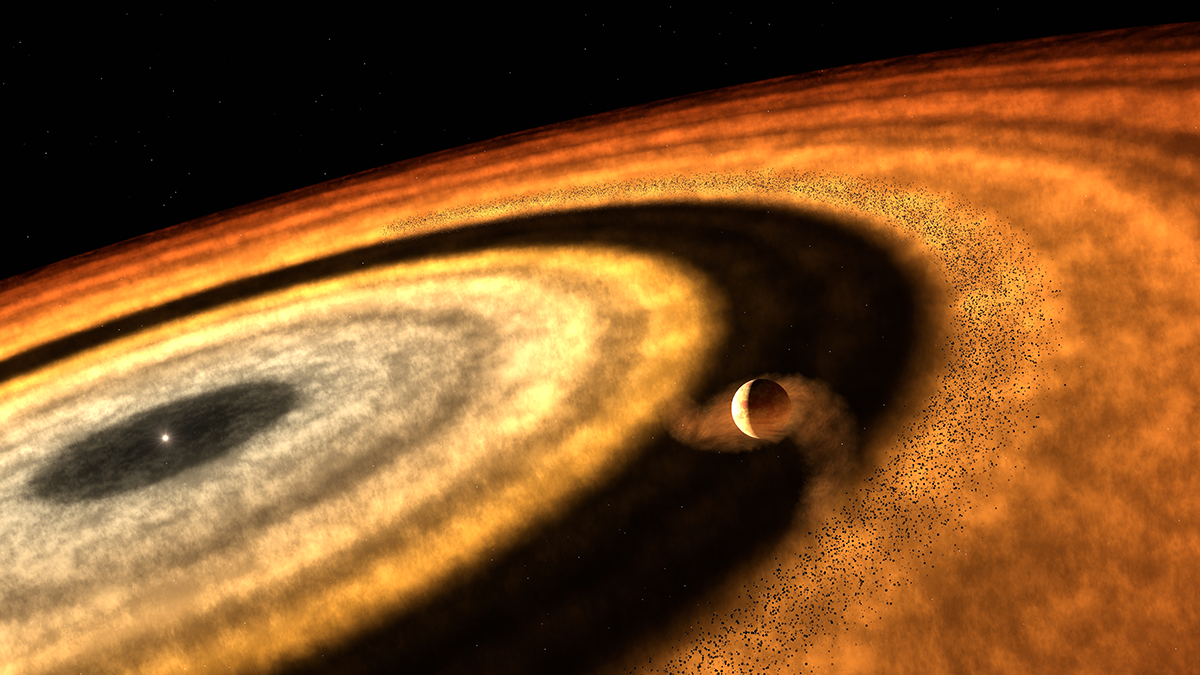
WASP-121b, an already unusual planet, might have a remote origin that explains some of its peculiar properties—from iron rain to the unexpected presence of methane.
silicon & silica
Atomic-Scale Insights into Supercritical Silicate Fluids
Water-induced depolymerization enhances fluid mobility in deep Earth, offering new insights into magma transport and isotope signatures in arc lavas.
Machine Learning Enhances Image Analysis in Biogeosciences
Machine learning can enhance our ability to identify communities of microorganisms and how they change in response to climate change over time.
Clays May Have Slowed Earth’s Recovery After the Great Dying
Without tiny marine organisms using silica for shells, Earth’s oceans generated more clay, released more carbon dioxide, and kept Earth warmer for longer.
Middle-of-the-Road Mountains Form the Best Carbon Sinks
Silicate rock weathering has a sweet spot: erosion that isn’t too fast or too slow.
Talc May Make Mexico’s Subduction Zone More Slippery
Production of the weak, water-bearing mineral at the interface between the Cocos and North American Plates could contribute to the occurrence of poorly understood episodic tremor and slow slip.
Silicate Weathering Throttles the Global Thermostat
The natural breakdown of some rocks sucks carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. Knowing how quickly it happens could help scientists engineer solutions to the climate crisis.
Unraveling the Mystery of a Rare Mineral on Mars
The discovery of tridymite in Mars’s Gale Crater triggered debate about the rare mineral’s origins. A research team recently suggested a scenario with explosive implications.
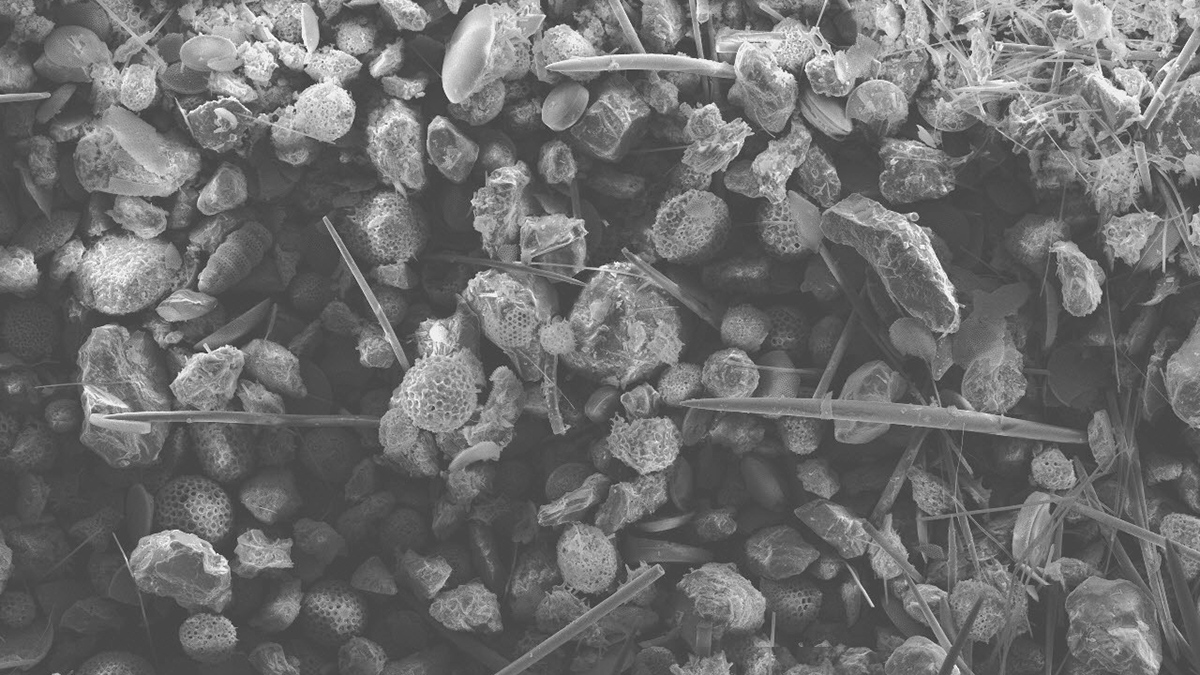
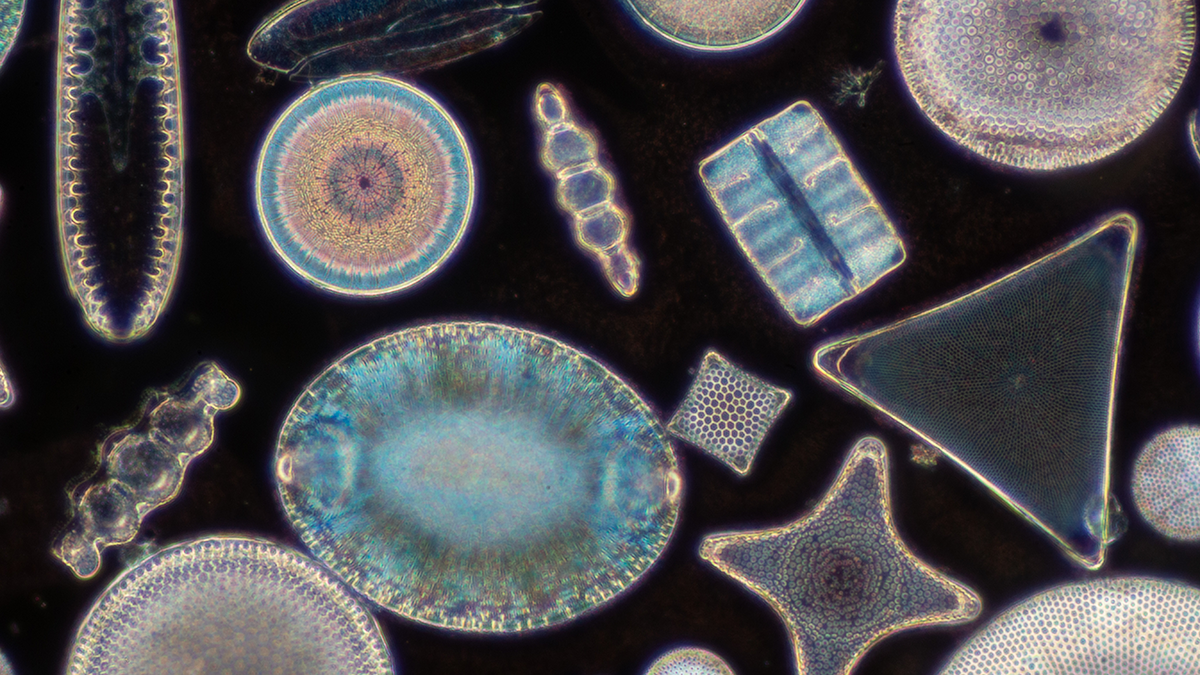
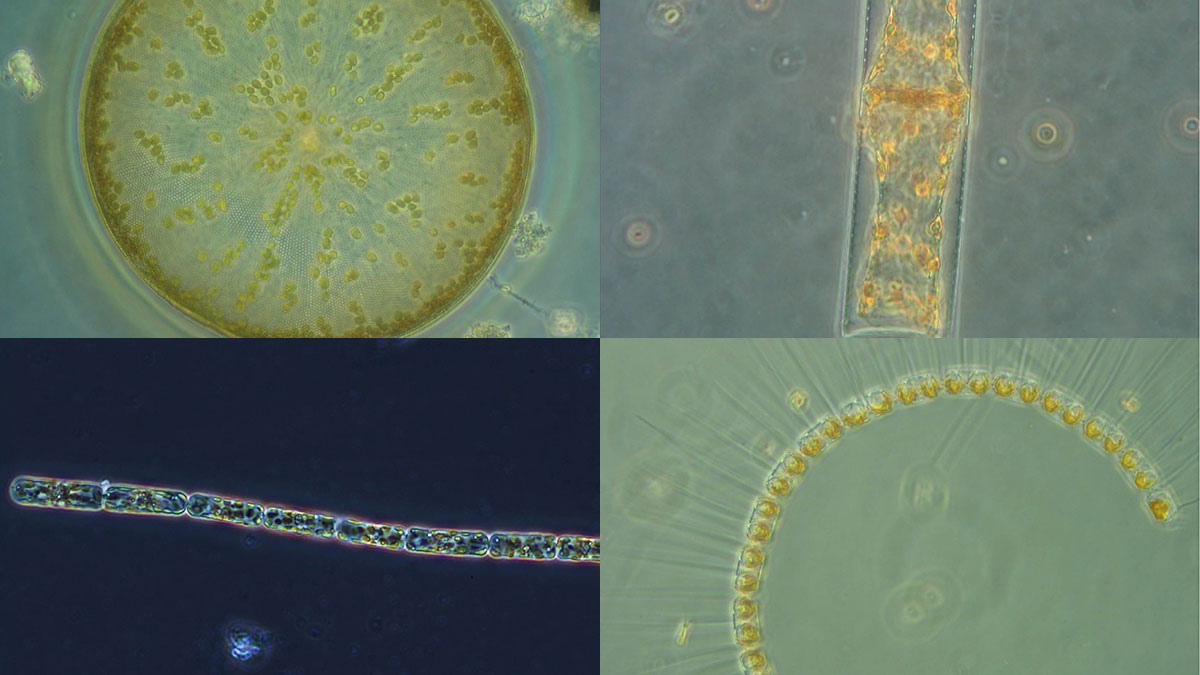
Ocean Acidification May Drive Diatom Decline
Diatoms contribute to global oxygen production, marine food webs, and carbon sequestration, but scientists predict that diatom populations will decline due to ocean acidification associated with climate change.
Small Catchments Sustain Silicon Signatures Following Storms
Watersheds have unique patterns of silicon export due to differences in subsurface water routing and biogeochemical reactions.