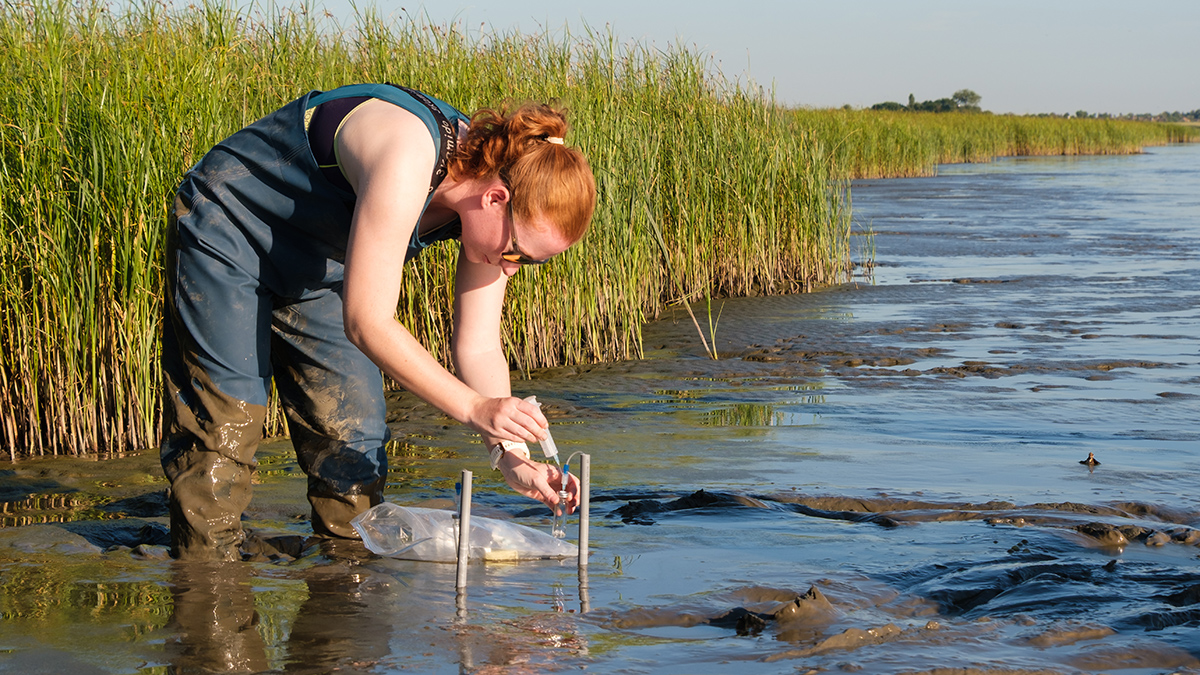
A new method that adds synthetic iron minerals to soils sheds light on hard-to-observe soil and sediment processes and may have a host of other applications in the Earth sciences and beyond.
rice
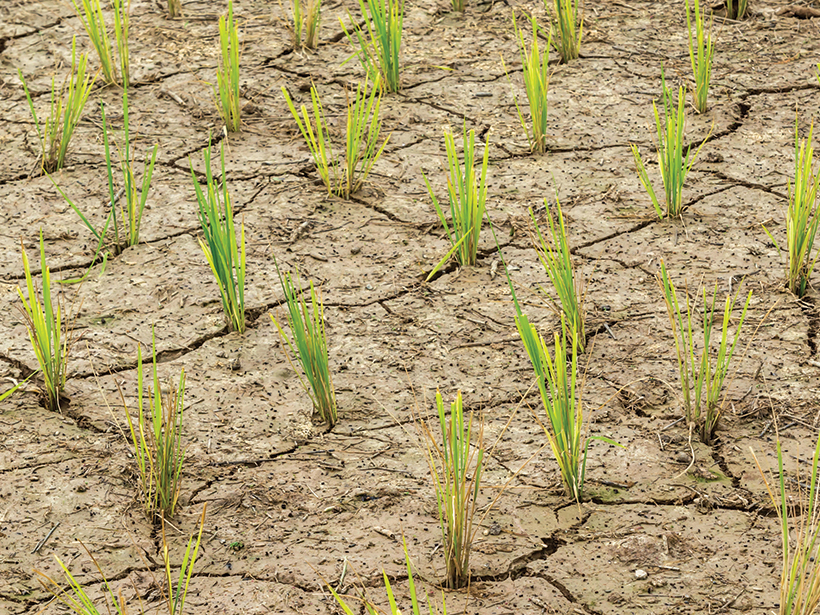
Rice Paddies, Like Cows, Spew Methane. A New Variety Makes Them a Lot Less Gassy.
Rice plants are a big source of methane, an extremely potent greenhouse gas. Scientists just developed a strain that cuts those emissions by 70 percent.
How Soil Symbionts Could Unlock Climate-Smart Agriculture
By tracing the evolutionary history of beneficial soil microbes, scientists hope to unearth a sustainable solution for producing food to feed a growing global population.
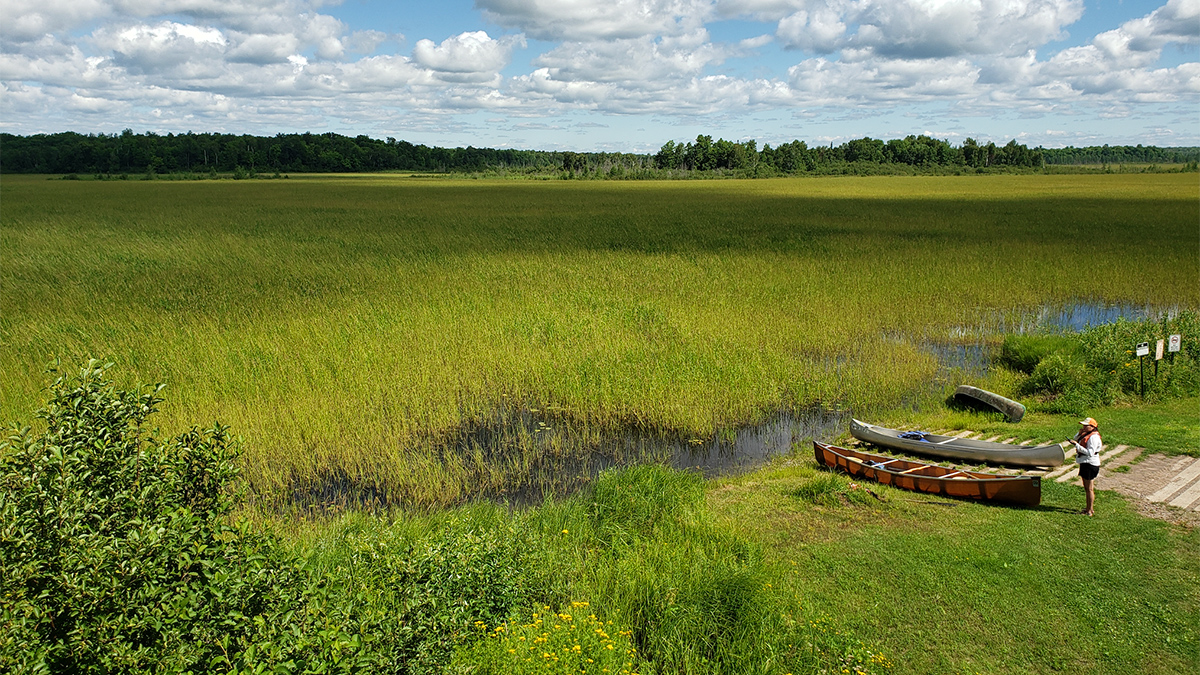
Climate Change Threatens the Future of Wild Rice
As a precious plant struggles to thrive in the U.S. Upper Midwest, researchers are taking steps to understand the reasons for its decline.
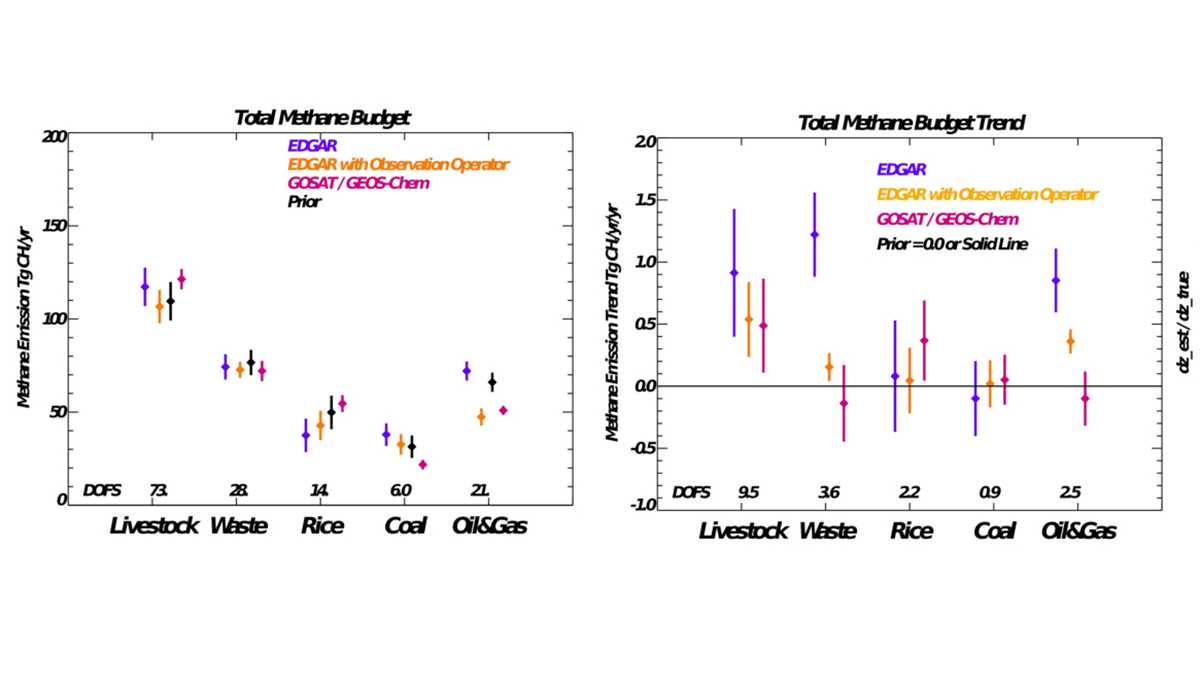
Using Bayesian Estimation to Improve Methane Inventories
A Bayesian, optimal estimation evaluation of state-of-the-art methane inventory with satellite-based emissions from 2009 to 2018 finds substantial differences for livestock, rice, and coal emissions.
Could “Lost Crops” Help Us Adapt to Climate Change?
Archaeology might not solve all the agricultural challenges that climate change will bring, but it could provide important lessons and a record of new ideas.
Siltation Threatens Historic North Indian Dam
Experts recommend reforestation campaigns to combat siltation at Bhakra Dam, one of the first infrastructure projects pursued by India after independence.
Climate Change Uproots Global Agriculture
Climate change is shifting where ideal growing conditions exist and is leaving farmers behind. How can we secure our future food supply and support the people who grow it?
Will Rising Temperatures Make Rice Too Toxic?
Greenhouse experiments reveal how higher temperatures act to elevate arsenic levels in rice and may help focus efforts to solve a crisis threatening food systems around the world.
North American Wild Rice Faces Sulfide Toxicity
Researchers have developed a model to inform the regulation of sulfate levels in freshwater environments that are threatening the iconic plant.