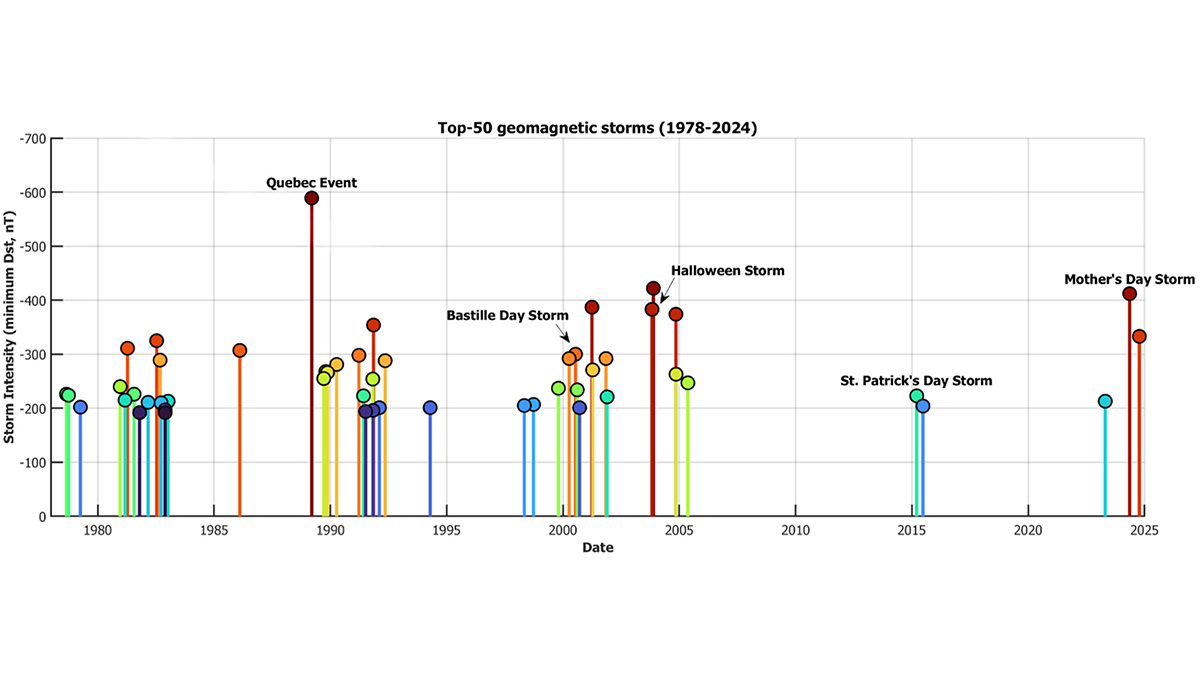
Mother’s Day Storm? Why not! Bastille Day Storm? Mais oui! Space scientists make the case for a standardized naming convention for geomagnetic storms, to increase public awareness and preparedness.
Andrew Yau
Editor, Perspectives of Earth and Space Scientists
Radio on Jupiter, Brought to You by Ganymede
Another first from NASA’s Juno spacecraft: the detection of Jupiter radio emissions influenced by the moon Ganymede, over a range of about 250 kilometers in the polar region of Jupiter.
A Whistle Here, There, and Everywhere on the Giant Planet
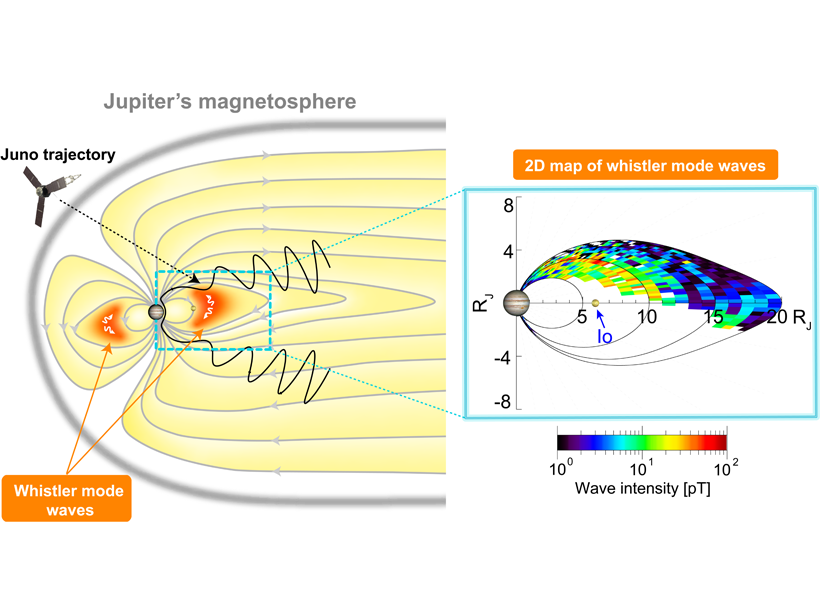
NASA’s Juno spacecraft is “hearing whistles” all over the place on Jupiter, a type of natural plasma waves called whistlers that are sometimes associated with atmospheric lightning.
All Hands on Deck to Catch Ion Cyclotron Waves
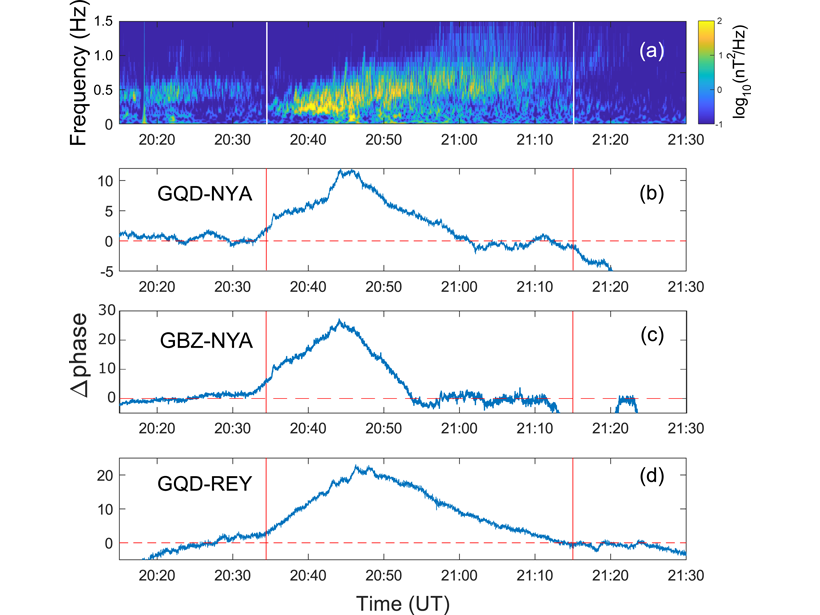
An international armada of orbiting satellites and ground VLF network join forces to form a “magnetosphere-ionosphere observatory” to size up electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves in the magnetosphere.
Power Outage When the Aurora Throws a Curve Ball
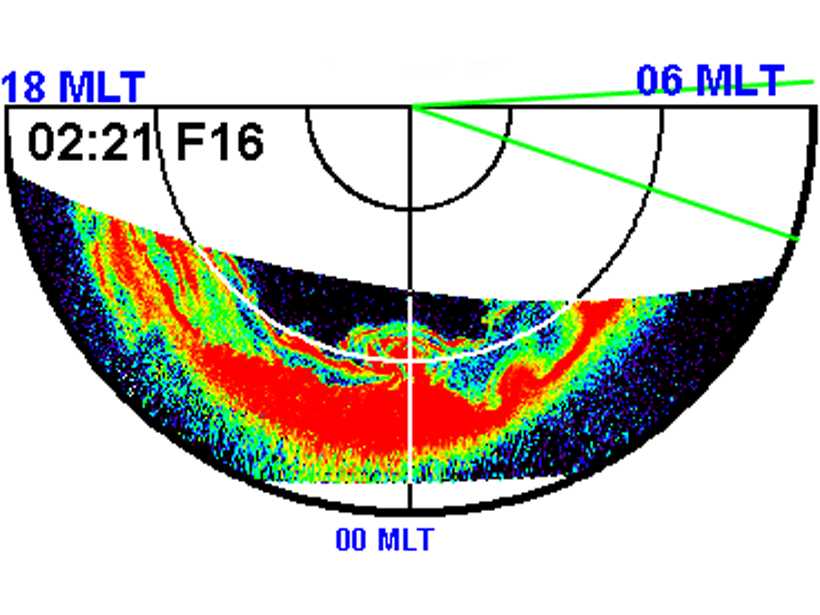
Omega-band aurora carries fast propagating electric currents in the azimuthal direction, producing geomagnetically induced currents that can cause power outage on the ground beneath.
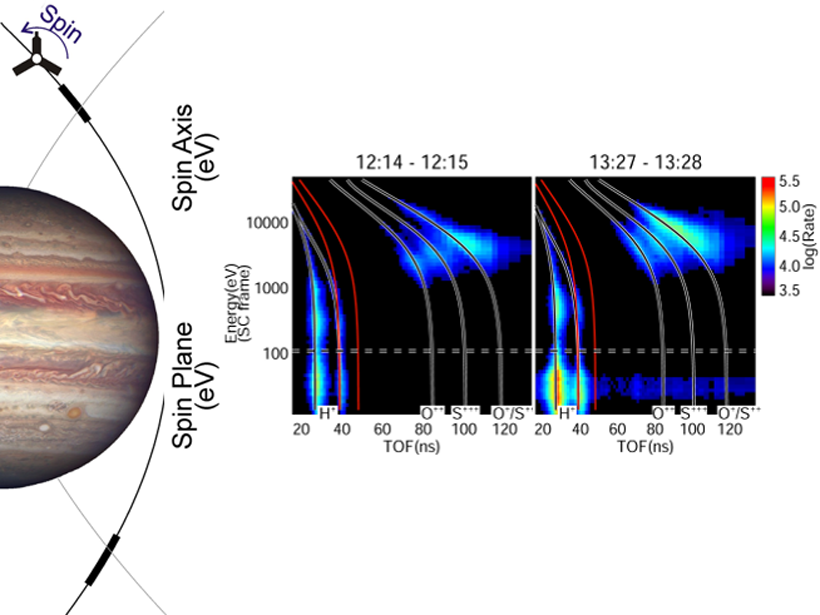
First Inside Look at Hot and Cold Ions in Jupiter’s Ionosphere
The first in-situ ion observations from NASA’s Juno spacecraft reveal the surprising, simultaneous presence of cold protons and hot oxygen and sulfur ions in the high-latitude ionosphere of Jupiter.
Molecular Ions Unexpectedly Frequent in Earth’s Magnetosphere
A Japanese satellite reveals rapid and surprisingly frequent transport of molecular ions from the ionosphere to the magnetosphere, under not only extreme but also moderate geomagnetic conditions.
Where Did the Water Go on Mars?
Primordial solar storm conditions are believed to have significantly enhanced the loss of water and other atmospheric volatiles in Mars’ history.
Subduction, Stratosphere, Starspots, and Sushi
Highlights from AGU’s joint meeting with the Japan Geophysical Union.
Close Encounter with Jupiter
First results from the Juno mission shed new light on Jupiter’s atmosphere, gravity, magnetic field, aurora, history, and more.