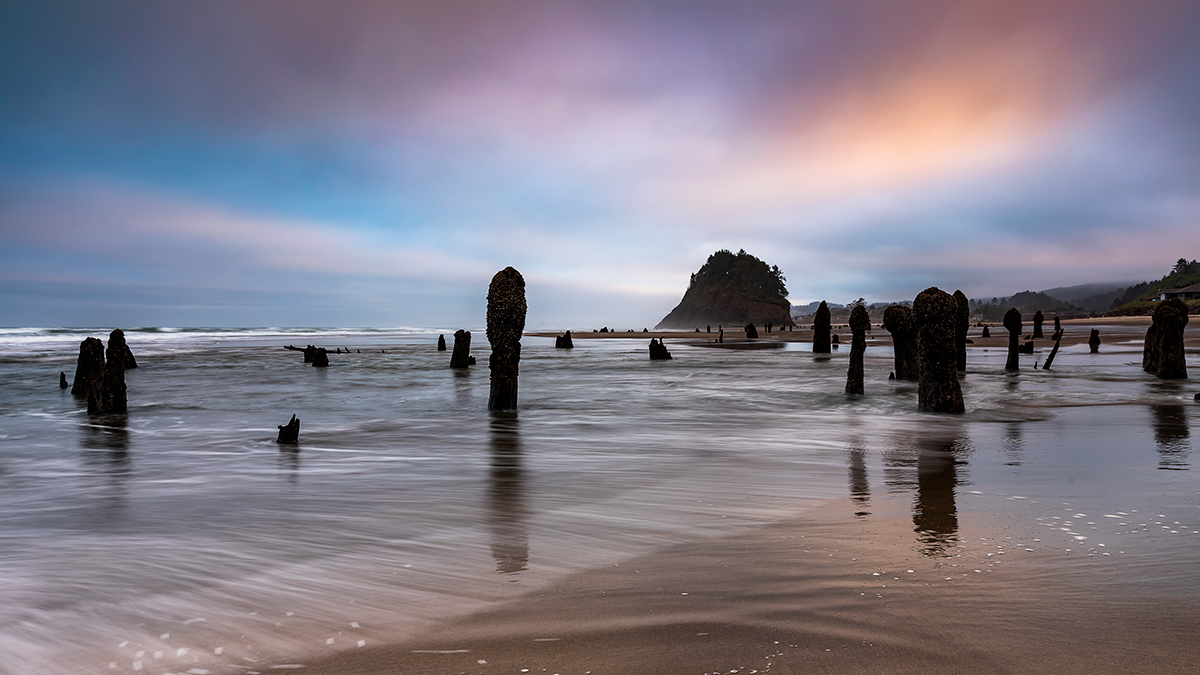
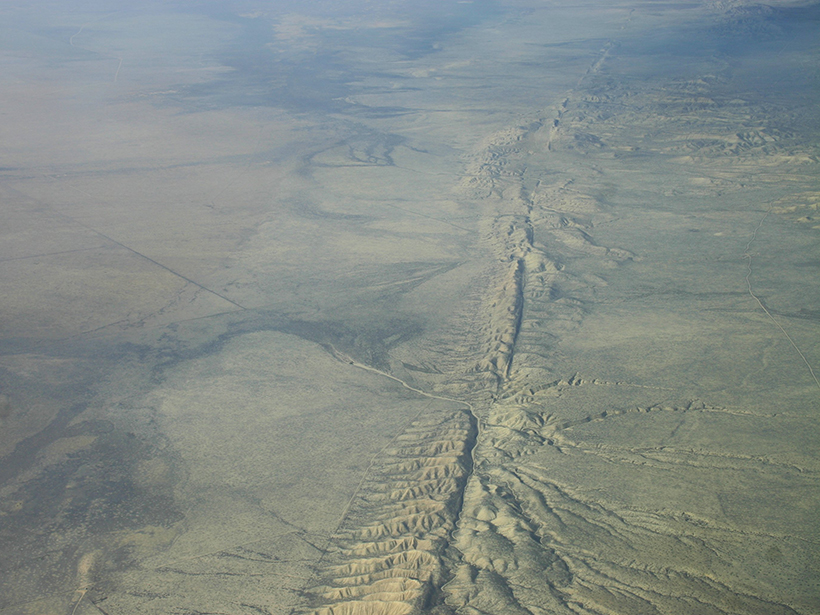
Roughly half of the earthquakes that occurred along the southern Cascadia subduction zone over the past 3,000 years were temporally associated with earthquakes along the northern San Andreas fault.
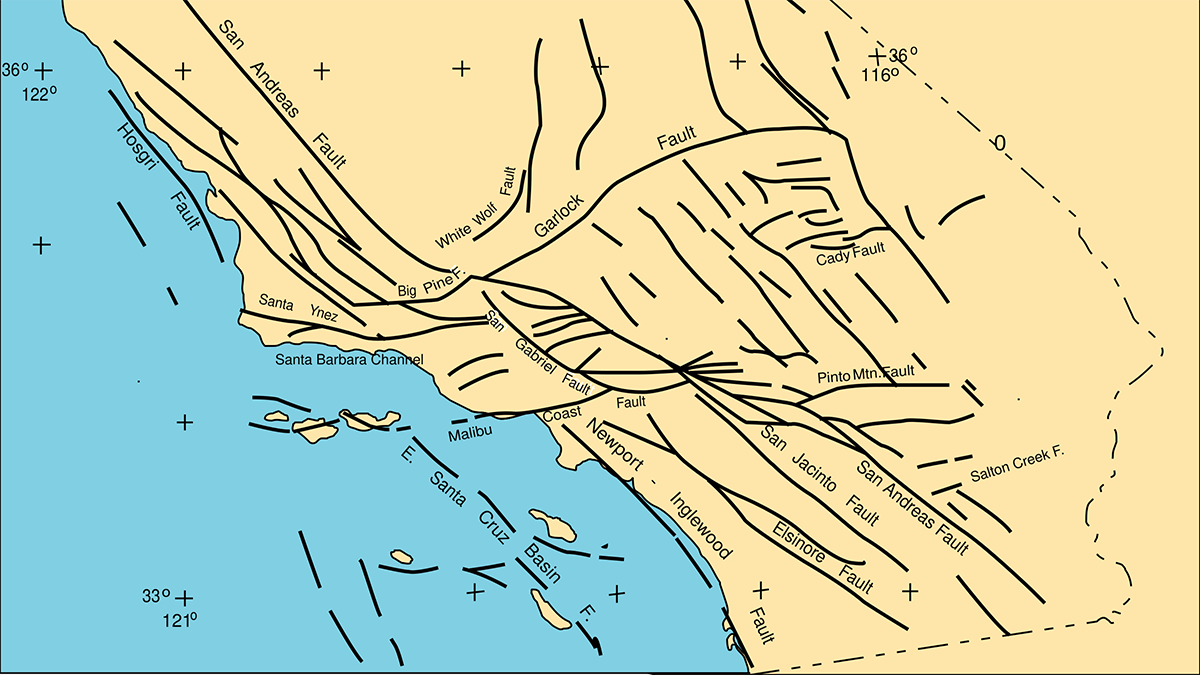
San Andreas Fault
Creeping Faults May Have Simpler Geometries
A recent study offers an alternative perspective on why some fault segments slide smoothly, whereas others get stuck and produce earthquakes.
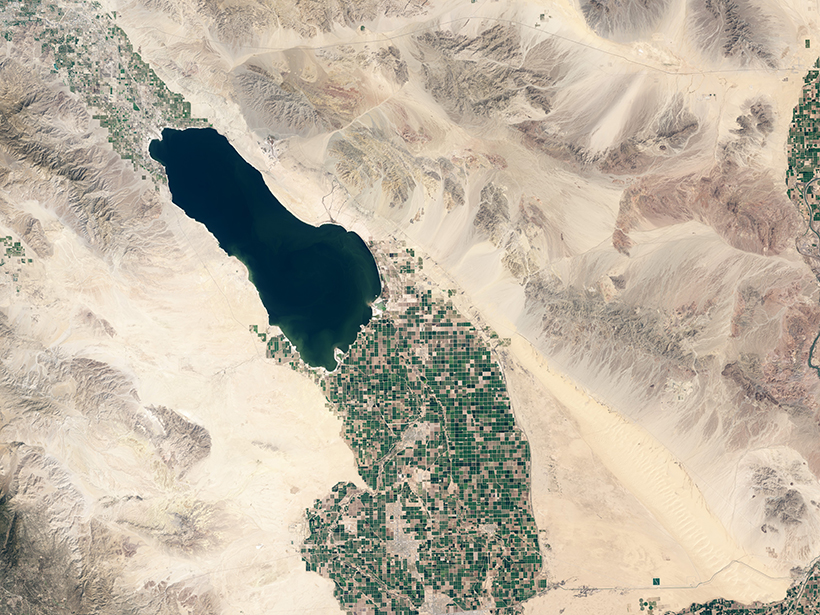
On-Again, Off-Again Lake Cahuilla Likely Enhanced Earthquakes in Southern California
The disappearance of the ephemeral lake has made earthquakes along the San Andreas Fault even more unpredictable.
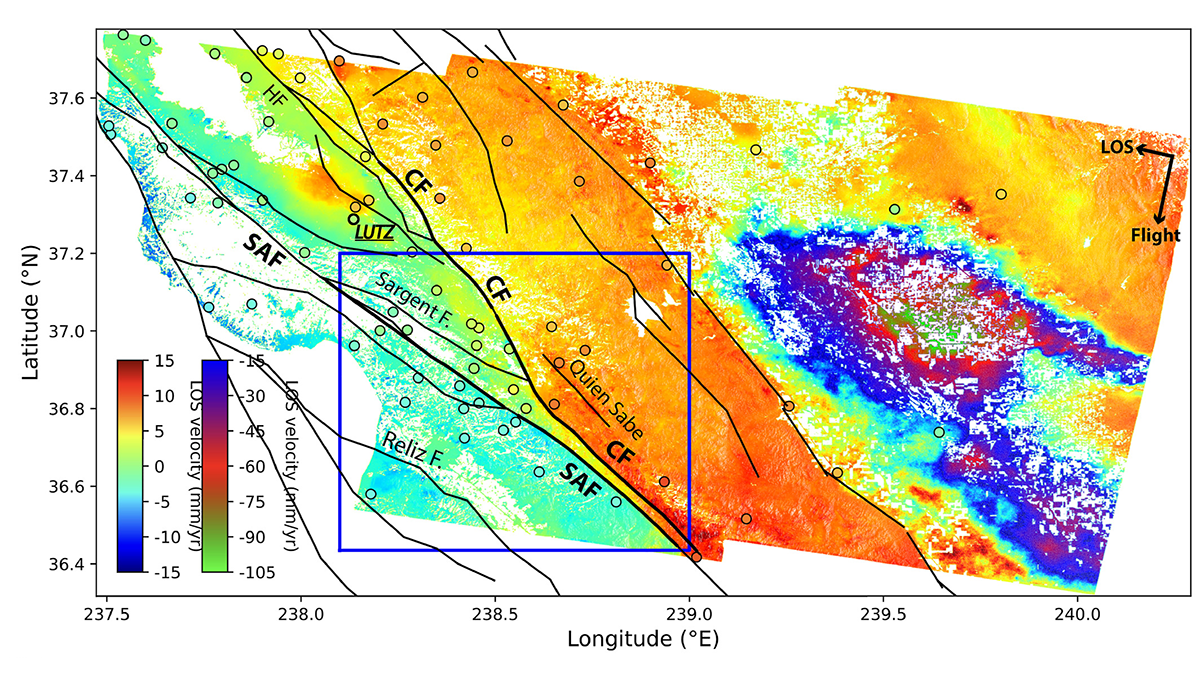
Radar Satellites Capture Subtle Slip Evolution on Faults
A five-year time series from radar satellite imagery tracks surface slip on major faults in the San Francisco Bay Area, capturing subtle velocity variations and controlling factors.
Accounting for Offbeat Earthquakes Could Improve Forecasts
A new model considers the full history of earthquakes on a fault, improving forecasts of when the next will strike.
How Land Deformation Occurs When Fault Sections Creep
Using a physical experiment, researchers show how off-fault deformation occurs along strike-slip faults with different types of motion.
A New Method Produces Improved Surface Strain Rate Maps
The transdimensional Bayesian approach handles GPS data limitations better than existing methods and may assist future seismic hazard assessment studies.
Distant Quake Triggered Slow Slip on Southern San Andreas
A high-resolution map of surface displacements indicates that the 2017 Chiapas earthquake caused substantial creep along a segment of the San Andreas Fault, located 3,000 kilometers away.
Tiny, Deep Quakes Increase on San Andreas as Tides Tug on Fault
When the gravity of the Sun and Moon causes Earth's crust to bulge every 2 weeks, slow-moving earthquakes proliferate in the lower reaches of the San Andreas, a new study finds.
The Role of Water in Earth's Tectonic Plumbing Systems
Tidal forces act on well water around the San Andreas Fault, giving researchers a new window into the hydrogeological structure of fault zones.