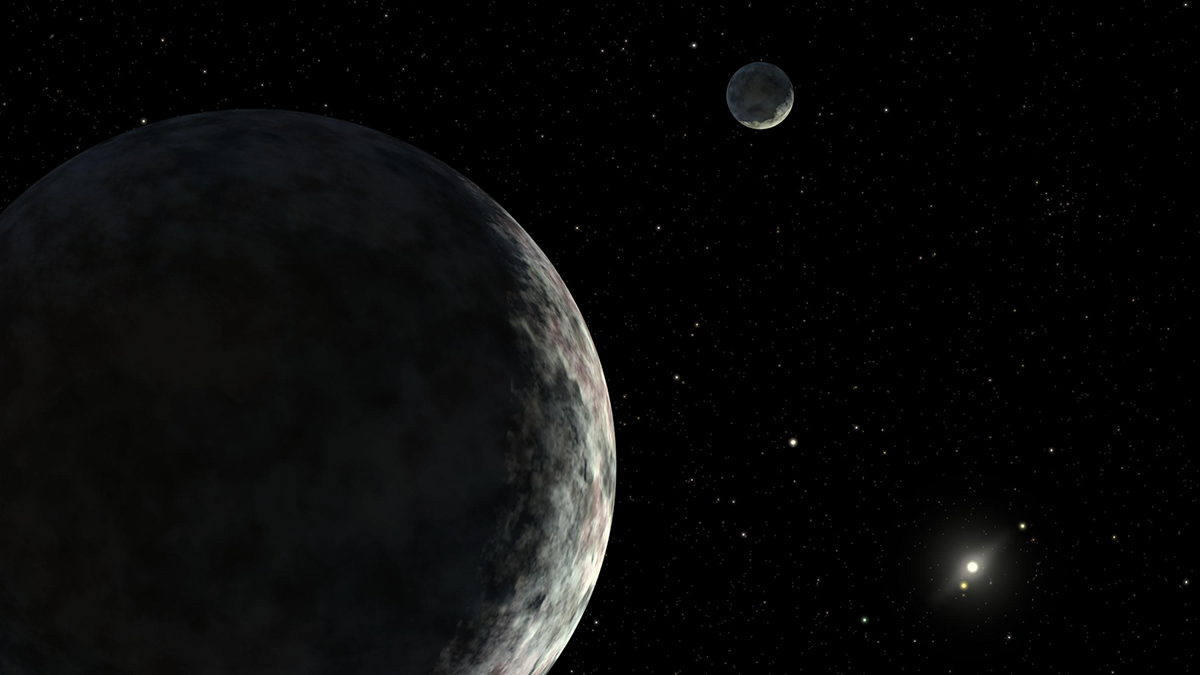
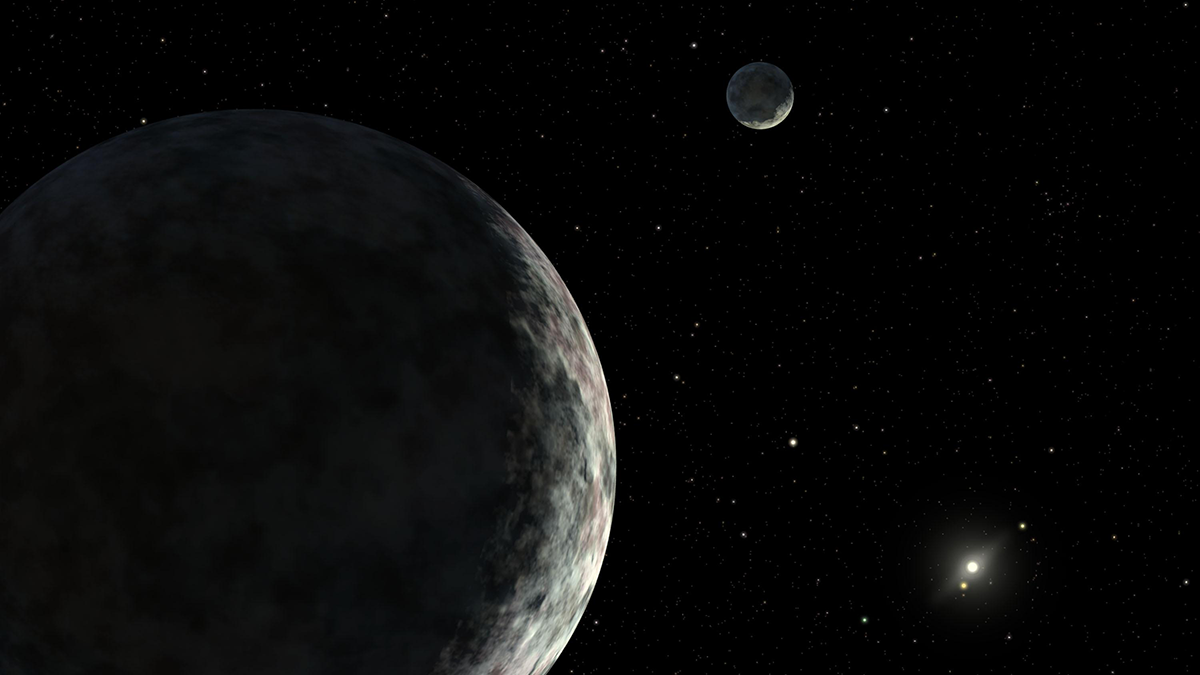
Los grandes cuerpos del Cinturón de Kuiper y más allá podrían haber albergardo océanos en la subsuperficiales.
methane
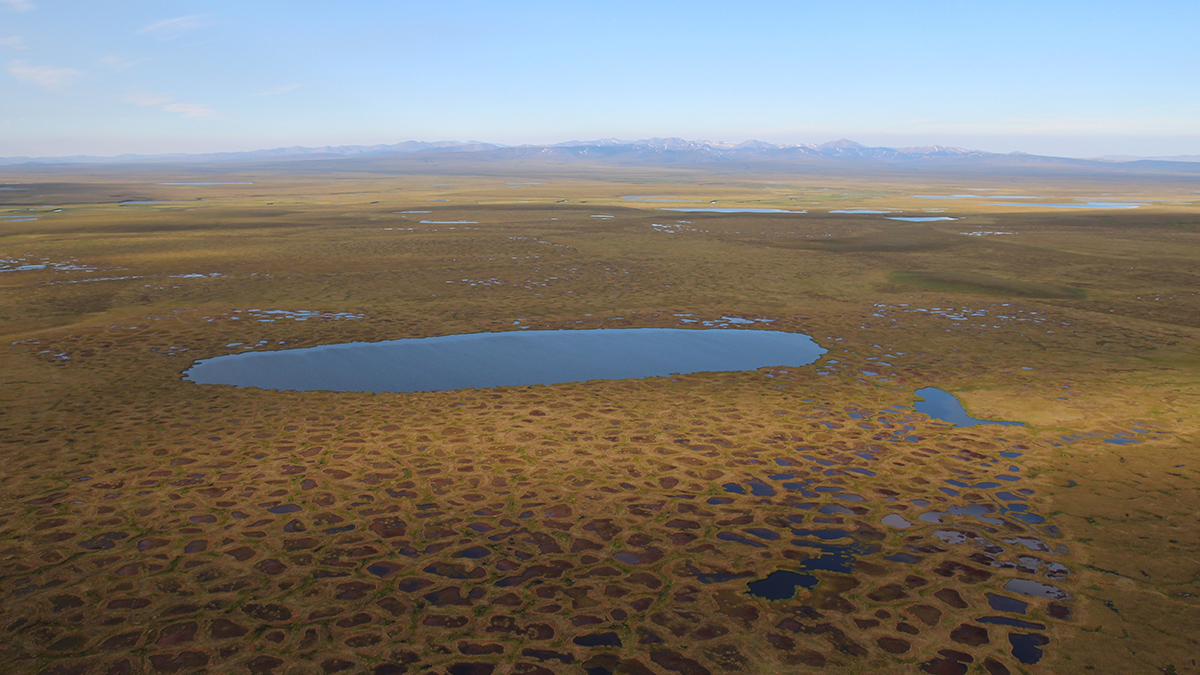
Northern Permafrost Region Emits More Greenhouse Gases Than It Captures
Permafrost underlies a quarter of the Northern Hemisphere. A comprehensive analysis shows that the area may have shifted from a sink to a source of greenhouse gases, bringing a longtime prediction to fruition.
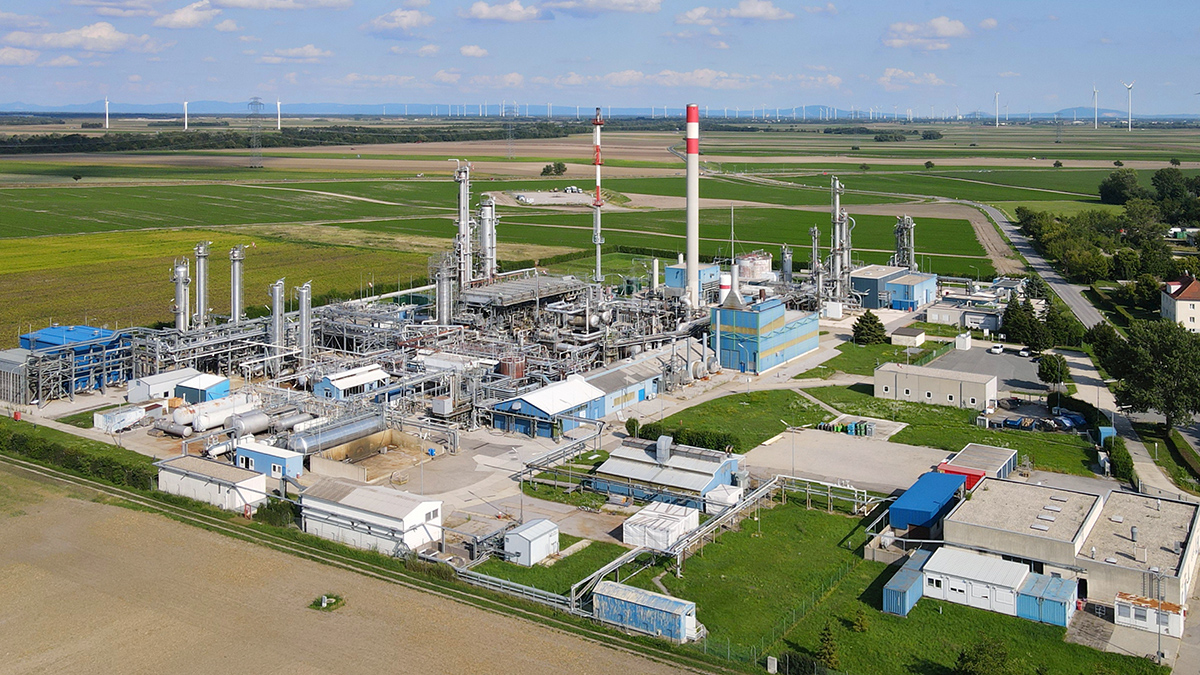
Methane Emissions from the Oil and Gas Industry Are Triple Current Estimates
A new study using aerial data reveals that fossil fuel extraction and processing are responsible for far more methane than previously believed.
When You’re a Wet(land), You’re A Wet(land) All the Way
Wetlands and their methane emissions require careful consideration for incorporation in Earth system models with many advances made over the past 30 years.
Salty Soil May Release Methane on Mars
Through roving and drilling, Mars Curiosity Rover may be breaking up the ground’s salty, hardened soils that seal methane, possibly causing a temporal, local methane spike.
Dwarf Planets Show Evidence of Recent Geologic Activity
Large bodies in the Kuiper Belt and beyond could have hosted subsurface oceans.
Planting Trees May Not Be as Good for the Climate as Previously Believed
The climate benefits of trees storing carbon dioxide is partially offset by dark forests’ absorption of more heat from the Sun, and compounds they release that slow the destruction of methane in the atmosphere.
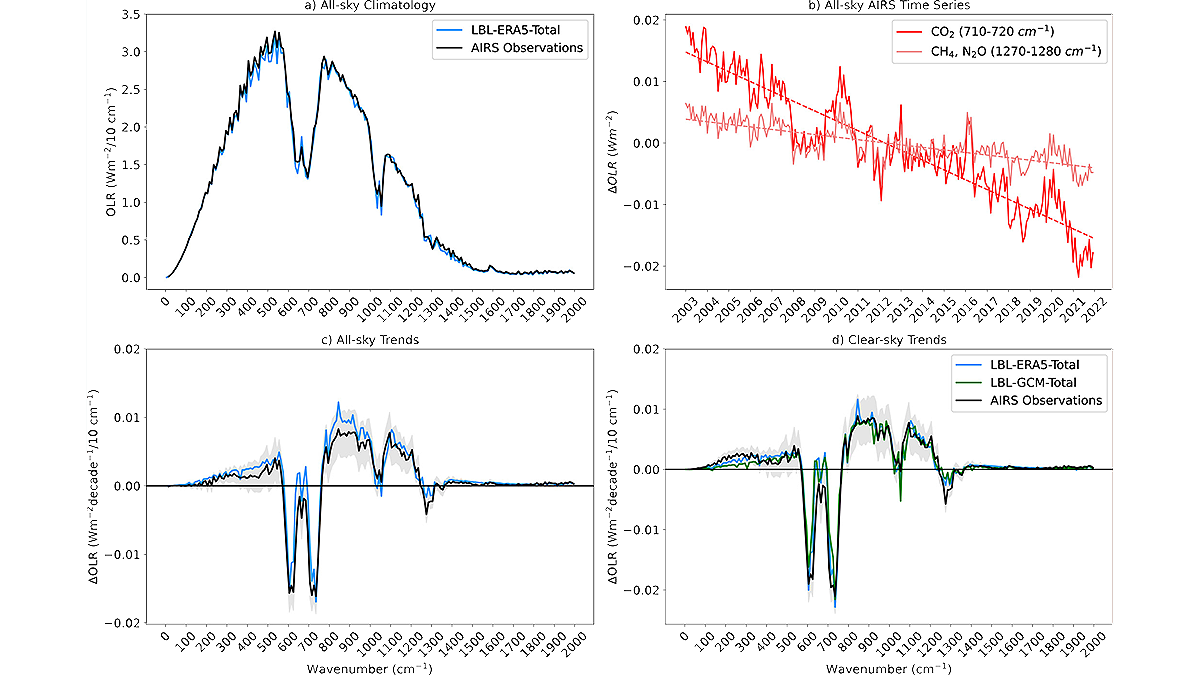
Using Satellite Observations for Attribution of Radiation Changes
Analysis of infrared satellite measurements identifies the climate response to an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Researchers Compare Observations Versus Modeling of Coastal Carbon Cycle
While storing carbon dioxide, the coastal ocean also releases methane and nitrous oxide. New research shows that understanding the impact of coastal oceans on climate requires more research into these fluxes and how they counteract each other.