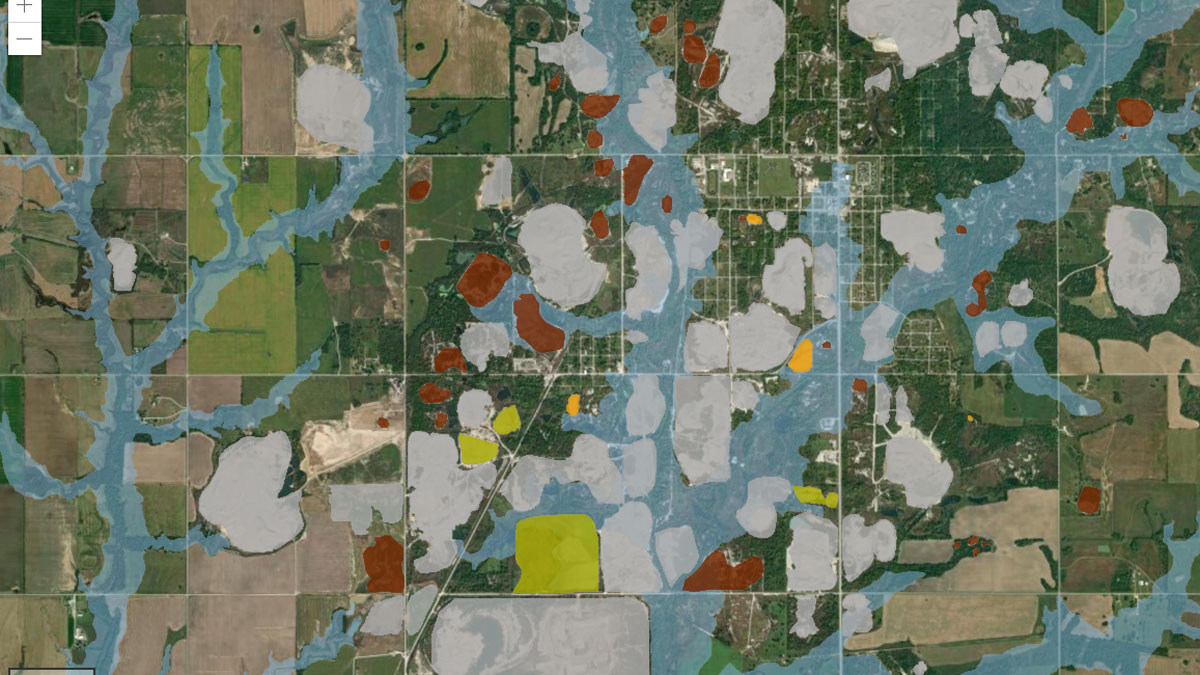
A new study highlights the partnership between scientists and nonscientist community members in building an interactive GIS map to show flooding risk in a Superfund site.
Oklahoma
Gigantic Jet of Lightning Mapped over Oklahoma
The most powerful gigantic jet ever recorded fortuitously appeared over a sensor array in Oklahoma, enabling scientists to map the structure of the phenomenon for the first time.
Lauren Haygood: Normalizing STEM in America’s Heartland
Community science builds bridges while generating valuable environmental data.
Understanding Earthquakes Triggered by Wastewater Injection
A deep dive into a 2015 Oklahoma earthquake reveals new insights into the dynamics of quakes induced by wastewater injection, and could help inform future earthquake hazard modeling.
Community Input Drives Superfund Research
Researchers identified geochemical tracers for lead and investigated Oklahomans’ concerns at the Tar Creek Superfund site.
Soil Moisture Drives Great Plains Cloud Formation
A new study shows that models that reproduce moisture on land are better at accurately recreating cumulus cloud behavior.
Sinking Wastewater Triggers Deeper, Stronger Earthquakes
The effects of pumping wastewater from oil and gas extractions may last a decade or more after the injections stop.
Forecasting Seismicity from Wastewater Disposal in Oklahoma
Mandated wastewater injection reductions in effect since 2016 are inadequate for preventing future, large-magnitude earthquakes in the state, according to a new induced seismicity model.
Catching Oklahoma’s Tiny Tremors in the Act
Scientists map thousands of microearthquakes in Oklahoma to take a closer look at the seismic effects of wastewater injection following oil and gas operations.
Fluid Injection Wells Can Have a Wide Seismic Reach
High-volume fluid injection can cumulatively increase underground pore pressure and induce earthquakes in regions unexpectedly far from injection wells, recent Kansas studies show.