Photographs and field observations yield a more complete historical record of the ebbs and flows of the so-called Blood Falls on Taylor Glacier.
News
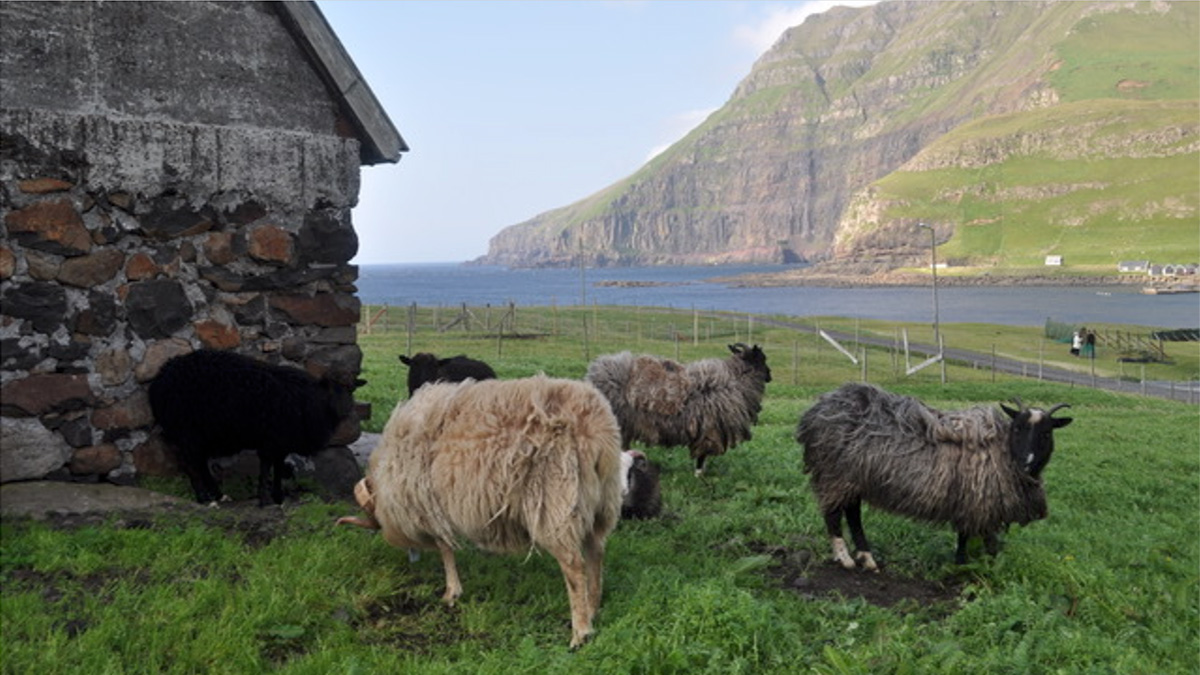
Ancient Eruptions Reveal Earliest Settlers on the Faroe Islands
Lake sediment is helping scientists resolve a decades-long historical mystery.
Projection: $110 Billion in Repairs for Russian Pipelines on Permafrost
Permafrost thaw is a major threat to pipelines in the Russian Arctic, particularly those carrying natural gas.
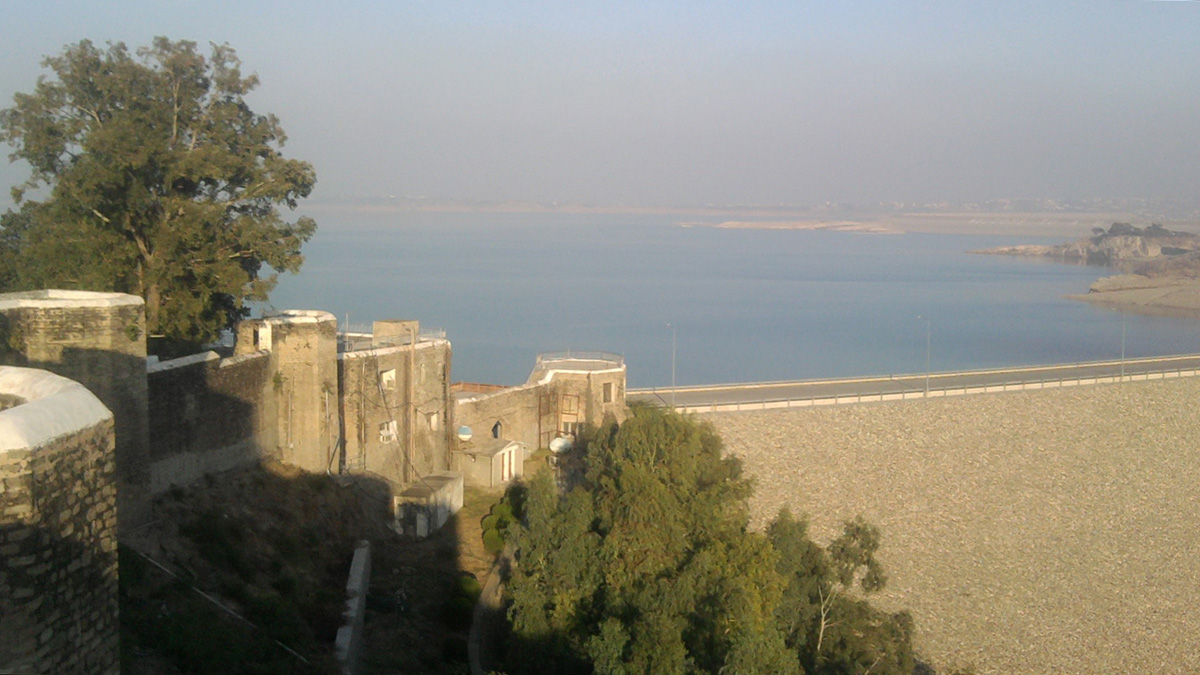
A Monsoon-Filled Reservoir Might Have Nudged a Fault to Fail
New research examines whether a sudden increase in water loading in Pakistan’s Mangla Dam might have been connected to the 2019 New Mirpur earthquake.
Wildfires May Alter the Nitrogen Cycle—and Air Pollution
Research indicates that wildfires could be bolstering soil emissions of air pollutants that contribute to smog and climate change.
Settlement of Rapa Nui May Have Been Doomed by a Dearth of Dust
Rapa Nui and Hawai‘i offer a tale of two island settlements: Hawai‘i was close enough to Asia for continental dust to help replenish soil nutrients depleted by agriculture. Rapa Nui wasn’t.
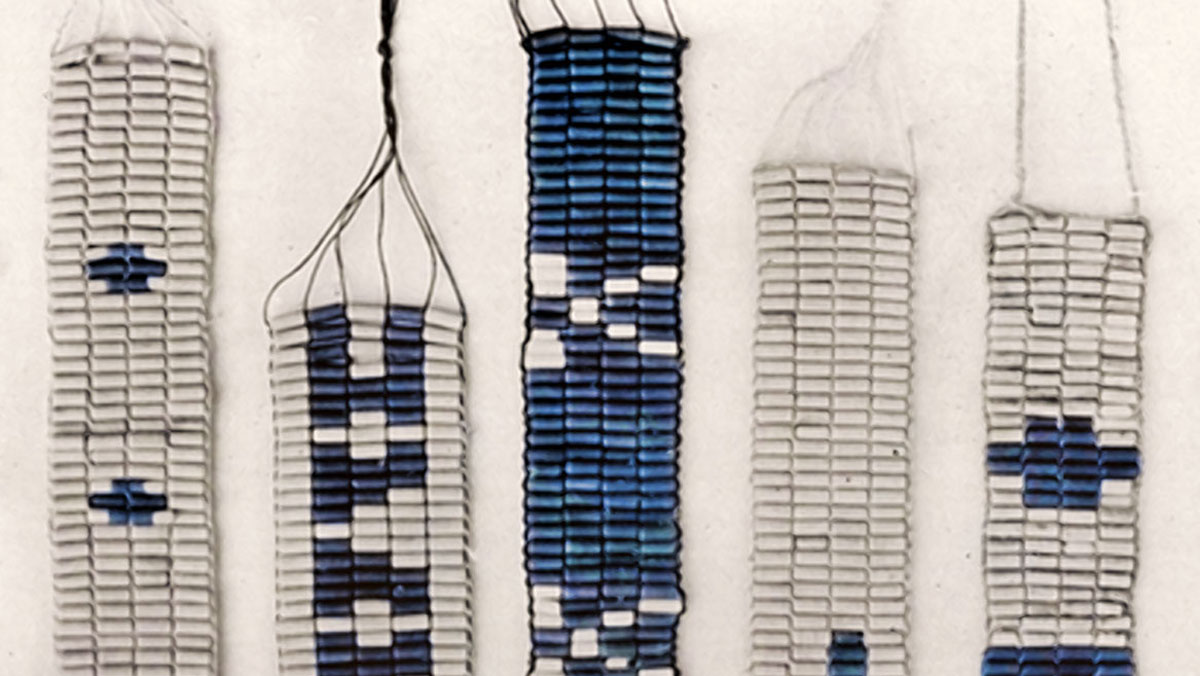
WAMPUM: An Indigenous-Designed Path to Sea Level Rise Adaptation
Northeastern and mid-Atlantic tribal nations lived sustainably on the coastline for centuries before colonization. How can their experiences inform strategies for sea level rise adaptation?
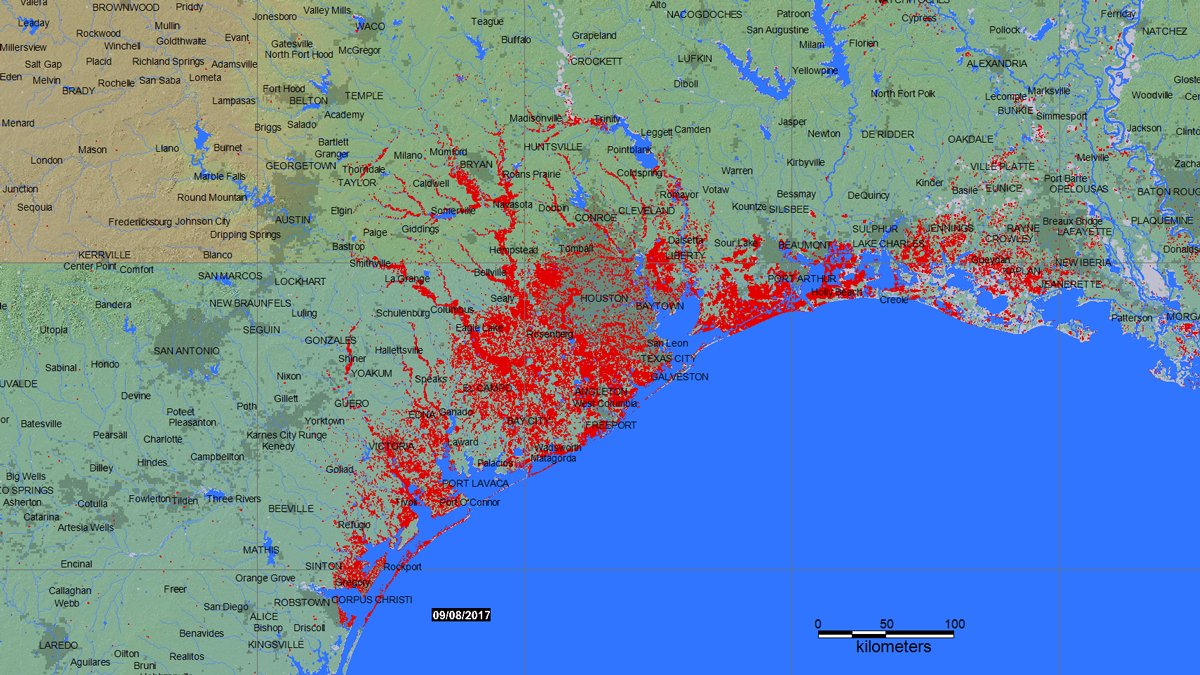
Remote Sensing Could Predict Well Water Quality After Floods
After a flood, most people rely on officials to test public water sources. Private well owners are on their own, with little data to guide testing and treatment. New research seeks to change that.
Misión a Venus podría ayudar a resolver un misterio atmosférico
La recientemente anunciada misión DAVINCI+ a Venus de la NASA investigará la atmósfera del planeta, esperando proporcionar información sobre los desconocidos parches oscuros que rodean dicho planeta.
New “Snakebot” Could Map Cambodian Minefields
By navigating under dense vegetation, an innovative robot could significantly reduce the monetary, environmental, and human cost of demining Cambodia.