The geomagnetic field changes regionally on centennial time scales. A recent study unlocks three historical archives from the “Four Corners” region (southwest USA) reconciling previous discrepancies.
Editors’ Highlights
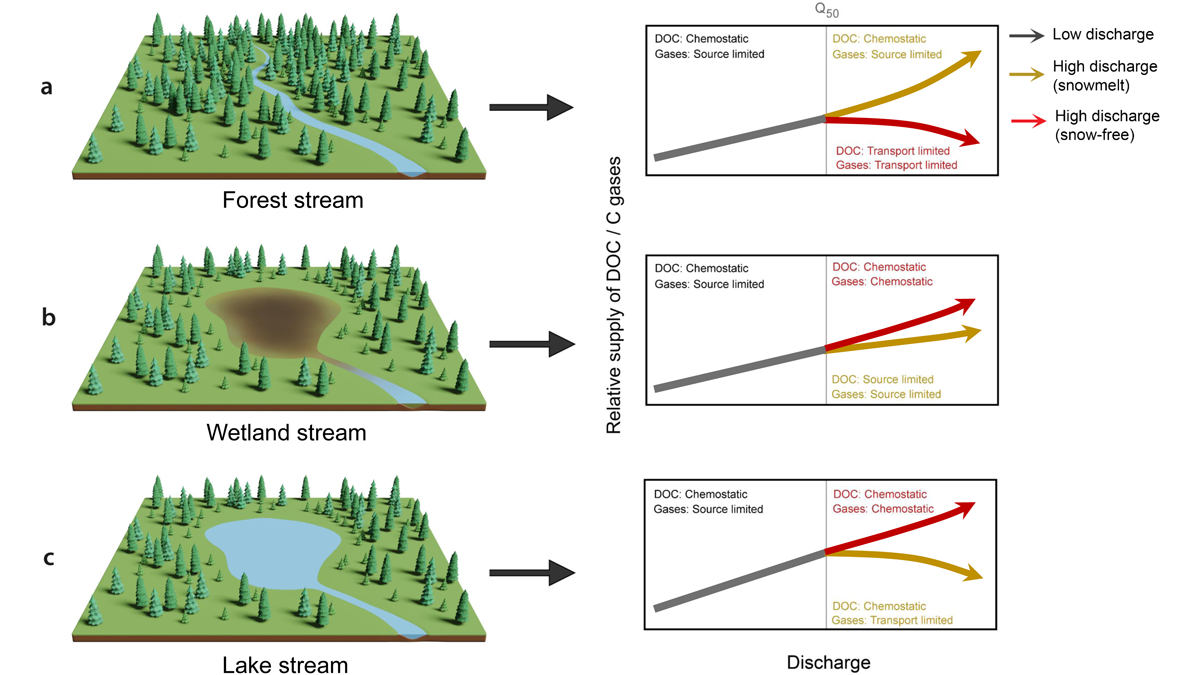
Export of Different Carbon Types from a Boreal Catchment
Carbon export in boreal catchments depends on the landscape setting and differs for snowmelt and rainfall events.
New Standards Spur Water Utilities to Improve Compliance
Although American water utility companies take time to modify procedures and technologies in response to new quality requirements, ultimately it reduces the rate at which they violate standards.
Transforming Hydrology by Integrating Sensors and Disciplines
Satellite sensing has transformed hydrology by providing global information on variables and fluxes. Breakthroughs will come from integrating sensing information and cross-disciplinary approaches.
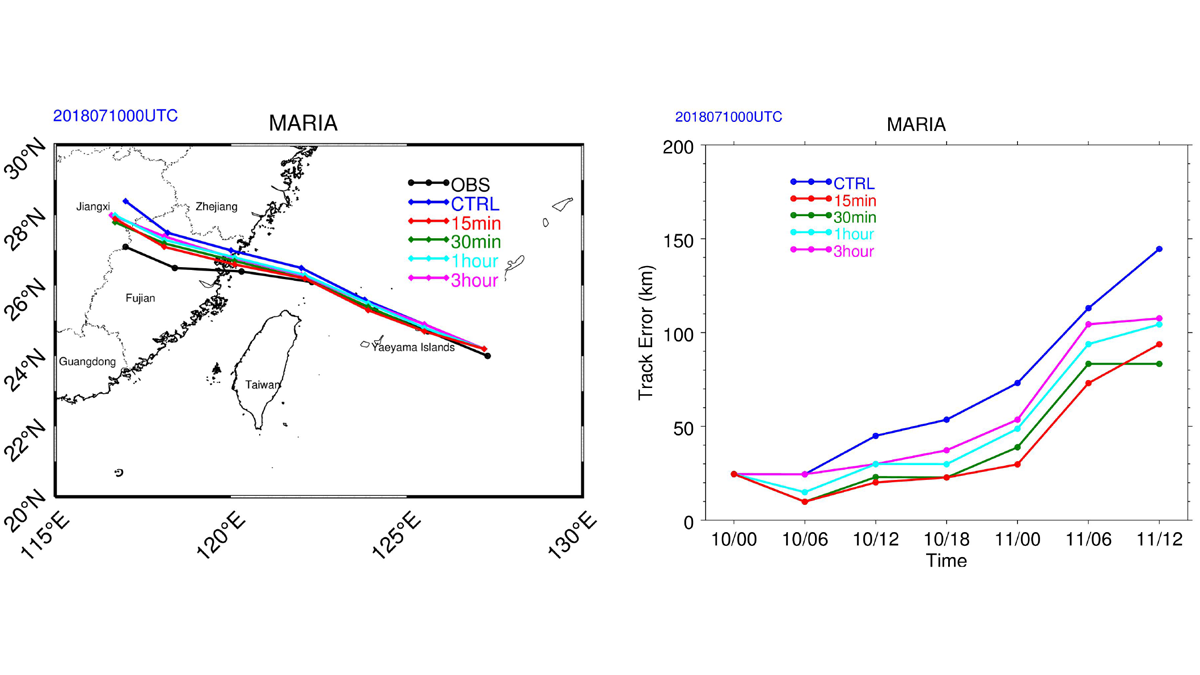
Impact of Geostationary Sounder on Typhoon Forecasts
An analysis of the impact of targeted observations from the Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder at high-temporal resolution on forecasts for Typhoon Maria in 2018.
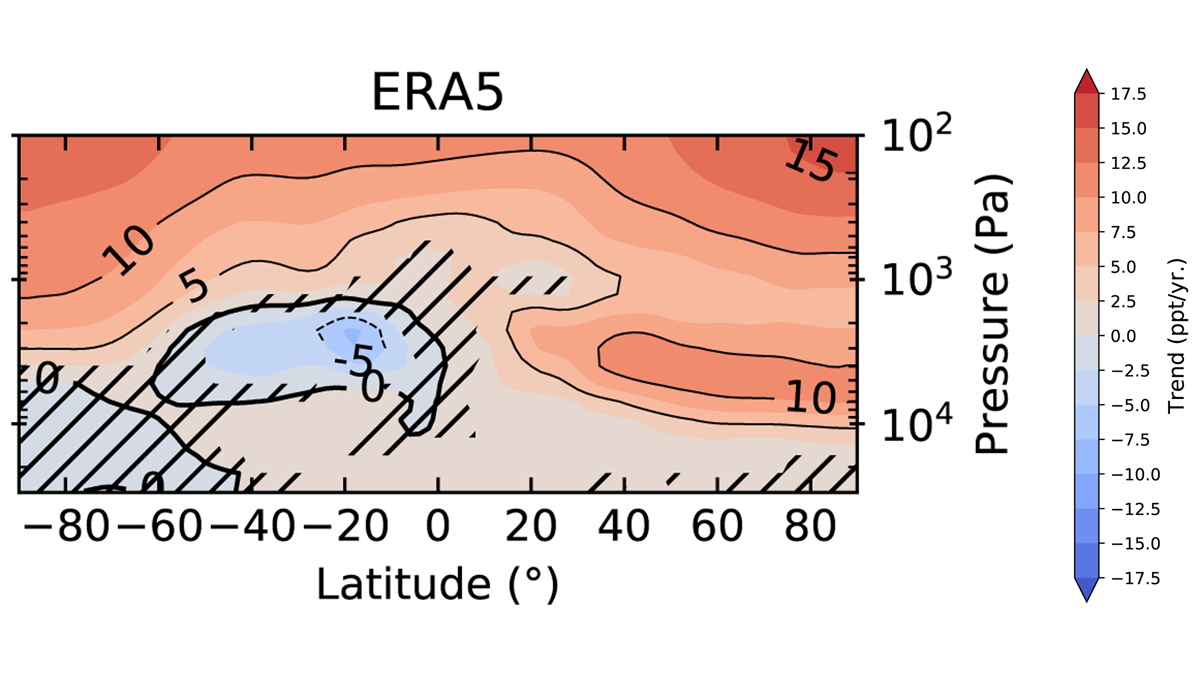
New Insights on Stratospheric Circulation from Fluorine Tracers
Stratospheric fluorine species have accumulated faster in the Northern Hemisphere over the past two decades reflecting interhemispheric differences in the Brewer-Dobson transport circulation.
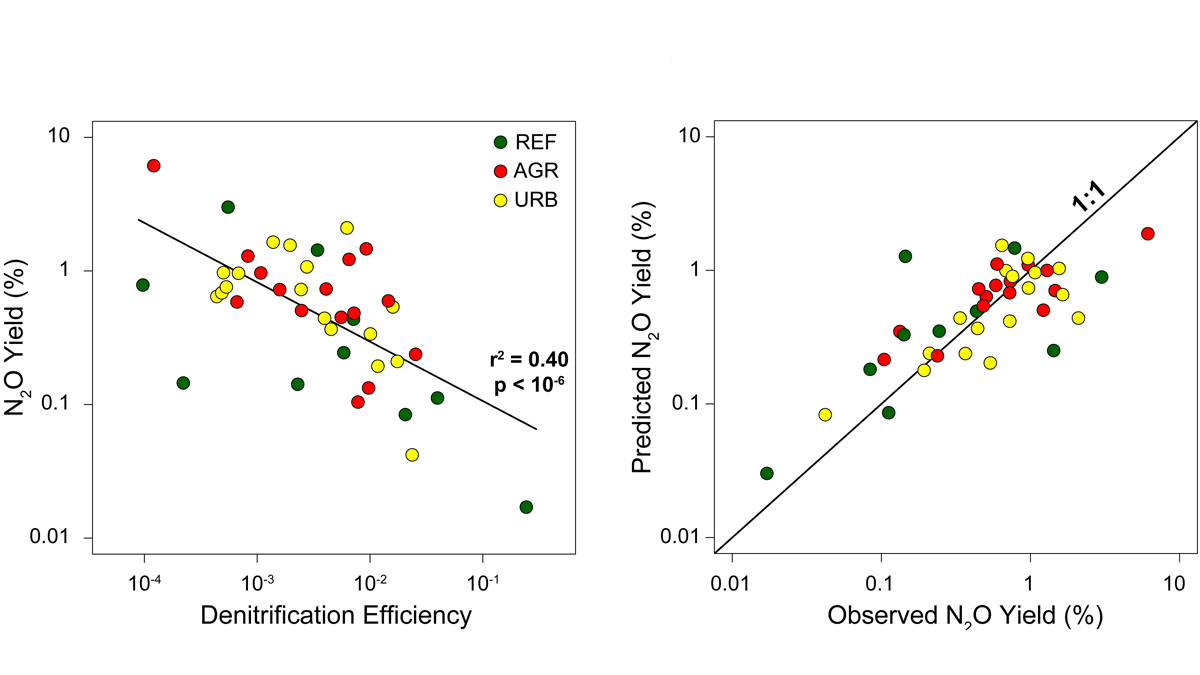
What Controls Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Rivers?
Statistical and numerical models show that denitrification efficiency is a key parameter controlling the production of N2O from rivers, providing a target for river restoration projects.
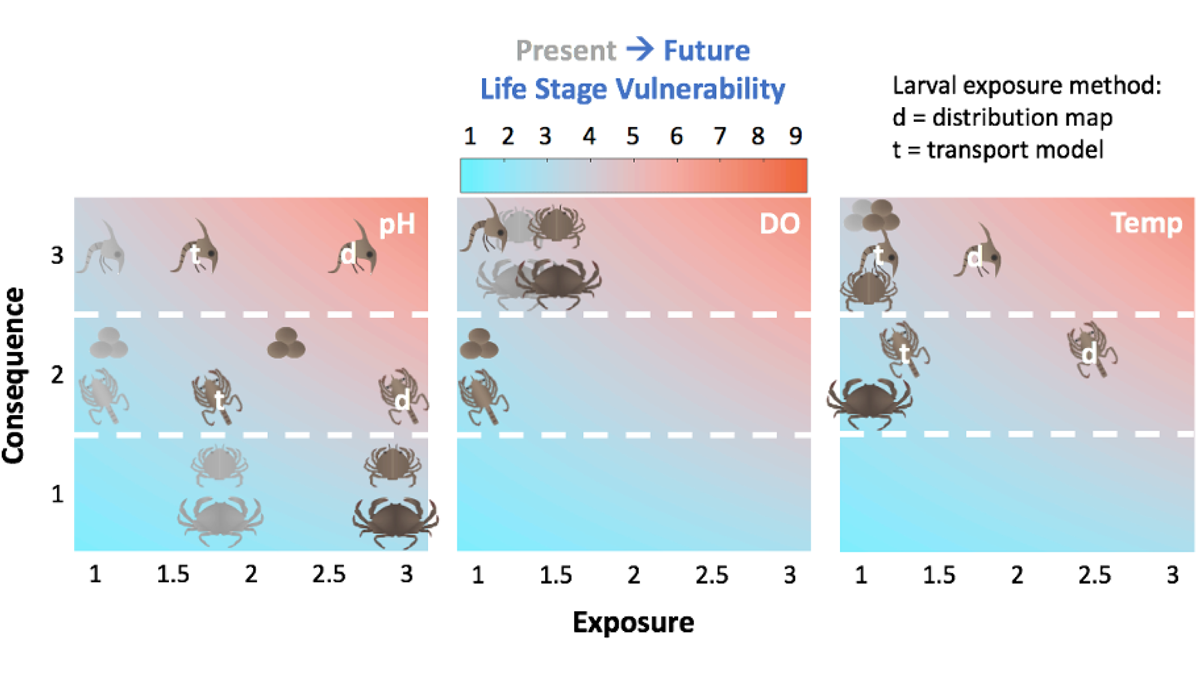
Dungeness Crab at Risk from Multiple Climate-Related Stressors
The lucrative Dungeness crab fishery is at risk because of the combined effects of projected climate-related habitat changes: lower oxygen, warming temperature, and increased acidity.
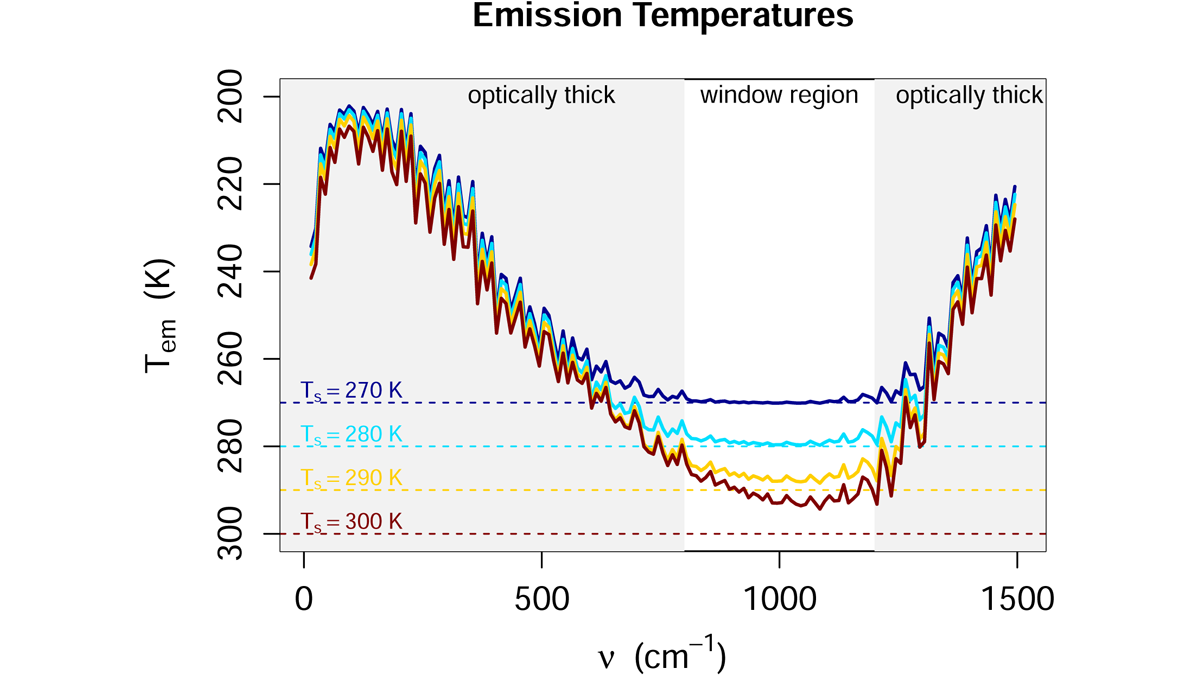
Simpson’s Law Role and Water Vapor Feedbacks
The choice of a fixed relative humidity leads to a simpler picture of climate feedbacks than fixing absolute humidity.
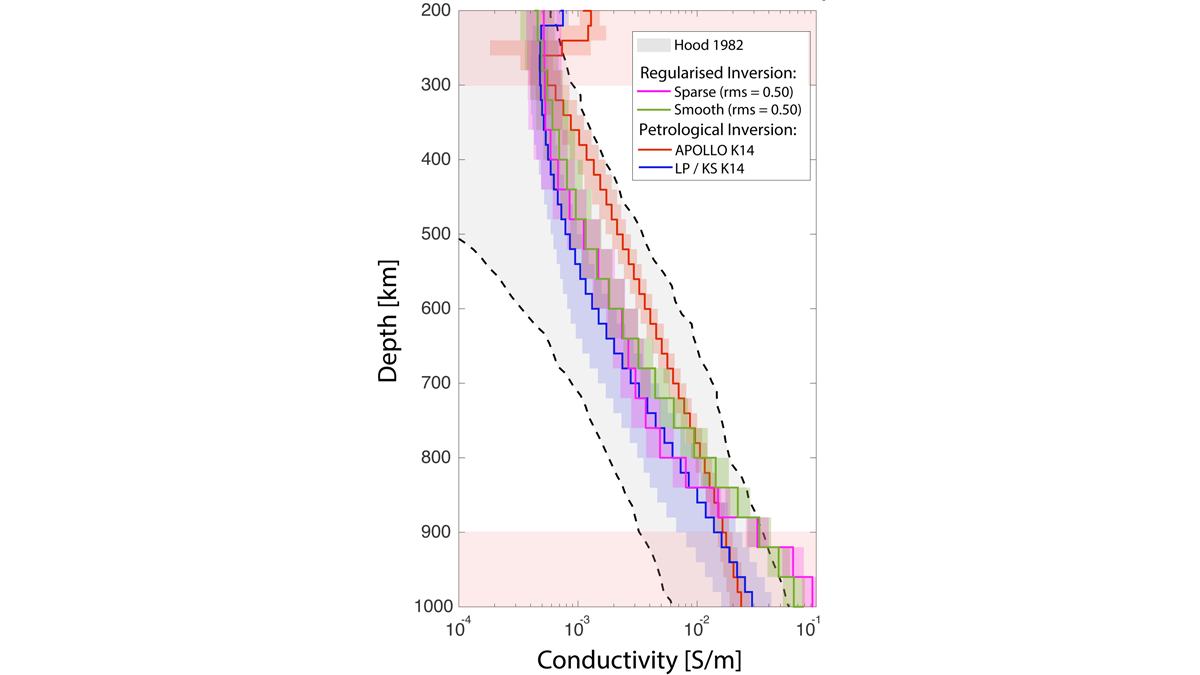
A Better Look at the Moon’s Middle Mantle
A new analysis strategy sheds new light on the electrical conductivity of the lunar mantle between 300 and 900 km depth.