Humid heat extremes are less frequently studied, but no less important, than those of dry heat.
Middle East
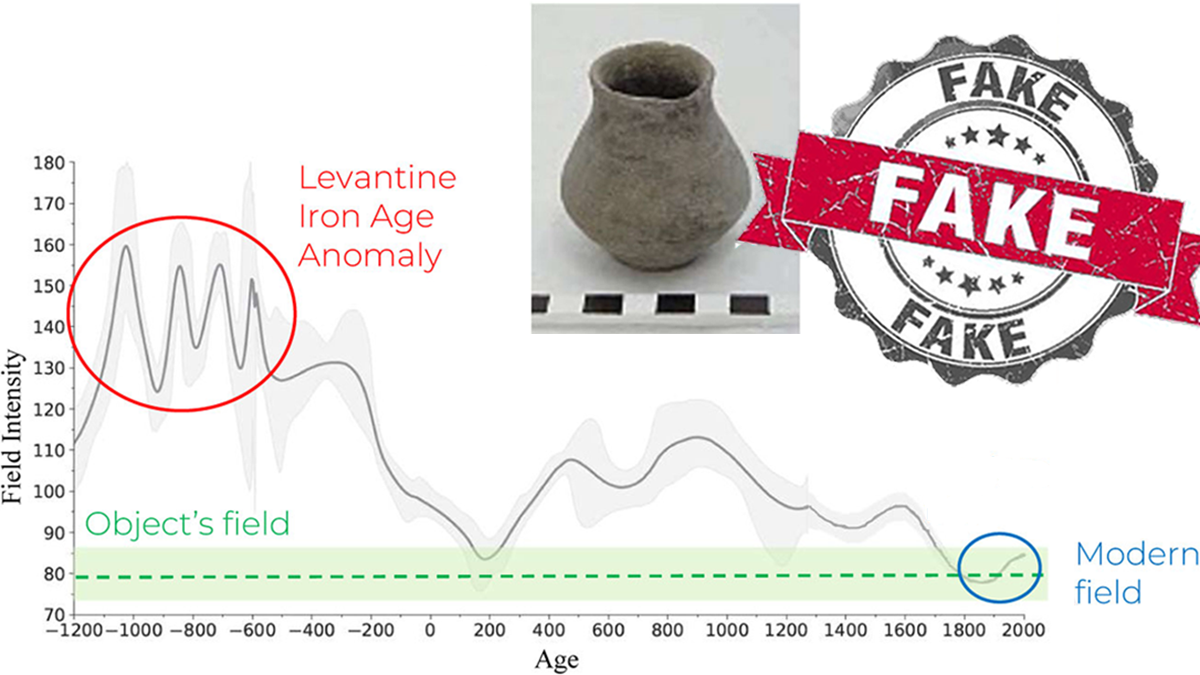
Credible or Counterfeit: How Paleomagnetism Can Help Archaeologists Find Frauds
Duplicating artifacts that preserve records from biblical times is a lucrative business. A method used for both dating artifacts and reconstructing Earth’s history could identify phony pieces.
The Middle East’s First Comprehensive Carbon Budget
The first greenhouse gas budget for Central and West Asia—24 countries, including Yemen, Türkiye, Kazakhstan, and Afghanistan—was just published.
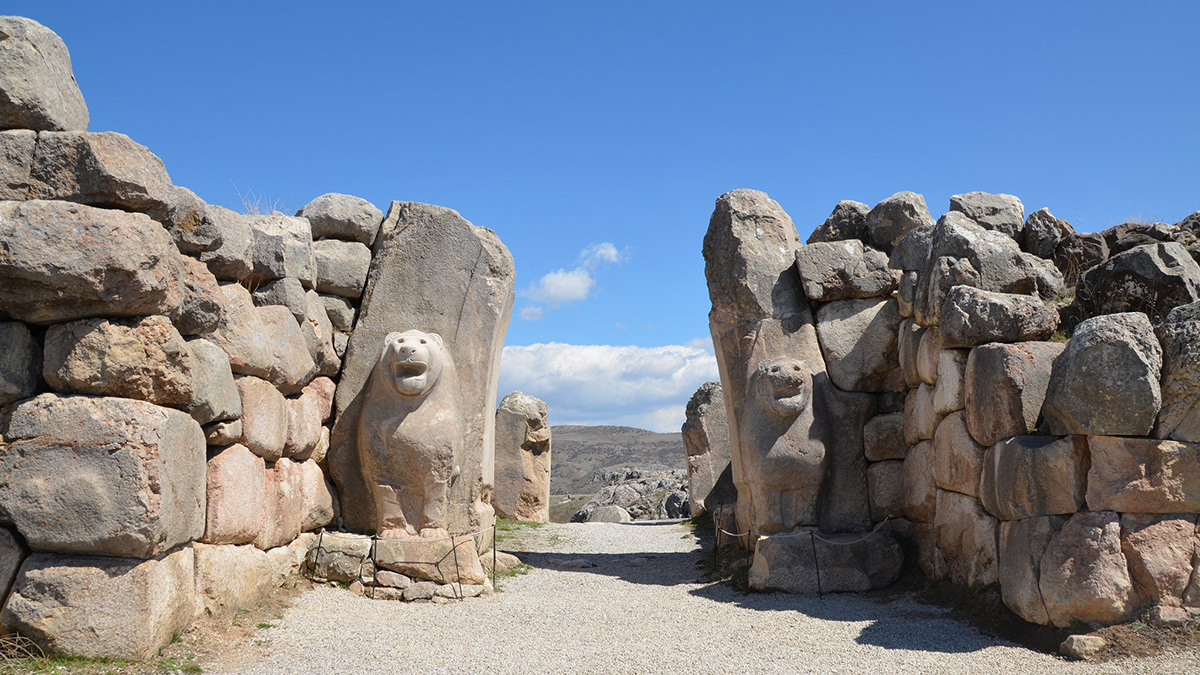
Tree Rings Hint at the Fall of the Hittite Empire
The Bronze Age civilization adapted to changes in climate but suffered during a prolonged crisis.
Bacteria Travel Thousands of Kilometers on Airborne Dust
As winds pick up dirt and sand, they also pick up any microbes adhering to those particles, potentially introducing them to new locations.
Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East Face Rapid Climate Change
Observational and modeling studies identify the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East as a prominent climate change hotspot associated with weather extremes that have major impacts on society.
Radiometric Dating Sheds Light on Tectonic Debate
The emplacement of the Samail Ophiolite in Oman has been a source of disagreement among geologists. New state-of-the-art research offers a fresh perspective on its timing and geometry.
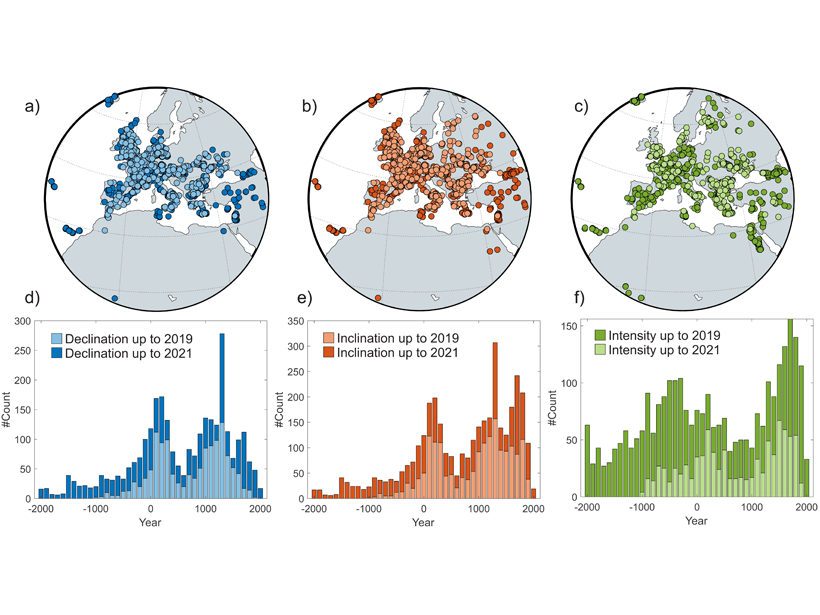
New Spherical Cap Field Model for Europe and Direct Environs
New data on ancient burnt structures is integrated into a superior spherical cap field model for Europe.
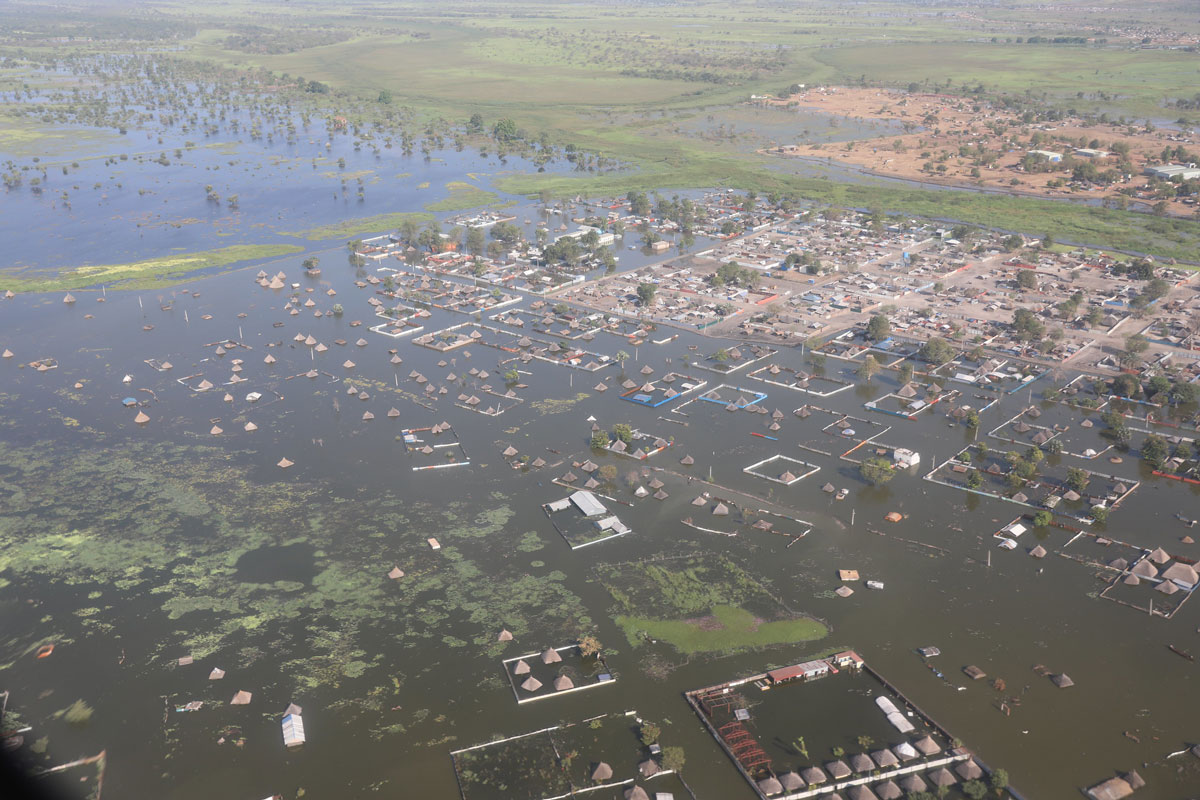
What Causes Flash Floods in the Middle East?
Researchers zero in on the large-scale meteorological processes driving extreme precipitation events in the hot, arid desert region.
Reduced Middle East Air Pollution Linked to Societal Disruption
Invasions, armed conflict, sanctions, and economic distress correlate with cleaner air in high-resolution satellite data that reveal air quality at the individual city level.