Using a sophisticated global climate model adapted to Mars, space scientists explore the hidden potential of wind energy on the Red Planet.
NASA
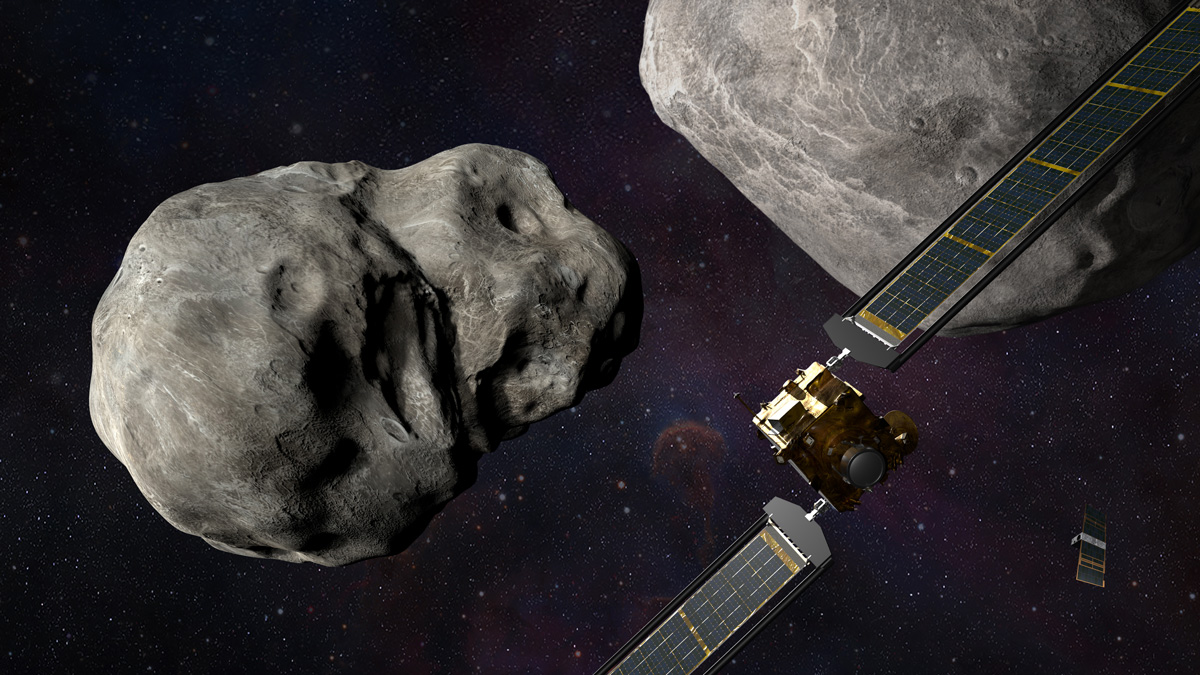
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test Is a Smashing Success
The mission, focused on the Didymos-Dimorphos binary asteroid system, proved that an asteroid’s orbit can be altered by kinetic impactor technology.
First in Line to Track Blue Water From Space
“Blue water” is the water in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. A new NASA mission will track blue water levels globally at least once a month. Early Adopters are eager and ready to use the data!
New Crowdsourced Science Project Will Study Sprites
The NASA-funded project is asking sky gazers, storm chasers, and scientists to capture photos of sprites and other optical phenomena that flash above thunderclouds after a lightning strike.
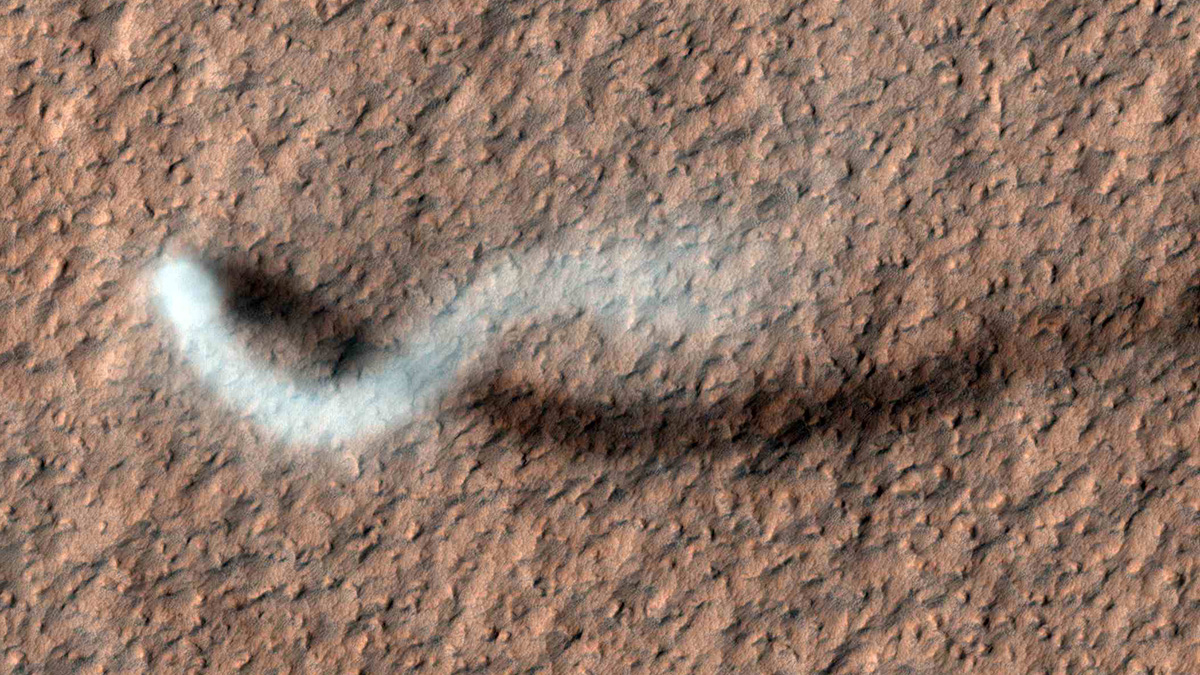
NASA’s Perseverance Rover Records the First Sounds of a Dust Devil on Mars
In a stroke of luck, the SuperCam microphone on Perseverance was turned on the moment a dust devil swept directly over the rover.
If There Is Phosphine on Venus, There Isn’t Much
New observations of the Venusian atmosphere collected from an airborne observatory showed no sign of the potential biosignature gas, casting additional doubt on a previous report of its detection.
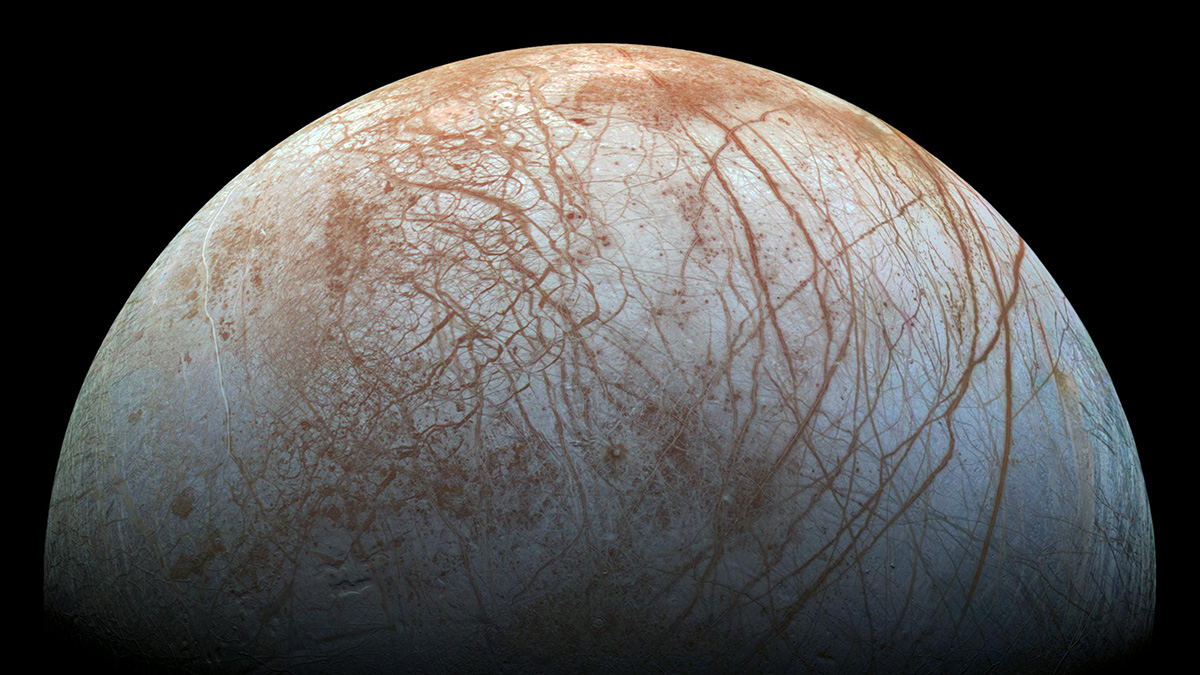
Europa’s Plate Tectonic Activity Is Unlike Earth’s
The moon of Jupiter has likely experienced intermittent, regional plate tectonic activity in the past, although the plates are currently dormant.
Powerful Impact Provides Insight into Deep Structure of Mars
Seismic signals detected by the InSight lander show that the planet’s lower mantle may be less homogenous than previous models have suggested.
Zipping Up Data to Zap Them Back from an Icy Moon
NASA wants to send instruments to distant moons like Europa and Enceladus to search for life. But getting vital data back to Earth over limited bandwidth will take some impressive compression software.
Optimizing Competing Instrument Needs with an Objective Metric
Intrinsic dimensionality can quantify the level of information obtainable for various possible instrument configurations.