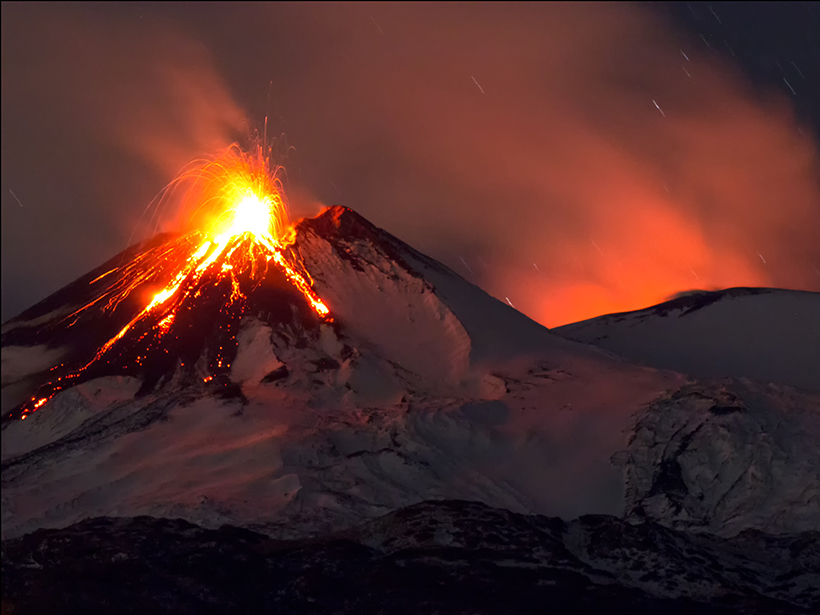
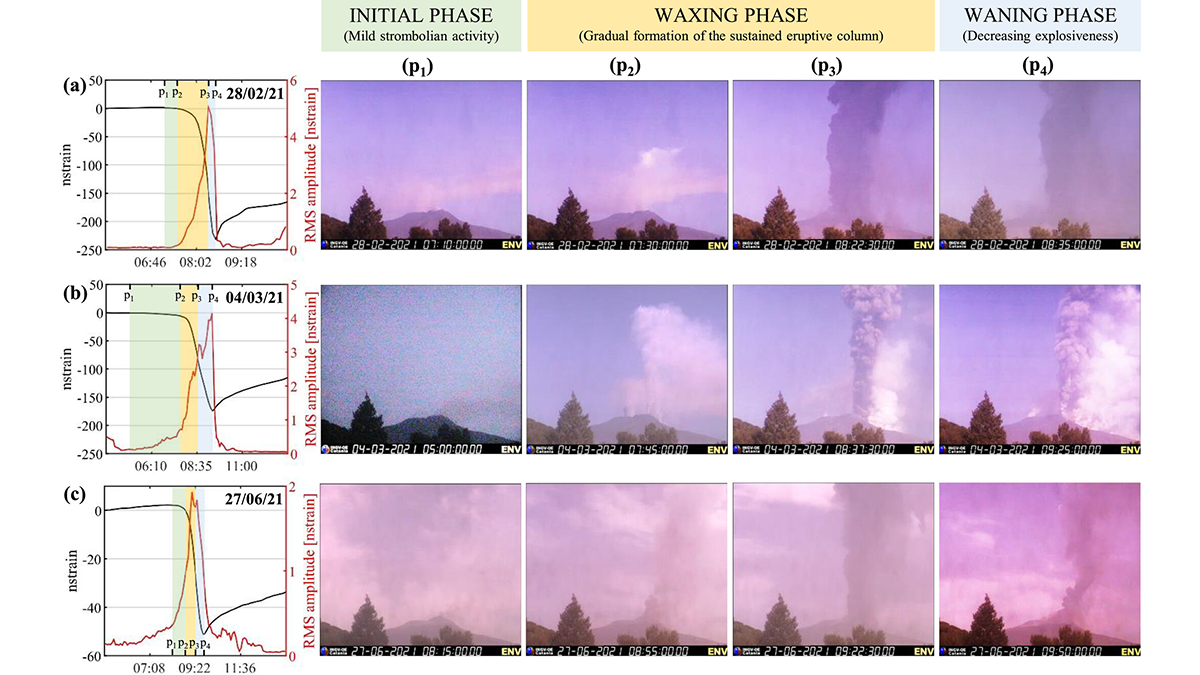
Scientists use over a decade of high-resolution data to demonstrate that strain signals provide a better match to eruptive style than seismic tremors.
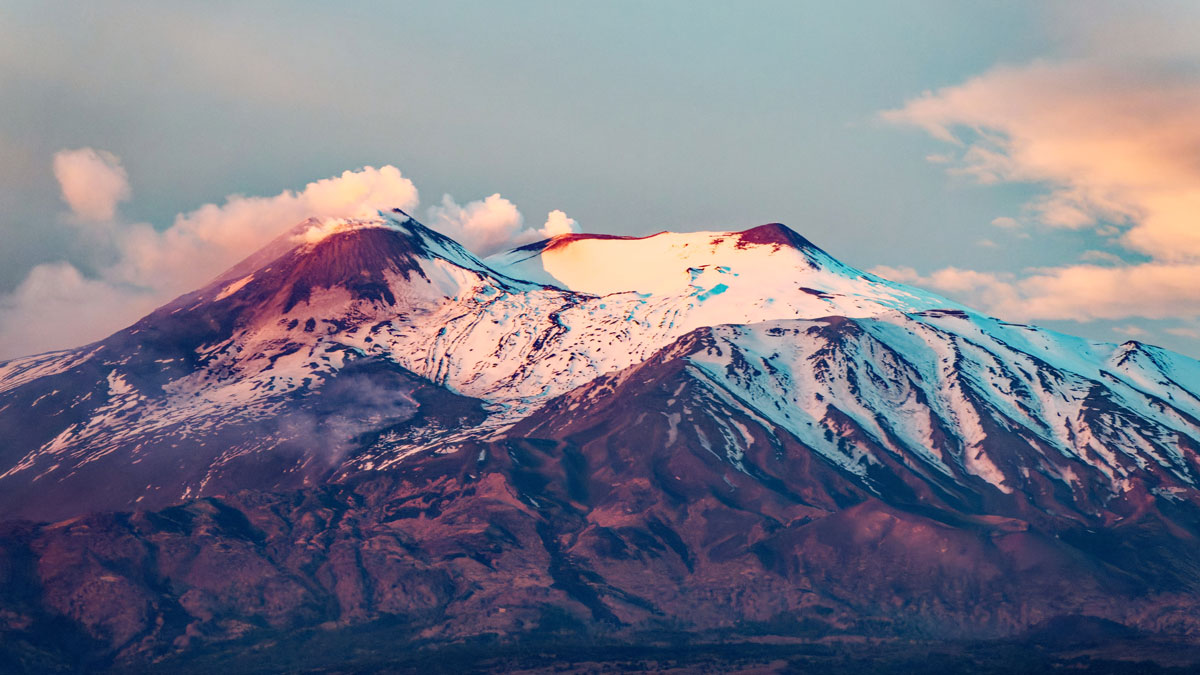
Mount Etna
Improved Imaging Offers New Insight into Mount Etna
Anisotropic tomography provides a more complete picture of the Sicilian volcano’s inner workings.
Supergreen Trees Can Signal Sites of Eruptions
Tree core chemistry can explain what happened before Mount Etna’s 2002 eruption and suggests that trees could play a role in rebuilding past eruptions.
Etna Under Pressure: Does Gas Buildup Foreshadow Eruption?
Pressure from both magma and gas can trigger eruptions. Monitoring degassing can help predict eruptions but only if the magma system is well understood first.
Volcano—Tectonic Interactions at Etna
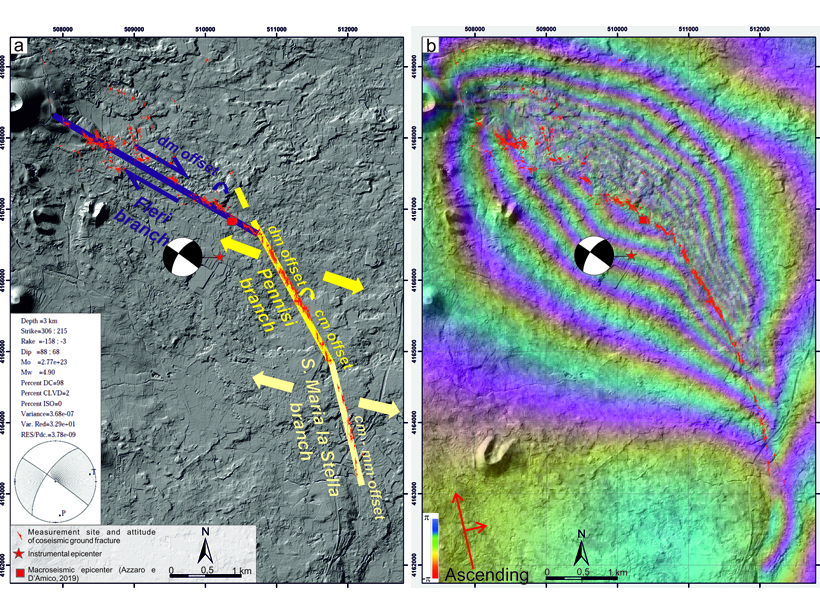
Mapping of a 2018 earthquake that ruptured the eastern flank of Mount Etna shows that it occurred on a tectonic lineament that predates the volcano, and the kinematics match nearby tectonic domains.
Radon Enrichment in the Volcanic Plume of Mount Etna
More than 70 passive sensors on Mount Etna have captured the first radon measurements in volcanic plumes and show that radon could affect people around volcanoes.
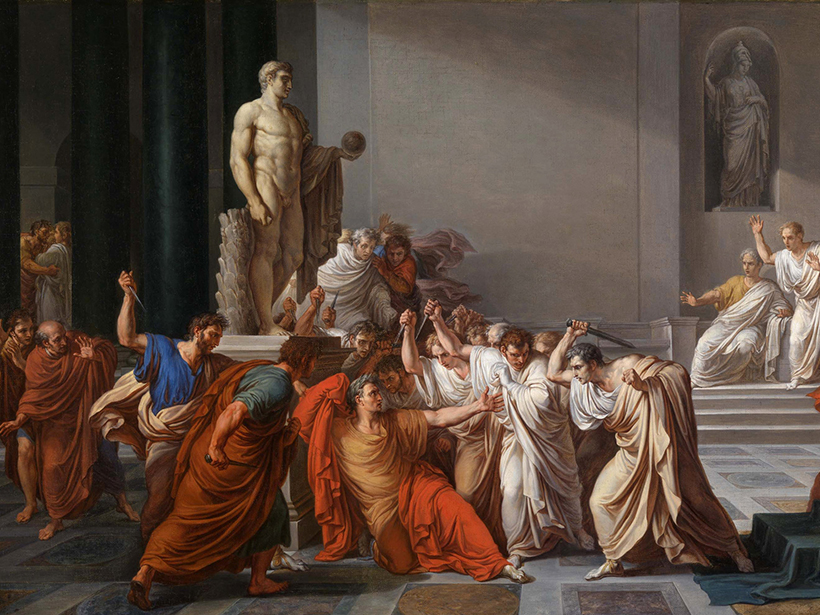
Podcast: Et Tu, Etna?
Global environmental calamity followed the death of Caesar. The source may have been a volcano in Sicily.
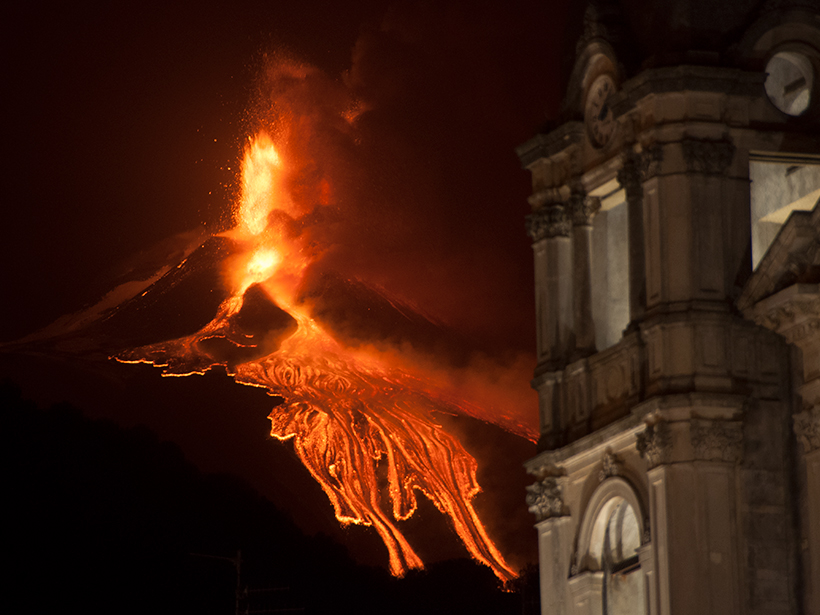
Radon Tells Unexpected Tales of Mount Etna’s Unrest
Readings from a sensor for the radioactive gas near summit craters of the Italian volcano reveal signatures of such processes as seismic rock fracturing and sloshing of groundwater and other fluids.
An Improved Model of How Magma Moves Through the Crust
Researchers have developed a new numerical model that can, for the first time, solve for both the speed and the path of a propagating dike.
Understanding Volcanic Eruptions Where Plates Meet
A new project elucidates the relationships between tectonics and volcanic systems and how they influence hazards on Italy's Mount Etna and Vulcano and Lipari islands.