Scientists model how Antarctic meltwater from specific locations could affect the Antarctic Bottom Water, ocean temperatures, and salinity.
C. Sullivan
Cody Sullivan, a Fall 2015 news intern for Eos.org, graduated in 2015 from Boston University with an M.S. in science journalism and holds a B.S. in ecology and evolutionary biology from the University of California, Santa Cruz. Prior to joining Eos.org, he interned at Business Insider and Tech Insider, focusing on environmental, life, and Earth sciences. Currently, Cody is a science writing fellow for the U.S. Forest Service.
Human-Made Fires Pollute Air with Ozone Half a World Away
Fires in Africa and Southeast Asia contributed to western Pacific pollution, a study finds. Prior understanding attributed hefty levels of the harmful agent and greenhouse gas to natural processes.
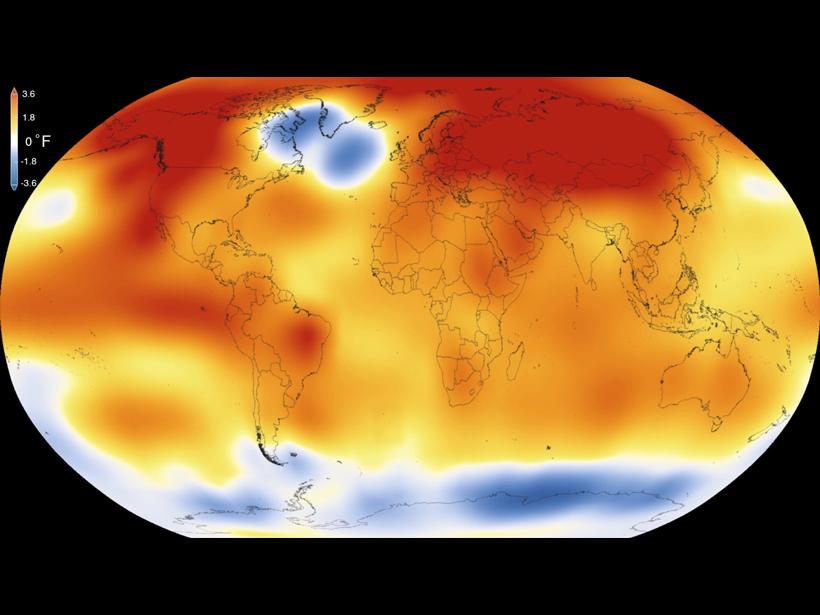
Record Global Warmth in 2015, but Some Places Bucked the Trend
As the planet's average surface temperature jumped to a new high last year, variations in ocean conditions on a smaller scale led to some distinct deviations from the overall pattern.
Quake or Bomb? Seismic Waves Speak Truth, Even If Nations Don't
When the Earth rumbles and no one knows why, seismologists can analyze the seismic event's waveforms to determine whether a hidden explosion or an earthquake caused the shaking.
Ancient Start of Animal Evolution Wasn't Delayed by Low Oxygen
New research finds that Earth had sufficient oxygen 1.4 billion years ago for animals to evolve. Therefore, low oxygen levels probably didn't hold back evolution, as scientists have long thought.
Vanishing Sea Ice Could Trigger More Arctic Precipitation
A promising method for evaluating Arctic precipitation predicts retreating sea ice will increase snow and rainfall in the Arctic and counteract some of global climate change's effects regionally.
Atmospheres Can Collapse on the Dark Sides of Planets
Planets that orbit close to their stars might lose their atmospheres along with any chance of life, but new models show a way in which these planets may retain their atmospheres and habitability.
Trying Out Muons to Detect Carbon Leaks
Scientists look into tracking carbon dioxide within a sequestration reservoir—and spotting possible leaks—by observing naturally generated, fast-moving muons that penetrate the underground storage area.
Salty Secret Might Aid Carbon Impact of Restored Wetlands
Research on a surprising way rainfall affected the salinity of a boreal peatland might help restorers of such wetlands wrecked by tar sands mining maximize carbon absorption of reclaimed marshes.
Earth's Water Came from Space Dust During Planetary Formation
A new analysis of lava from the deep mantle indicates that water-soaked dust particles, rather than a barrage of icy comets, asteroids, or other bodies, delivered water to the newly forming Earth.