Plant roots mediate solute transport through the soil immediately surrounding them by introducing polymers and other binding compounds that disrupt water transport pathways between soil pore spaces.
D. Scott Mackay
Editor, Water Resources Research
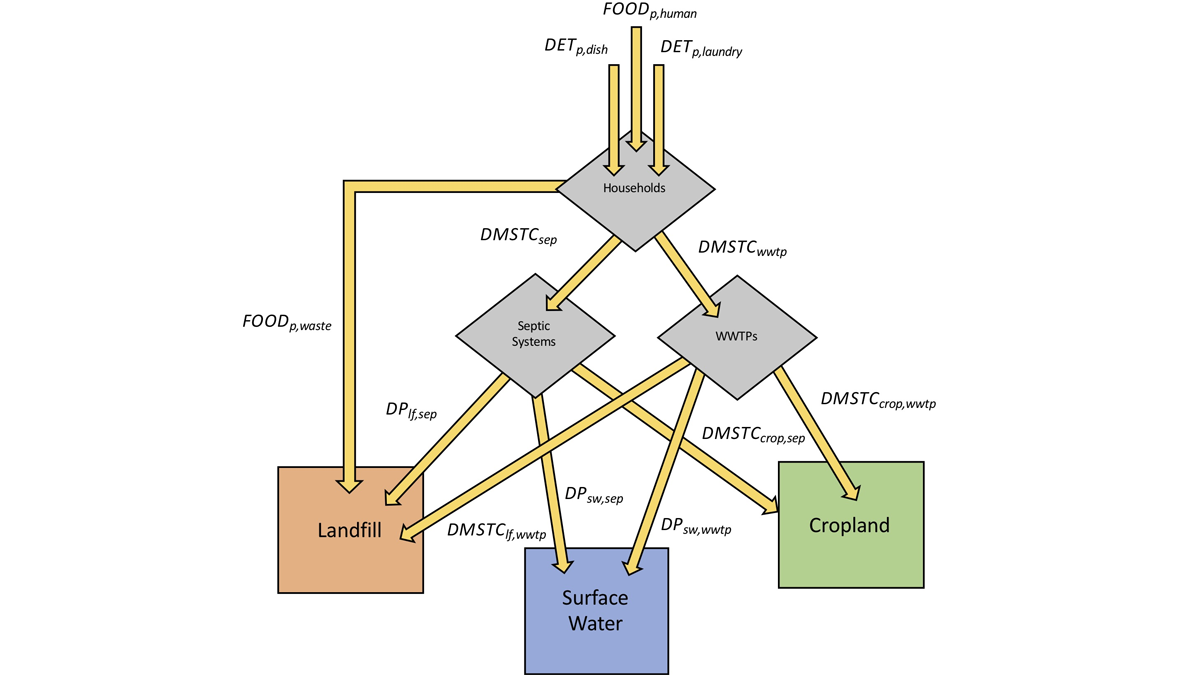
Water Quality Policy Must Consider Stored Watershed Phosphorous
Phosphorous stored in watersheds and affects water quality for decades. A new model predicts phosphorus accumulation and depletion, and the consequences for water quality conservation measures.
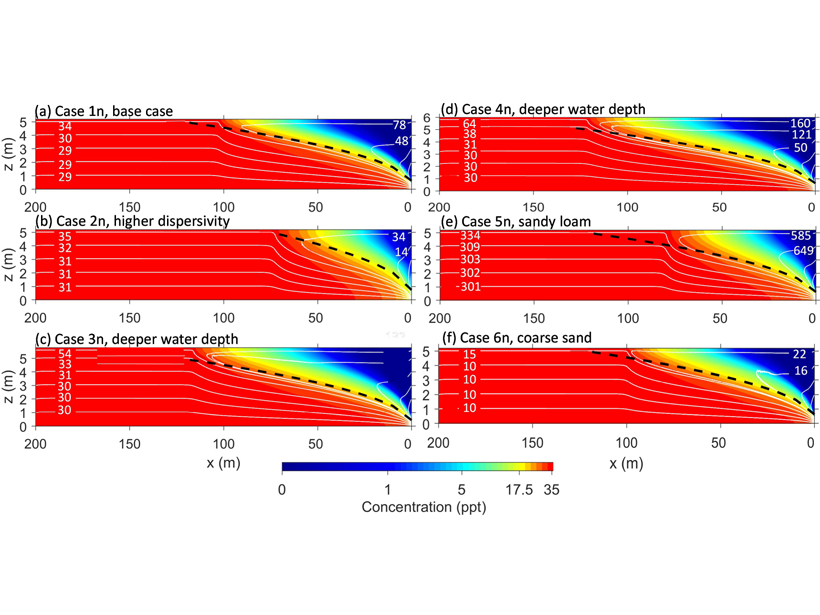
Evaporation Reverses Groundwater Flow and Forms Hyper-Salinity
A numerical model of groundwater-surface water systems shows how floodplain evaporation can reverse stream-groundwater flow and produce strong buoyancy changes associated with salinity.
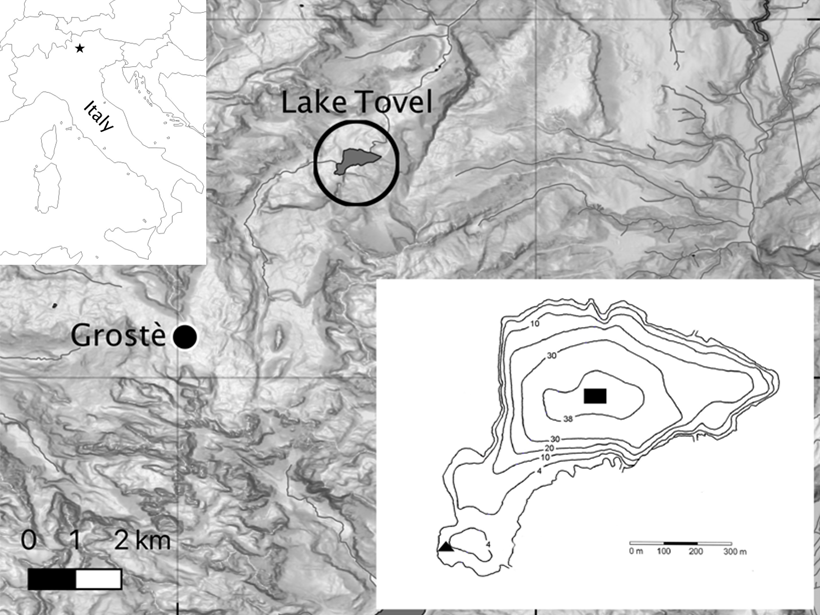
Climate Warming Improves Oxygen Mixing in a High-Altitude Lake
Long term weather and lake data from a high elevation lake in the Alps demonstrate that climate warming may actually improve the ability of high-altitude deep lakes to mix their waters.
New Isotope Model Predicts Denitrification from Riparian Zones
A new model quantifies the relative contributions of denitrification and other processes of nitrogen uptake, such as by plants, from groundwater in riparian areas around streams.
Ecohydrology: What’s in a Name?
Scientists were studying ecohydrology for decades before it became an official ‘ology’. Find out how this field has evolved over the past century.
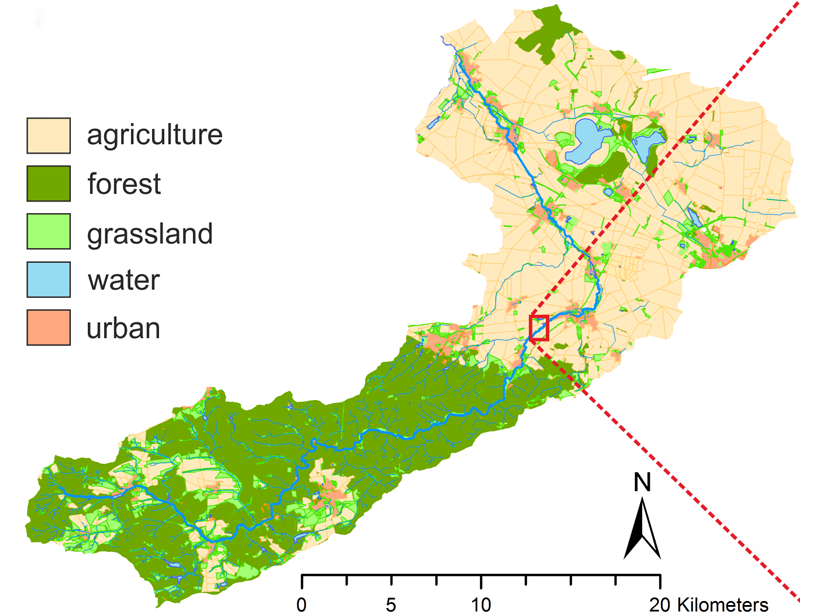
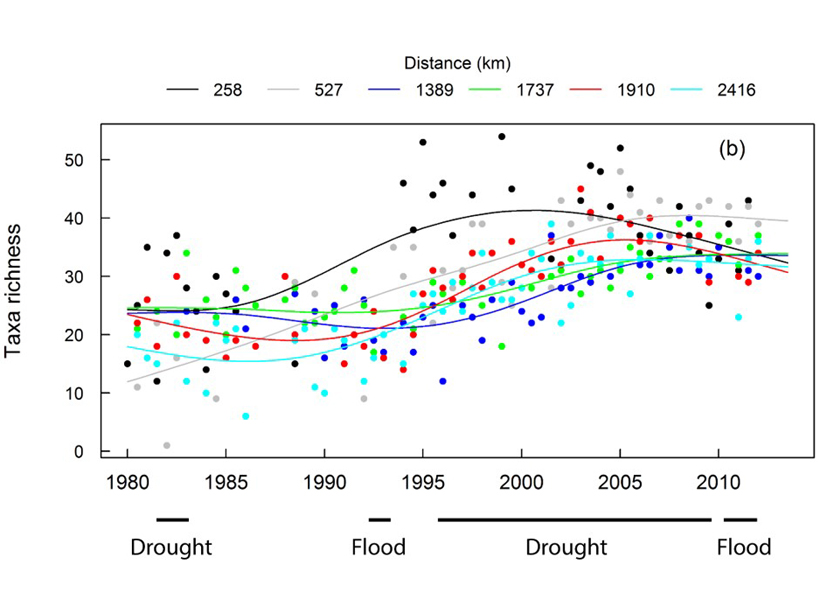
Long-term Dataset Reveals How Management Affects River Biology
River systems are affected by societies against a backdrop of climate change. A new dataset reveals how these forces affect river flow, chemistry, and the biological health of the river.
Massive Scale Evaporative Water Losses from Irrigation
Evaporation can demonstrate the effects of crop irrigation on decadal trends in evapotranspiration at a regional spatial extent.