Polarity reversals in the solar wind magnetic field disconnect the magnetic field trailing behind Venus, allowing ions from the atmosphere to escape.
A. K. Higginson
Aleida Higginson received her B.Sc. in astrophysics in 2011 from Florida Institute of Technology and is currently a Ph.D. candidate at the University of Michigan. She is physically located at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and uses numerical simulations to research the origin of the slow solar wind.
Patches of Low Electron Density Help to Heat the Ionosphere
Simulations show how changes in electron density can trap electromagnetic waves and heat electrons in the ionosphere.
Can Solar and Space Physics Students Find Research Careers?
Research shows that 80% of graduate students who received their Ph.D. between 2001 and 2009 continued to publish for at least 3 years, and 60% are still publishing.
Electrons Thrown Off Course in Near-Earth Magnetic Reconnection
NASA Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission detects energy differences in electrons scattered by magnetic reconnection.
Half of Atmospheric Joule Heating Is Due to Small Oscillations
Scientists use sounding rockets to show that small oscillations in electric fields can be just as important for atmospheric Joule heating as the presence of the electric field itself.
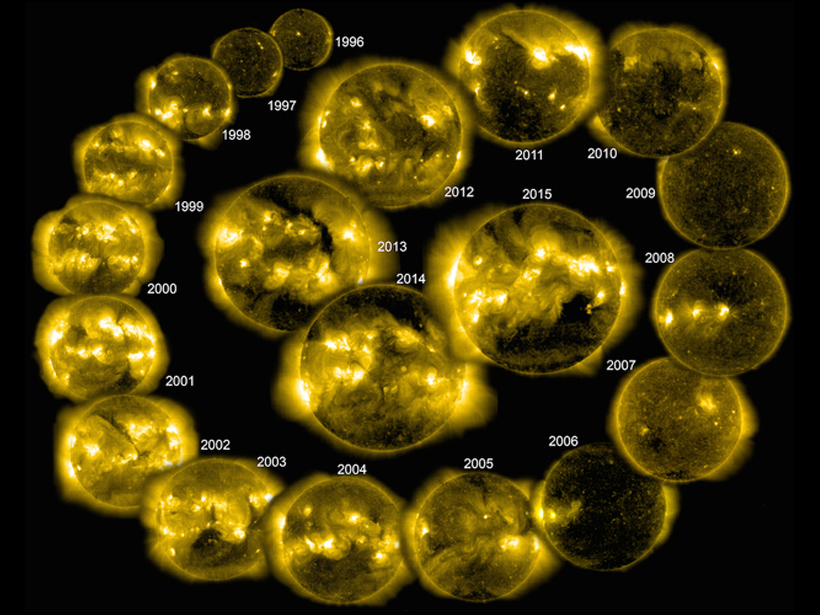
Sun's Magnetic Fields Best at Forecasting Solar Cycle Peaks
Models based on the Sun's polar magnetic fields performed best in simulating the solar cycle and predicting solar behavior.